W47 2024: Orange Weekly Update

1. Weekly News
Global
Northern Hemisphere Citrus Production Forecast Reveals Decline
The World Citrus Organization (WCO) projects a significant decline in Northern Hemisphere citrus production for the 2024/25 season, estimating 27.3 million tons, an 8.73% drop from the previous season and 5.88% below the four-season average. Particularly in countries like Italy and Turkey, orange production is expected to decline sharply, with Italy forecasting a 17.51% reduction. Climatic challenges, drought, heat, and pests have impacted citrus quality and harvest timing. Egypt anticipates a 19.55% decrease, while Morocco and Israel expect growth of 11.97% and 18.5%, respectively. Spain, a significant producer, will see a 3.3% drop in overall citrus production, with lemons down 21%. Geopolitical instability and inflation are also pressuring consumer demand, contributing to market volatility.
Brazil
Brazil Faces Record Low Orange Production Due to Severe Drought
Brazil's orange production is forecasted to hit its lowest level since 1988/89, with a projected yield of 232.38 million boxes, a 24% year-on-year (YoY) decline from the previous season. Severe drought, heightened by historic low water levels in the Amazon basin, and an outbreak of citrus greening disease have heavily impacted primary orange-producing regions like São Paulo and Minas Gerais. High temperatures and soil moisture loss have further reduced crop quality. Consequently, orange prices have surged by 78% YoY in 2024. As the world's largest orange juice exporter, Brazil's production challenges have tightened global supply, driving orange juice futures up by over 50% since early 2024, with ripple effects on global markets.
Egypt
Egypt Prepares for a Promising Orange Season for 2024/25
Egypt is expected to start its orange and mandarin export season on December 1, 2024, with favorable weather increasing production and fruit quality compared to last year. Ideal conditions, including temperature fluctuations and cold nights, have improved fruit size, color uniformity, and resistance to pests like fruit flies. Demand for Egyptian oranges remains strong in key markets such as Russia, Saudi Arabia, the Netherlands, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE), with adverse weather in Spain further increasing European demand. Improved logistics, including express shipping from Damietta Port to Italy and beyond, have reduced export costs and times, enhancing market reach. With competitive pricing and growing global demand, Egypt anticipates a successful season, solidifying its position as a leading orange exporter.
Europe
Orange Prices in Europe Show Mixed Trends as Greece and Portugal See Price Increases in 2024
In 2024, orange prices in Europe showed significant variations, reflecting local dynamics and broader market trends. The European Union’s (EU) average price for oranges in Sep-24 fell by 17.83% YoY to USD 77.12 per 100 kilograms (EUR 73/100 kg), driven by increased competition and climatic challenges. However, Greece recorded a substantial 30.18% rise, reaching USD 75.05/kg (EUR 71.04/100 kg), while Portugal experienced a 21.75% increase to USD 86.88/100 kg (EUR 82.24/100 kg) due to strong demand and possibly improved market positioning. Major producers like Spain and Italy continue to shape the EU's price trends, highlighting the complexities of maintaining competitiveness amid fluctuating conditions in the citrus market.
Spain
Severe Floods in Spain Disrupt Global Orange Supply
Severe floods in Valencia, Spain, on October 29, 2024, caused extensive damage to the citrus industry, with losses exceeding USD 205 million (EUR 192 million). This disruption has strained the European market, which relies heavily on Spanish oranges for food and beverages. Globally, orange juice production faces additional challenges from Brazil's smallest crop yield in over 30 years due to drought, citrus greening, and Florida's similar struggles. As a result, orange juice prices have surged by 130% YoY. Mediterranean countries like Greece, Morocco, Egypt, and South American nations such as Argentina and Peru are stepping up exports to fill the gap in European demand. However, global supply remains limited, with higher prices and reduced availability continuing to affect the citrus industry.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Orange Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Orange Pricing Important Exporters (W47 2023 to W47 2024)
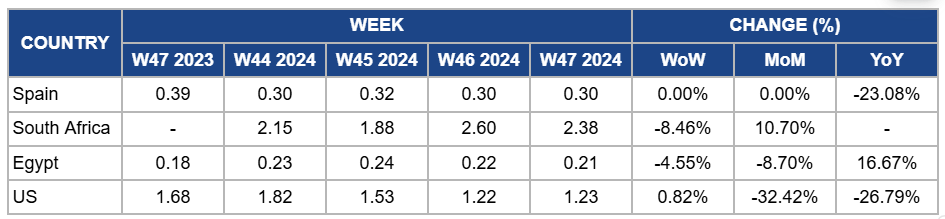
Spain
Spain's orange prices remained steady at USD 0.30/kg in W47, with a 23.08% YoY decline. This is due to the lingering effects of severe floods in Valencia, which caused extensive damage to the citrus industry and disrupted supply chains. While the floods have strained production and impacted market availability, the price stability reflects a balance between reduced domestic supply and increased imports from Mediterranean countries like Morocco, Egypt, and Greece. Additionally, limited global supply and high production costs, coupled with increased demand for oranges in the European market to compensate for shortages in orange juice production, have tempered further price declines.
