W18 2025: Beef Weekly Update
.jpg)
In W18 in the beef landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- In Argentina, meatpacking plants are struggling with layoffs and declining output due to low export competitiveness caused by an unfavorable exchange rate and high duties.
- Bolivia continues to enforce a beef export ban to curb soaring domestic prices, amid concerns of illegal exports and a push for tighter government control.
- In Thailand, cattle farmers protested US beef imports over food safety concerns, fearing negative impacts on local markets and trade reputation.
- Ukraine imposed a livestock grazing ban along its EU border to contain FMD outbreaks.
- The US meat industry faces significant financial losses due to China’s retaliatory tariffs and export restrictions.
- Uruguay has capitalized on rising US tariffs to boost its beef exports to the US as other countries redirect their shipments to other destinations.
1. Weekly News
Argentina
Argentine Beef Sector Struggles with Declining Exports and Competitiveness Issues
Argentine meatpacking plants are facing significant challenges, including layoffs and early vacations. Notably, Azul Natural Beef, one of the Argentine meatpacking companies, recently laid off 40 employees, citing declining exports, poor exchange rate competitiveness, and internal management issues. These challenges are widespread among members of the ABC Consortium, which represents the country's top meat exporters. The primary problem lies in Argentina's diminished global competitiveness, driven by an unfavorable exchange rate and steep export duties. Although the country achieved a record 930 thousand metric tons (mt) of beef exports in 2024, performance has since declined. According to the Ministry of Agriculture, slaughter volumes have dropped by 2.5% year-on-year (YoY) so far in 2025, while beef exports fell by 33% YoY in the first two months of 2025 and plunged by 40% YoY in Mar-25.
Bolivia
Bolivia Maintains Beef Export Ban Amid Soaring Domestic Prices
The Bolivian government will maintain its beef export ban until domestic prices decrease and consumer access improves. This follows complaints about high prices despite earlier commitments from ranchers and meatpackers to reduce costs. At a recent meeting with the National Confederation of Meat Workers of Bolivia (Contracabol), authorities agreed to regulate auction centers, conduct a livestock census, and enforce local price controls. Although Bolivia has over 11 million cattle, sufficient for local needs, allegations of unauthorized exports by Frigorífico BFC SA have raised concerns. Contracabol now proposes that the government take over beef exports to prevent smuggling and protect national interests. Meanwhile, the state is building its first meat processing plant in Beni, though its launch date remains unclear.
Thailand
Thai Cattle Farmers Oppose US Beef Imports Due to Safety Concerns
The Thai Beef Cattle Association, along with over 60 allied organizations, held a protest at the Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives to oppose the government’s plan to allow imports of United States (US) beef in exchange for trade deficit goods. Thai cattle farmers fear the move will further harm the domestic market, already pressured by cheaper imports from Australia and New Zealand. The association submitted a protest letter to the prime minister, citing concerns that US beef violates Thai laws banning growth hormones commonly used in American livestock production. They also plan to petition the Ministries of Finance and Commerce, warning that the policy could negatively impact over 1.4 million Thai cattle farmers and damage Thailand’s reputation in global markets, particularly with countries like Malaysia, Vietnam, and China that maintain strict standards on growth hormone use.
Ukraine
Ukraine Implements Grazing Ban to Contain FMD Spread
In response to foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) outbreaks in Slovakia and Hungary, Ukraine has imposed a ban on grazing livestock within a 10-kilometer zone along its border with the European Union (EU). The ban aims to prevent the disease's spread and protect domestic animals, such as cows, pigs, goats, and horses, from infection. The State Food and Consumer Protection Service of Ukraine emphasized the importance of biosecurity measures, advising farmers to avoid contact between animals during grazing. The virus spreads through infected animals, their products, and even via contact with animals in the incubation period.
