W42 2025: Beef

In W42, global beef prices strengthened across major markets, supported by resilient demand and tightening supplies. Spain’s confirmation of its first Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD) case on October 4, 2025, prompted trade restrictions from nearly 20 countries, severely disrupting its live cattle exports to Morocco and threatening the stability of its beef sector. To mitigate the impact, Spain should expedite vaccination campaigns and pursue regionalized trade agreements to enable limited market access from disease-free zones. In the United States (US), supply shortages have driven prices higher, leading the government to expand its low-tariff import quota for Argentine beef to 80 thousand metric tons (mt). However, this decision faced criticism from domestic ranchers concerned about competitive pressures. Meanwhile, Argentina is expected to strengthen its recovery through investments in export infrastructure and diversification into new markets. Brazil continues to dominate global beef exports, while Australia, Uruguay, and Paraguay also benefit from strong international demand and favorable trading conditions.
1. Weekly Price Overview
Global Beef Prices Strengthen with High Demand and Limited Supply
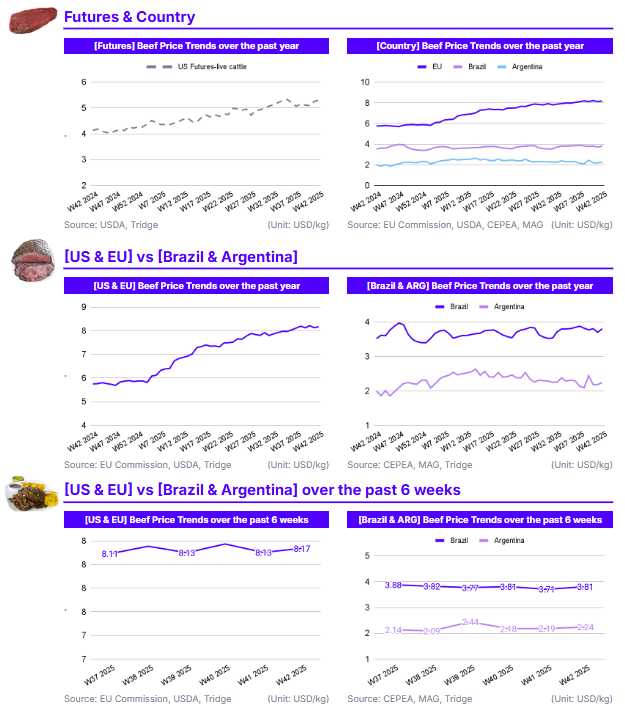
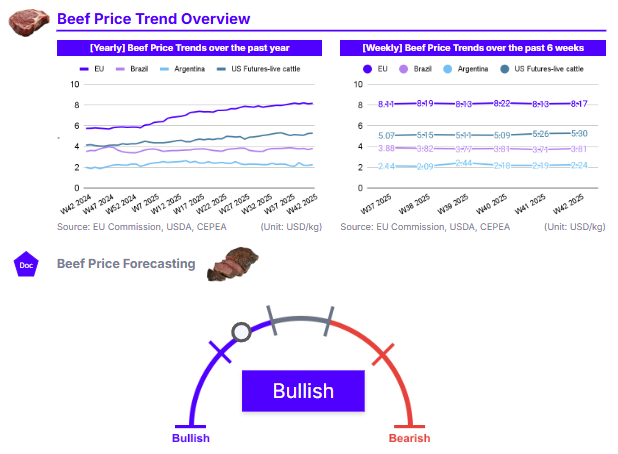
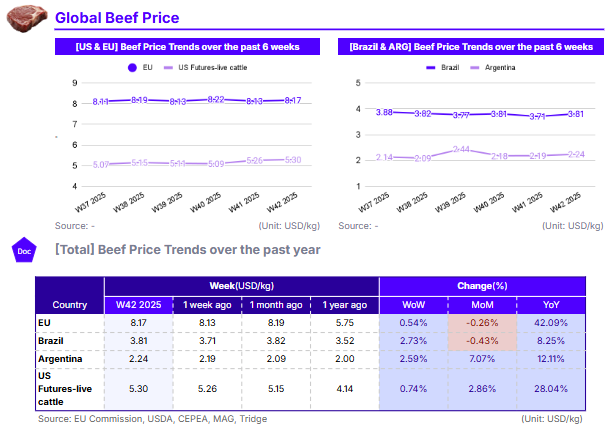
In W42, European Union (EU) beef cattle prices increased by 0.54% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 8.17 per kilogram (kg), reflecting a significant 42.09% year-on-year (YoY) surge. The continued price elevation likely stems from stable domestic demand alongside persistent supply constraints linked to structural challenges in production. In Brazil, beef prices rose 2.73% WoW and 8.25% YoY to USD 3.81/kg, supported by a rebound in demand as domestic consumption nears its seasonal peak, while export shipments remain strong. Similarly, Argentina saw beef prices climb 2.59% WoW and 12.11% YoY to USD 2.24/kg, driven by a revival in consumption compared with 2024, when economic headwinds had dampened demand. In the US, live cattle futures averaged USD 5.30/kg, up 0.74% WoW and 28.04% YoY. Although wholesale price data are currently unavailable due to the government shutdown, market indicators point to elevated beef prices amid a tightening supply. As of July 1, the US cattle herd totaled 94.2 million heads, including 28.7 million beef cows, a modest recovery yet still slightly below 2023 levels. This highlights ongoing supply-side constraints in the market.