South Africa
Orange prices in South Africa declined by 8.46% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 2.38/kg in W47 due to improved market supply as harvesting activities resumed in primary citrus-producing regions, alleviating some of the earlier constraints caused by adverse weather. However, month-on-month (MoM) prices dropped by 10.70% due to persistent challenges, including high processing costs and fluctuating export demand, which have pressured growers to adjust prices to remain competitive in international markets. These factors and stabilized domestic distribution contributed to the downward price trend.
Egypt
In W47, orange prices in Egypt dropped by 4.55% WoW to USD 0.21/kg, with an 8.70% MoM drop due to the anticipation of the upcoming harvest season, which is expected to boost supply and drive further market adjustments. Producers have been strategically lowering prices to clear remaining stock from the previous season and prepare for the export season. However, a 16.67% YoY increase is due to robust international demand, particularly from key export markets, and a tighter supply outlook than the previous year, driven by limited carryover stocks and increasing global citrus shortages.
United States
Orange prices in the United States (US) slightly increased by 0.82% WoW to USD 1.23/kg in W47 due to localized supply disruptions caused by heavy precipitation and flooding in Northern California, a key citrus-growing region. These weather conditions have impeded harvest activities and transportation, temporarily tightening local supply and putting upward pressure on prices. However, prices dropped by 32.42% MoM and 26.79% YoY due to improved overall local production earlier in the season and increased imports from other citrus-producing regions, offsetting the effects of regional weather disruptions. Additionally, weaker demand compared to the previous year has contributed to sustained price declines on a broader scale.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Diversify Sourcing Channels to Mitigate Citrus Supply Disruptions
Citrus producers and distributors should diversify their sourcing channels to mitigate the ongoing supply challenges caused by flooding in Spain and drought in Brazil. By increasing imports from countries like Greece, Morocco, Egypt, Argentina, and Peru, they can reduce reliance on a few markets and ensure stable supply for the European market. This strategy should be coupled with enhancing partnerships with local suppliers to improve logistics and reduce the impact of further disruptions on pricing and availability.
Expand Orange Sourcing to Offset Brazil's Production Decline
Producers and distributors should explore additional sourcing regions to counter Brazil's significant decline in orange production. Strengthening relationships with other citrus-producing countries, such as those in the Mediterranean and South Africa, can help stabilize supply chains and mitigate price volatility. Furthermore, investing in alternative processing strategies, such as juicing from non-traditional citrus varieties, can alleviate pressure on the global orange juice market. This approach will ensure more consistent pricing and availability despite Brazil's challenges.
Strengthen Market Positioning to Counter Price Fluctuations
European producers should improve market positioning to compete amidst fluctuating orange prices. They can capitalize on the growing demand by enhancing the value proposition of local varieties, particularly in countries like Greece and Portugal. This could involve offering differentiated products, such as organic or premium citrus, and investing in marketing strategies that highlight their unique qualities. Additionally, collaboration between local producers in Spain, Italy, and other Mediterranean countries can help stabilize pricing dynamics and ensure a more substantial presence in domestic and export markets.
Sources: Tridge, Agrotimes, AlHabouny Group, European Commission, Food&Drink, NASA, Producereport