United States
China’s Retaliatory Tariffs and Export Restrictions Disrupt US Meat Markets
The United States Meat Export Federation (USMEF) reports that China’s retaliatory tariffs have severely impacted US beef and pork exports, posing significant financial risks to the meat industry. Currently, US pork and pork by-products are subjected to a 172% tariff, while US beef and beef by-products face a 147% tariff. The USMEF warns that losing access to the Chinese market could result in substantial losses, with the pork industry facing a potential loss of USD 8 to USD 10 per head and a total annual loss of USD 1 billion, while the beef industry could lose over USD 4 billion annually. The situation is further exacerbated by China's unique demand for certain beef and pork products, such as spare ribs and pig feet, which are difficult to redirect to other markets. Additionally, China has not renewed export registrations for nearly 400 US beef processing plants and nine pork plants, creating further challenges for red meat exports, even if tariffs are lifted.
Uruguay
Uruguay Capitalizes on Global Meat Market Shifts and Increased US Tariffs
In Apr-25, the international meat market faced uncertainties due to potential tariff changes from the US government, specifically a 10% tariff on all countries. However, the National Meat Institute (INAC) of Uruguay noted that the tariff scenario inadvertently benefited Uruguay, as it prompted Australia to redirect some of its beef exports away from the US to China, Japan, and South Korea. Additionally, INAC highlighted the rise in US livestock prices and the historically low cattle stock, which created a need for new beef sources, keeping the market optimistic. Uruguay also sought to capitalize on China's demand, especially amid the US-China trade tensions, although shipping fresh cuts posed challenges due to limited air freight capacity. To address these challenges, INAC increased its promotional efforts, attending trade fairs and forging partnerships with distributors, all supported by a doubled budget of USD 5.3 million. As a result, beef export prices reached their highest levels in the last week of Apr-25 since Jun-22. The US emerged as Uruguay's top beef export destination in Apr-25, showing a significant increase compared to the previous year.
2. Weekly Pricing
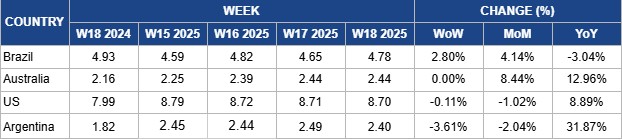
Weekly Beef Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Beef Pricing Important Exporters (W18 2024 to W18 2025)
Brazil
In W18, Brazil’s wholesale boneless rear beef price rose by 2.80% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 4.78 per kilogram (kg), marking a 4.14% month-on-month (MoM) increase, but 3.04% lower YoY. The WoW rise was influenced by currency exchange fluctuations, as the local price remained steady at BRL 27/kg. According to Safras and Mercado, beef cattle prices in the wholesale market remain firm over the week, supported by expectations of stronger demand in early May-25 due to salary inflows and Mother's Day, which typically boosts beef consumption. However, the physical cattle market began the week with attempts to negotiate lower purchase prices, and several meatpackers stayed out of the market, assessing options amid a shorter trading week due to the Labor holiday. Safras and Mercado also noted slight improvements in slaughter schedules, adding that deteriorating pasture conditions are expected to play a key role in shaping prices throughout May-25.
Australia
Australia’s National Young Cattle Indicator averaged USD 2.44/kg in W18, unchanged from the previous week but up 8.44% MoM and 12.96% YoY. According to Meat and Livestock Australia (MLA), all cattle indicators recorded strong growth as market activity rebounded following recent long weekends. Yardings surged to 77.07 thousand heads, over 150% higher YoY, marking the sixth-largest weekly volume this year and aligning with levels seen before the holiday disruptions. Prices for male cattle, including restocker steer, feeder steer, and heavy steer, rebounded after declining the previous week due to weak processor demand. In particular, restocker steer prices reached their highest point since early 2025. Processor demand during a full operational week also supported gains in the heavy and feeder steer markets. Meanwhile, restocker heifer prices remained stable, as they had not dipped during the short trading weeks and continued to hover near Jan-25 highs.