2. Price Analysis
Global Beef Trade Realigns as Spain Faces Export Ban and South America Strengthens Market Position
The confirmation of the first LSD case in Spain on October 4, 2025, has triggered severe trade restrictions, with around 30 export certificates blocked by nearly 20 countries, including Morocco, Brazil, China, and the United Kingdom (UK). The disease’s emergence has halted Spain’s live cattle trade with Morocco, which normally accounts for 43% of Spain’s live beef exports. The suspension threatens broader economic stability across Spain’s beef sector, as producers await the effectiveness of vaccination and containment measures. This situation will likely lead to a drop in cattle prices in Spain as supply will increase due to reduced export activity.
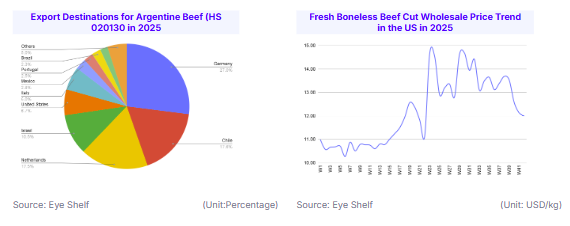
In the US, live cattle shortages have pushed prices to record highs in 2025, prompting the US government to quadruple the low-tariff import quota for Argentine beef to 80 thousand mt in an attempt to lower consumer costs. However, this move has drawn backlash from US ranchers who argue it undermines domestic producers.
Meanwhile, Argentina is showing signs of recovery, with beef exports expected to reach 830 thousand mt in 2025, just 10% below last year’s levels, and potentially hit 1 million metric tons (mmt) by 2026. Brazil continues to dominate global trade, exporting a record 315 thousand mt of beef in Sep-25, up 25% YoY, with 187 thousand mt shipped to China alone. Other exporters such as Australia, Uruguay, and Paraguay are also benefiting from strong global demand and favorable trade conditions.
3. Strategic Recommendations
Strategic Policy Responses to Spain’s LSD Outbreak and Supply Pressures in the US and Argentina
Given the recent LSD outbreak, Spain should expedite the deployment of vaccination campaigns in affected areas and enforce strict livestock movement controls to prevent further spread. Simultaneously, the Ministry of Agriculture should initiate bilateral negotiations with key trading partners, particularly Morocco and China, to establish regionalization-based trade protocols that could allow exports from disease-free zones.
In the US, the government should complement the expanded low-tariff import quota for Argentine beef with incentives for domestic herd rebuilding. These could include low-interest credit lines for ranchers, pasture restoration programs, and feed cost stabilization mechanisms to encourage a sustainable recovery of domestic supply. Moreover, the government should reinforce market transparency and monitoring systems to prevent distortions arising from increased imports while ensuring beef remains affordable for consumers.
Argentina should focus on strengthening export infrastructure to sustain its projected recovery, targeting 1 mmt of beef exports by 2026. This requires investment in cold chain logistics, certified slaughter facilities, and compliance systems aligned with international standards. At the same time, Argentina should diversify its export markets beyond China, expanding into the EU, Middle East, and the US, to mitigate market concentration risks.