W22 2025: Beef Weekly Update
.jpg)
In W22 in the beef landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- In 2025, Australia is expected to sustain near-record beef production seen in 2024, supported by strong inventories and favorable weather, with 75% allocated for export.
- Brazil faces falling cattle prices due to seasonal slaughter and shifting protein preferences. However, its official recognition as FMD-free without vaccination boosts long-term export prospects.
- In Mexico, a USD 21 million US investment in a sterile fly plant aims to curb a screwworm outbreak that paused live cattle exports.
- In the US, holiday-driven beef demand pushed prices up, but weakening sentiment and rising costs threaten sustained demand.
1. Weekly News
Australia
Strong Global Demand Supports Steady Outlook for Australian Beef in 2025
In 2025, Australian beef production is projected to remain close to the record level of 2.57 million metric tons (mmt) set in 2024, supported by strong cattle inventories and favorable seasonal conditions. According to Rabobank, high production will be met with growing global demand, helping stabilize prices and deliver solid returns for producers. While per capita domestic consumption may slightly decline due to economic pressures, total domestic consumption is expected to remain steady, with exports continuing to account for around 75% of production. The United States (US) is expected to remain Australia’s largest beef export market, while Asian demand is anticipated to improve gradually. Global beef production is forecast to decline, led by Brazil, the US, and China, reducing export competition and supporting Australian trade. Cattle prices are expected to stay steady with some upside, and producer profitability will benefit from higher receipts despite rising costs, with incomes projected to remain stable through 2025.
Brazil
Brazilian Cattle Prices Fell in May-25 Due to Seasonal Slaughter and Market Pressures
In May-25, Brazil's beef cattle industry experienced a sharp drop in prices per arroba, particularly in Minas Gerais, where prices fell by 9.7% over the month. This decline coincided with a seasonal increase in slaughter activity, giving meatpackers more leverage to push prices lower. Across major regions, forward arroba prices fell month-on-month (MoM) between 2.7% and 9.7%. The market also grew cautious mid-month following the detection of avian influenza at a commercial farm in Rio Grande do Sul, raising concerns about potential impacts on the protein market. Despite a limited immediate effect on wholesale protein prices, wholesale beef prices also dropped, reflecting slower turnover between retail and wholesale sectors and consumers’ growing preference for cheaper proteins. Notably, the rear quarter of beef fell by 4.4% MoM and the forequarter by 5% MoM.
Brazil Officially Recognized as FMD Free Without Vaccination
On May 29, 2025, the World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH) officially recognized Brazil as free of foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) without vaccination, marking a historic achievement for its livestock sector. This milestone boosts Brazil’s position as a global leader in meat production and opens access to higher-value international markets. Officials highlighted the responsibility to maintain herd health and meet global quality demands. The certification followed rigorous studies and a strategic vaccination withdrawal under the National Surveillance Program, confirming the virus's absence in Brazil and enhancing export opportunities globally.
Mexico
Mexico-US Collaboration Targets Screwworm Outbreak with New Fly Production Facility
The US will invest USD 21 million in a sterile fly production plant in Chiapas, Mexico, to fight the screwworm infestation that led to a suspension of Mexican live cattle exports. Following discussions between US and Mexican agricultural authorities, the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) mission will soon evaluate the situation. The plant will boost breeding of sterile flies to disrupt the pest’s reproductive cycle, complementing current efforts from a Panama-based facility. Mexico has also strengthened livestock controls to protect northern regions. Since mid-Apr-25, screwworm cases have dropped by over 50%. However, recent human infections in Chiapas and Campeche have heightened concerns, prompting continued US-Mexico cooperation.
United States
US Beef Demand Soars Amid Holiday Surge, But Risks Loom Ahead
A surge in Memorial Day buying pushed US beef prices to record highs, highlighting strong domestic demand despite forecasts showing stable consumption levels for 2025. This suggests increased demand, as prices have risen 10% to 15% while real consumer spending on beef is up 5% year-to-date (YTD). However, this price upward trend is not linked to exports, as US beef exports are down 7% from 2024, with shipments to China dropping 32% year-on-year (YoY).
In contrast, robust US demand has boosted Australian beef and cattle prices, with the US share of Australian exports rising from 22% to 29%, offsetting weak demand from struggling Asian economies like Japan and South Korea. Although China has stepped up imports from Australia amid its ban on US beef, its domestic beef sector remains under pressure, limiting further demand. Looking ahead, with US beef production expected to decline as herd rebuilding begins, US import needs are projected to stay elevated in coming years, supporting Australian exports. However, risks loom as US consumer sentiment weakens, fast-food chains shift toward cheaper proteins, and household financial stress grows due to inflation, rising tariffs, and higher mortgage rates. A downturn in US beef demand poses the most significant threat to the optimistic global beef price outlook.
