
1. Weekly News
Belarus
Belarus Aims for Self-Sufficiency in Apple Production
During a recent visit to a fruit-growing farm near Molodechno, the President of Belarus highlighted the nation’s ambition to achieve self-sufficiency in fruit production, emphasizing apples. He underscored the importance of reducing reliance on imported apples by enhancing domestic production capabilities and establishing adequate storage facilities. The President instructed the Minister of Antimonopoly Regulation and Trade to evaluate the country’s apple consumption needs and market potential to satisfy domestic demand and improve export opportunities. The President announced plans to allocate at least 1 thousand hectares (ha) of additional land to support this initiative to expand apple production.
Europe
EU Faces Below-Normal Apple Harvest in 2024/25
The 2024/25 agricultural season is expected to yield a below-normal apple harvest across the European Union (EU). Poland is projected to face the most significant decline, with an estimated harvest of about 20% year-on-year (YoY) lower. Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and Greece are also anticipated to experience weak yields, although Germany's Bodensee region may see a 13% YoY increase. Greece's production has suffered due to high temperatures and a heatwave in Jul-24. These affected thefruit size but did not compromise quality. In Italy, the harvest is forecasted to decrease by 1%, totaling just over 2.16 million tons, while Spain is monitoring import situations amidst weaker EU production and potential price increases. Despite these challenges, France's apple harvest outlook remains stable, benefiting from declining yields across the EU.
India
Monsoon Effects and Rising Demand for Imports Influence the Start of India's Apple Season
The Indian apple market is facing significant challenges stemming from erratic rainfall, climate change, and extreme weather, affecting the start of the apple season. This year's monsoon has brought intense rainfall to southern India. At the same time, other regions have faced extreme heat and insufficient early rains, driving up demand for imported apples like New Zealand Galas and Turkish Red Delicious, which are sold at premium prices. Despite some quality concerns, Polish apples have also entered the market at high rates. In Himachal Pradesh, growers worry about severe rainfall and landslides, yet northern regions remain primarily unaffected, allowing for a timely harvest of high-quality produce. A new 25-kilogram (kg) packaging standard has stabilized prices, though initial high prices are starting to decline as supplies normalize. While both Himachal Pradesh and Kashmir expect a typical season, imported apples will continue to play a significant role in the market. Turkish Gala apples are experiencing lower-than-expected quantities, prompting early orders from Indian importers, although logistical challenges related to the Red Sea could complicate transit. Overall, the future of the Indian apple market will hinge on the balance between domestic and imported varieties, demand dynamics, and logistical considerations.
Spain
Basque Country Apple Harvest Begins with Lower Yields
Apple harvesting has begun in the Basque Country, specifically in Gipuzkoa, Bizkaia, and Araba. However, apple production this season is expected to decrease by around 40% YoY. This decline can be due to the cyclical nature of apple harvesting, which tends to fluctuate annually, along with adverse weather conditions experienced this year, including a cold winter followed by a summer heatwave. While the Goierri area of Gipuzkoa is enjoying a better harvest due to more favorable weather, the overall output remains low. The Euskal Sagardoa Designation of Origin anticipates that approximately 2.5 million kg of apples will be harvested, highlighting the importance of long-term collaboration between cider makers and producers to improve local production and quality.
Ukraine
Declining Apple Prices in Ukraine Amid Low Demand and Oversupply
In Ukraine, apple prices have been on a downward trend for the past three weeks, primarily due to low demand and an oversupply of autumn varieties with limited storage capabilities. In W38, high-quality apples prices stood at USD 0.29 to USD 0.44/kg, reflecting a return to levels seen during the same period last year. Market experts anticipate potential significant fluctuations in apple prices throughout the year, driven by several adverse factors, including abnormal weather conditions and supply disruptions related to ongoing military actions. Historically, the lowest apple prices in Ukraine occur in late autumn and winter, following the harvest when market supply peaks.
United States
Washington Apple Harvest Projected at 124 Million Boxes Amid Drought Management
Washington is expected to harvest approximately 124 million 40-pound (lb) boxes of apples this 2024/25 season. The President of the Washington State Tree Fruit Association emphasized that a normal-sized crop simplifies management and marketing throughout the year. Despite drought conditions, growers and irrigation districts have successfully managed water supplies through effective preparation. However, concerns about water availability for later-harvested varieties persist. The apple harvest in Washington typically begins around August 1 and continues into mid or late November for specific varieties. This year's crop quality appears promising, generating optimism about consumer satisfaction, especially for popular varieties such as Gala, Granny Smith, and Red Delicious.
