
In W6 in the banana landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- Adverse weather conditions in key banana-producing regions have disrupted production and logistics, tightening supply and affecting prices. Severe floods in Australia and localized weather disruptions in Ecuador, the Philippines, and Colombia have further heightened these challenges.
- Countries like Azerbaijan and New Zealand are investing in domestic banana production, reducing reliance on imports and increasing market diversity.
- Mexico and Peru continue expanding their export reach, particularly for the organic segment, with Mexico targeting Asian markets and Peru strengthening cooperative-driven supply chains.
1. Weekly News
Australia
Severe Floods Expected to Disrupt Banana Supply in Australia
Australia faces a looming banana shortage as severe floods in north Queensland devastate farms and disrupt transport routes to southern states. With over 90% of the country’s bananas produced in this region, the closure of the Bruce Highway and inland routes due to heavy rains has delayed shipments, pushing cold storage facilities to capacity and raising concerns about supermarket supply shortages. The flooding, which dumped over 600 millimeters (mm) of rainfall on plantations around Tully, has submerged crops and infrastructure, forcing farmers into urgent pre-rain harvesting. The Bureau of Meteorology warns of further monsoonal rains that could exacerbate distribution challenges. At the same time, industry experts fear losses may exceed those caused by Tropical Cyclone Jasper in 2023, which destroyed up to 35% of crops on some farms. Beyond immediate damage, submerged plants are unlikely to survive, and extensive infrastructure losses add to growers' difficulties. While it is too early to predict price hikes, past natural disasters have historically led to significant banana price surges across Australia.
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan Enters Banana Market with Locally Grown Produce
Azerbaijan has launched its first domestically grown bananas alongside traditional Ecuadorian imports, marking a milestone in local agricultural development. Grown without agrochemicals in a 10-hectare (ha) greenhouse in Buzovna, Baku, the initial harvest produced around 600 tons, with plans for gradual expansion. Known for their rich taste but shorter shelf life, these bananas are now available in major retail and wholesale markets. AZERA Holding, through its subsidiary Fruit Land, a leading player in Azerbaijan’s agricultural industry specializing in high-quality fruit production, aims to scale up production every nine months, providing a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to imports while maintaining competitive pricing.
New Zealand
New Zealand Expands Local Banana Cultivation
Banana farming is expanding in New Zealand, particularly in Northland, where growers are increasing production to meet rising consumer demand for locally sourced fruit. One farm currently cultivates 1.1 thousand banana plants and also plans to expand to 1.6 thousand, featuring varieties such as Misi Luki, Dwarf Cavendish, Hua Moa, and Goldfinger, which offer distinct flavors and unique ripening characteristics compared to imported Cavendish bananas. These locally grown bananas are distributed through wholesalers to markets, supermarkets, and restaurants, reflecting a growing shift toward domestic production. With Northland’s favorable climate, more farmers are exploring banana cultivation, signaling the potential for a thriving local industry.
Mexico
Mexico’s Banana Industry Expands Global Reach Despite Seasonal Slowdown
Banana production in Mexico slows from January to March due to cooler temperatures, particularly in Tecomán, Colima, but recovers by April, ensuring a steady year-round supply. Initially focused on the domestic market, the industry has expanded significantly, especially in the northern regions. Since 2005, the exports have grown and reached North America, Europe, and Asia. The introduction of organic banana exports in 2013 further strengthened Mexico’s position as a key supplier, particularly to Japan and China, where demand continues to rise. With the Asian market offering strong growth potential, Mexico remains focused on further expanding its export footprint.
Peru
Peru’s Organic Banana Industry Faces Challenges but Remains Competitive
Once the world’s leading producer of organic bananas, Peru faced stagnation from 2017 to 2018 due to extreme weather events. In the Piura region particularly, heavy rains, droughts, and the threat of Tropical Fusarium Race 4 (FocTr4) have impacted export volumes. Despite these challenges, Peruvian bananas remain competitive for their quality, with over 9 thousand small producers relying on cooperative efforts to maintain market presence, especially in the United States (US), which accounts for 54% of exports. Rising logistical costs continue to pressure the industry, but cooperatives are improving efficiency, exploring processed banana products, and adopting technological solutions to ensure long-term sustainability.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Banana Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
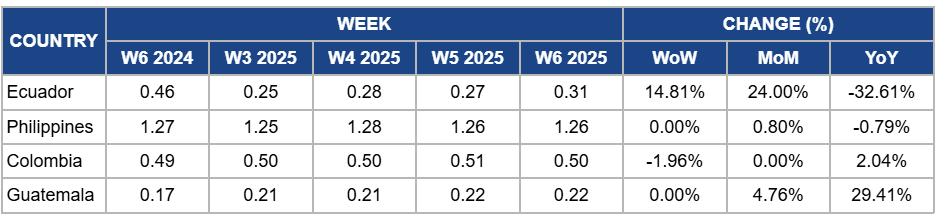
Yearly Change in Banana Pricing Important Exporters (W6 2024 to W6 2025)
Ecuador
Ecuador's banana prices surged by 14.81% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 0.31 per kilogram (kg) in W6, with a 24% month-on-month (MoM) increase. This is due to weather disruptions from showers and thunderstorms affecting harvest and logistics, which tightened supplies. However, year-on-year (YoY) prices dropped by 32.61% due to higher production levels and weaker export demand compared to last year's market conditions.
Philippines
In the Philippines, banana prices remained steady at USD 1.26/kg in W6, with only a 0.80% MoM increase due to stable local demand and minor supply disruptions from scattered rains and isolated thunderstorms. However, there is a slight drop of 0.79% YoY due to ample production across all growing regions, ensuring consistent market availability.
Colombia
In Colombia, banana prices dropped by 1.96% WoW to USD 0.50/kg in W6, with no MoM change due to stable supply despite localized weather disruptions from isolated thunderstorms. However, there is a 2.04% YoY increase in banana prices due to strong export demand from the US, and higher production costs, including increased transportation expenses, and rising costs of agricultural inputs such as fertilizers and pesticides, supported by a slight price uptick.
Guatemala
Guatemala's banana prices remained steady at USD 0.22/kg in W6, with a 4.76% MoM increase and a 29.41% YoY surge due to strong export demand from the US and Europe, as well as rising production costs, including higher fertilizer prices and increased labor expenses. Stable supply conditions have helped maintain weekly price stability.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Expand Market Presence Through Value-Added Products
To capture higher margins, Peruvian banana cooperatives should strengthen their market position by diversifying into processed banana products, such as dried bananas and banana flour. Enhancing logistics efficiency and adopting technology-driven solutions can help mitigate rising costs and maintain competitiveness in key export markets like the US.
Strengthen Alternative Supply Chains
Australian banana distributors should secure alternative transport routes and explore sourcing from unaffected regions to maintain steady supermarket supplies. Retailers can adjust procurement strategies to mitigate potential price surges and ensure consistent availability for consumers.
Strengthen Asian Market Presence
Mexican banana exporters should expand distribution in Japan and China by leveraging the growing demand for organic bananas. Strengthening partnerships with key importers and optimizing cold chain logistics will enhance market penetration and ensure product quality.
Sources: Tridge, Abc News, CEDEPAS Norte, Gov Uk, Minval, Rnz, Smh