2. Weekly Pricing
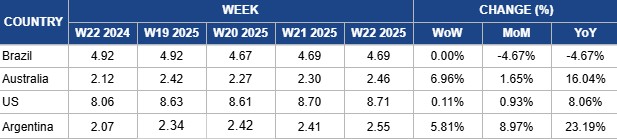
Weekly Beef Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Beef Pricing Important Exporters (W22 2024 to W22 2025)
Brazil
In W22, Brazil’s wholesale price for boneless rear beef remained steady week-on-week (WoW) at USD 4.69 per kilogram (kg). However, prices were still down 4.67% both MoM and YoY. The stable WoW USD price likely reflects exchange rate fluctuations, as the price in local currency rose slightly by 0.38% from BRL 26.50/kg in W21 to BRL 26.60/kg in W22. According to Safras and Mercado, the wholesale beef market remains stable but fragile, with slow movement between wholesale and retail sectors. Prices have fallen over the month, although better sales are expected in early Jun-25. Concerns are growing over declining chicken prices amid the bird flu situation, as consumers may shift to cheaper proteins like chicken, sausages, and eggs this year. Meanwhile, the physical beef cattle market shows some negotiations above average reference prices, as smaller meatpacking plants reduce slaughter volumes and make measured purchases at higher prices, avoiding sharp price spikes.
Australia
In W22, Australia’s National Young Cattle Indicator (NYCI) averaged USD 2.46/kg, up 6.96% WoW, 1.65% MoM, and 16.04% YoY. According to Meat and Livestock Australia (MLA), prices rebounded to early-May-25 levels as east coast rainfall reduced supply. National yardings dropped 6% WoW to 57.69 thousand heads, with declines in all states except Queensland, where supply rose 37% WoW. The Processor Cow and Dairy Cow Indicators led weekly gains, while the Restocker Yearling Steer remained at a premium, returning to early-2025 price levels.
United States
In W22, US lean beef (92% to 94% lean) averaged USD 8.71/kg, rising 0.11% WoW and 0.93% MoM, likely driven by strong Memorial Day demand and an early buildup ahead of the summer grilling season. Prices were also 8.06% higher YoY, supported by tightening domestic supply. As of January 1, 2025, the US cattle herd declined to 86.7 million heads, with beef cow numbers hitting a 74-year low at 28 million. Supply constraints are expected to intensify after the May 11 suspension of live cattle imports from Mexico due to a screwworm outbreak, potentially driving prices higher through peak summer demand.
Argentina
In W22, Argentina’s average steer beef price rose 5.81% WoW to USD 2.55/kg, up 8.97% MoM and 23.19% YoY. The weekly gain was likely driven by increased holiday demand due to the celebration of the First National Government on May 25, 2025. Meanwhile, the strong annual growth reflects a rebound in domestic consumption following economic challenges in 2024. Domestic demand is rebounding in 2025, increasingly competing with exports. Exporters face challenges including longer payment terms and a 6.75% withholding tax, making the domestic market more attractive. Analysts note that strong internal demand has shifted market dynamics, as average domestic beef consumption is expected to rise to between 48 kg to 49 kg per capita in the first half of 2025, up from 43 kg last year. Consequently, the share of exports has dropped from over 30% in 2024 to 24% of total production in 2025.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Diversify Export Markets to Strengthen Resilience
To support Australia’s strong production outlook and maintain stable prices through 2025, beef exporters should diversify beyond traditional markets, such as the US, by strengthening trade ties with emerging Asian economies like Vietnam, the Philippines, and Indonesia. While the US is expected to remain the largest market, reliance on a single destination increases vulnerability to geopolitical or economic disruptions. Investment in marketing campaigns, bilateral trade agreements, and tailored product offerings for different consumer segments in Asia can boost competitiveness. Moreover, value-added beef products such as marinated cuts, ready-to-cook meals can appeal to urban middle-class consumers in Asia, helping to drive demand even in weaker economic conditions.
Implement Flexible Pricing Strategies and Promote Value Cuts
Amid Brazil’s seasonal cattle price decline and weakening wholesale demand, producers and meat processors should adopt dynamic pricing strategies to maintain profitability. Offering bulk discounts and value beef cuts, such as forequarter meats, can help retailers respond to consumers’ growing preference for cheaper proteins. At the same time, marketing campaigns emphasizing nutritional value and versatility of beef, even in lower-priced cuts, could sustain consumer interest. Encouraging domestic consumption through foodservice partnerships and meal kits featuring affordable beef options could also help mitigate the impact of lower export prices.
Capitalize on FMD-Free Status to Enter Premium Markets
Brazil’s FMD-free certification without vaccination presents an opportunity to penetrate high-value markets such as Japan, South Korea, and the European Union (EU), which maintain strict animal health standards. Brazilian exporters should quickly engage with regulators and importers in these regions to renegotiate access terms and establish long-term supply contracts. Producers should also invest in traceability, cold chain logistics, and certifications to meet premium market demands. Promoting Brazil’s improved animal health status in branding and marketing can support premium pricing and brand repositioning in global markets.
Strengthen Cross-Border Coordination and Surveillance
To sustain screwworm containment in Mexico, authorities should establish a permanent cross-border surveillance framework with the US, focusing on rapid detection, reporting, and response. The upcoming USDA evaluation and USD 21 million investment in a sterile fly production facility in Chiapas should be accompanied by technical training programs for local staff, investment in digital monitoring tools, and community awareness campaigns to identify outbreaks early. Mexico should also explore regional collaboration with Central American countries to ensure comprehensive pest control along the wider migratory corridor of livestock, enhancing long-term disease mitigation efforts.
Sources: Tridge, ARR.News, AuctionPlus, Canal Rural