United States
In W18, US lean beef (92% to 94%) averaged USD 8.70/kg, marking a slight 0.11% WoW decline and a 1.02% drop MoM, likely due to softened demand following recent record highs. Despite three consecutive weekly declines, prices have consistently hovered above the USD 8.70/kg level, indicating continued market strength. YoY prices remain elevated, up 8.89%, driven by tightening domestic supply amid a shrinking cow herd. According to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), the US cattle inventory fell to 86.7 million heads as of January 1, 2025, the lowest since 1951. Consequently, Q1-2025 beef production was revised down by 65 million pounds (lbs), with total 2025 output projected at 26.69 billion lbs, down 1% YoY and 6% from 2022. Additionally, a new 10% baseline tariff on all beef imports could further tighten supply and support upward price pressure as summer demand intensifies.
Argentina
Argentina’s average steer beef price dropped to USD 2.40/kg in W18, down 3.61% WoW and 2.04% MoM, likely due to subdued demand. Despite the decline, prices remained 31.87% higher YoY, reflecting overall lower beef consumption in 2024 amid economic challenges. Meanwhile, supply concerns are mounting. The USDA projects Argentina’s beef production will decline by 3% YoY to 3.08 million metric tons (mmt) in 2025, following a reduced cattle slaughter estimate of 13.4 million heads after early sell-offs triggered by drought and high production costs. The national herd has shrunk to 52.37 million heads, its lowest in years, driven by poor calving rates and adverse weather. However, recent rains may aid pasture recovery and support a gradual rebound by year-end. Domestic consumption for 2025 is expected to remain steady at around 2.31 mmt, on par with 2024. While beef remains a dietary staple, economic strain has curbed per capita intake, with pork and poultry gaining popularity. As the economy shows signs of recovery, a rebound in consumer spending could lift domestic beef prices.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Enhance Export Competitiveness through Policy Reform
To address declining exports and plant closures in Argentina’s beef sector, the government should review and adjust its export tax policy and currency exchange regime. Reducing or eliminating the 6.75% export duty and introducing a preferential exchange rate for meat exporters would significantly enhance competitiveness. In tandem, support measures such as low-interest financing for struggling processors and incentives for value-added beef products could stimulate domestic production and maintain employment. Close coordination with industry bodies like the ABC Consortium is essential to ensure that reforms are targeted and impactful.
Build Domestic Industry Protection Frameworks
To protect the domestic cattle sector from potentially unfair competition, Thailand should strengthen its sanitary and phytosanitary (SPS) inspection regime to ensure imported US beef complies with local hormone-free standards. Simultaneously, the government could introduce temporary safeguard measures, such as quotas or tariffs, while initiating structured dialogues with US trade representatives to find mutually acceptable terms. Support packages for local farmers, including feed subsidies or market access programs, should be prioritized to maintain Thailand’s export reputation in Southeast Asia and avoid damaging farmer livelihoods.
Diversify Export Markets and Push for Diplomatic Engagement
Given the steep tariffs and regulatory challenges in China, the US meat sector should accelerate efforts to diversify its export base by targeting growth markets in Southeast Asia, Latin America, and the Middle East. Simultaneously, the US government should prioritize diplomatic negotiations with China to renew processing plant registrations and address non-tariff barriers. Domestically, financial assistance and marketing support for affected processors and cold storage providers can help mitigate short-term revenue losses and preserve industry jobs. Encouraging innovation in offal and by-product utilization may also open alternative commercial pathways.
Strengthen Cold Chain Logistics for Export Resilience
To fully capitalize on global shifts and rising demand from China and the US, Uruguay should invest in cold chain infrastructure and logistics, especially air freight partnerships, to enable the shipment of fresh beef cuts. Public-private collaborations can fund temperature-controlled storage and transportation improvements. Uruguay should also continue expanding its international marketing presence and consider negotiating bilateral trade agreements to lock in its competitive advantage. Maintaining high-quality standards and traceability systems will further solidify its reputation as a reliable beef supplier in volatile markets.
Sources: Tridge, Agromeat, Agropolit, Canal Rural, Foodmate, UkrAgroConsult