2. Weekly Pricing
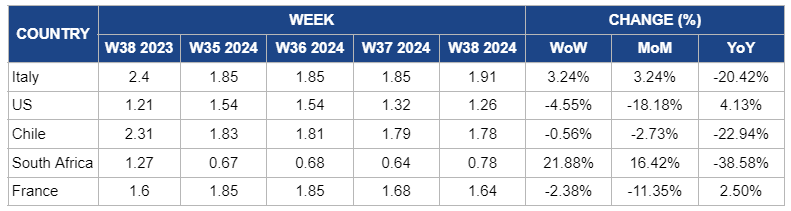
Weekly Apple Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Apple Pricing Important Exporters (W38 2023 to W38 2024)
Italy
In W38, apple prices in Italy rose by 3.24% both week-on-week (WoW) and month-on-month (MoM), reaching USD 1.91/kg. This increase is due to a limited harvest in Val Venosta. While slightly below its full potential, the harvest is still adequate to satisfy domestic market demand and fulfill the specific supply needs of key target countries. However, prices decreased significantly by 20.42% YoY due to last year's higher production levels, which led to increased availability and competitive pricing in the market during 2023.
United States
In W38, apple prices in the United States (US) dropped significantly by 4.55% WoW to USD 1.26/kg. This decline is due to the anticipated increase in apple harvest for the 2024/25 season, contributing to an oversupply in the market. Additionally, there is a 18.18% MoM decrease. Despite concerns about water availability for later-harvested varieties, effective water management and the promising quality of this year’s crop, particularly popular varieties like Gala, Granny Smith, and Red Delicious, have led to a competitive pricing environment.
Chile
In W38, Chile's apple prices decreased slightly by 0.56% WoW to USD 1.78/kg. Additionally, there is a 2.73% MoM decline and a 22.94% YoY decrease. This trend is due to the continued easing of production limitations and improved weather conditions, contributing to a gradual market stabilization. The slight price reduction reflects ongoing adjustments as producers balance supply levels with steady demand. The YoY decline is due to the elevated price base from last year when production challenges led to higher prices. Overall, the market is progressively finding equilibrium as conditions stabilize.
South Africa
In South Africa, apple prices increased by 21.88% WoW to USD 0.78/kg in W38, reflecting a 16.42% MoM increase. This is due to rising production costs linked to pest management challenges, particularly the woolly apple aphid, which has impacted output in key growing regions. The need for more sustainable pest control methods and supply disruptions has contributed to the price surge. However, there is a 38.68% YoY decline due to improved overall yields in 2024 compared to last year's weather-related production losses, which had driven prices higher during the same period.
France
Apple prices in France declined by 2.38% WoW to USD 1.64/kg in W38, reflecting an 11.35% MoM decrease. This is due to a continued recovery in production in regions like Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur and Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes, which has helped ease supply pressures. The recent harvest from these areas has contributed to short-term price declines despite overall reduced production levels in the country. However, YoY prices increased by 2.5% due to lingering supply shortages from key regions like Nouvelle-Aquitaine and Occitanie, which faced production challenges earlier in the season.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Diversify Sourcing Strategies to Mitigate Apple Supply Risks
Apple distributors in the EU should diversify their sourcing strategies to mitigate risks associated with the anticipated below-normal harvest for the 2024/25 agricultural season. By identifying and establishing relationships with suppliers in regions with stable production, such as France, and exploring imports from non-EU countries, distributors can ensure a consistent supply of apples. Additionally, flexible pricing strategies can help adapt to potential market fluctuations and maintain competitiveness despite reduced local yields.
Optimize Storage and Marketing for Autumn Apple Varieties
Apple producers in Ukraine should focus on improving storage capabilities and optimizing marketing strategies for autumn apple varieties to address the current oversupply and low demand. By investing in better cold storage solutions, producers can extend the shelf life of their apples, allowing them to sell during periods of higher demand and reduce price volatility. Additionally, targeted marketing campaigns highlighting the quality and availability of autumn apples can help stimulate consumer interest.
Strengthen Import Channels and Enhance Domestic Apple Marketing
Indian apple importers should focus on securing reliable supply chains for premium imported varieties like New Zealand Galas and Turkish Red Delicious to meet rising demand amid domestic challenges. At the same time, domestic growers, especially in regions unaffected by extreme weather, should ramp up marketing efforts to highlight the quality and freshness of locally produced apples, ensuring they remain competitive against imported varieties.
Sources: Tridge, Sinor, Euskadi, 24tv, CR Fruits International, The Conversation, AG Info, Freshplaza





