
In W22 in the maize landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- Brazil’s corn production forecast for 2024/25 was raised to 128.5 mmt, thanks to strong Safrinha crop yields. However, slow harvest progress limits immediate supply.
- Brazilian maize prices were steady WoW but fell MoM due to ample supply and weaker demand. Argentina’s maize production prospects improved, but prices declined both WoW and MoM due to global supply increases and export challenges.
- Nigeria experienced a sharp 100% YoY corn price surge driven by erratic rainfall, climate impacts, and rising input costs. This caused retail prices for boiled and roasted corn to nearly double compared to 2024.
- US corn prices rose MoM and YoY, supported by rapid planting progress and strong crop conditions.
- Meanwhile, Ukraine’s corn exports fell 29.2% YoY, but improved weather and export logistics stabilized domestic prices, which were steady WoW and down MoM.
1. Weekly News
Brazil
Brazil’s 2024/25 Corn Output Raised to 128.5 MMT on Strong Safrinha Yields Despite Slow Harvest
AgRural raised its forecast for Brazil’s 2024/25 total corn production to 128.5 million metric tons (mmt), higher than the 124.8 million mmt forecasted on May-25. The revision is mainly due to better-than-expected yields in the second corn crop (Safrinha), which accounts for about 75% of Brazil's total corn output. In particular, the top-producing state, Mato Grosso, showed strong yield performance. However, harvest progress in the center-south region remained slow, with only 1.3% of second-corn areas harvested as of May 29 2025, a modest 0.4% increase week-on-week (WoW) due to rain and lower temperatures. Some regions, including Mato Grosso do Sul and Paraná, experienced isolated frost events, but damage appeared limited.
Nigeria
Corn Prices in Enugu Doubled YoY in Jun-25 Due to Climate Disruptions and Rising Input Costs
Corn prices in Enugu, Nigeria, surged 100% year-on-year (YoY) as of early Jun-25 due to the effects of climate change, mainly reduced and erratic rainfall patterns. This has disrupted corn cultivation, leading to lower yields and diminished supply in local markets. Farmers currently harvesting their crops also face higher input costs, including increased prices for labor, transportation, and essential materials like charcoal and packaging. These compounded factors, combined with lower production, elevated costs, and supply constraints have increased the retail price of boiled and roasted corn, making it less affordable for many consumers. In 2024, seven pieces of corn stood at USD 0.63, but in 2025, the same quantity now costs USD 1.26. Each piece retails for between USD 0.25 and 0.32 in early Jun-25, depending on size. While prices will ease later in the season with broader harvests, short-term supply shortages continue to pressure prices.
Ukraine
Ukraine’s 2024/25 Grain Exports Declined 22.5% YoY Due to Lower Corn Shipments
The Ministry of Agrarian Policy and Food of Ukraine reported that as of June 2, 2025, Ukraine exported 38.31 mmt of grain and pulse crops in the 2024/25 marketing year (MY), which is 22.5% lower YoY. Corn exports totaled 20.58 mmt, decreasing by 6.02 mmt or 29.2% compared to the previous year.
United States
Iowa Corn Crop in Strong Condition as Planting Nears Completion in W22
As of the week ending June 1 2025, dry weather with occasional isolated showers provided Iowa farmers with 5.4 days suitable for fieldwork, allowing continued progress in planting, hay cutting, and spraying activities. Despite some dryness, topsoil moisture was rated 28% short to very short, and subsoil moisture 32% short to very short, while crop development remained ahead of average. Corn planting reached 97%, with 87% emerging, six days ahead of 2024 and one day ahead of the five-year average. The corn crop was reportedly in strong condition, with 84% rated good to excellent.
Minnesota Corn Crop Recovers Strongly After May-25 Weather Fluctuations
Minnesota corn crops are rebounding strongly after enduring significant weather fluctuations on May-25. Abnormally warm temperatures hit the region in early May, followed by cool, wet conditions that stressed young crops. The lack of sunlight and warm soil caused corn to appear yellow. However, improved weather over the past week has helped the crops recover, and fields show healthier growth. The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) supports this recovery, rating 76% of the state’s corn as good to excellent, highlighting a turnaround in crop health.
Southern Illinois Corn Acreage Set to Rise in 2025
Farmers in Southern Illinois are gearing up for the 2025 planting season amid shifting market dynamics and weather-related challenges. A recent study by the University of Illinois and Ohio State University projects Illinois corn acreage to rise to 11.1 million acres, up from 2024, reflecting a broader national trend toward increased corn and reduced soybean plantings. However, significant rainfall in Southern Illinois has delayed fieldwork, with many farmers completing planting only by late May-25. The upcoming pollination period in late Jul-25 and early Aug-25 will be crucial for determining crop success. Farmers remain attentive to market prices and input costs, which, together with weather conditions, will influence planting decisions and yield prospects.
2. Weekly Pricing
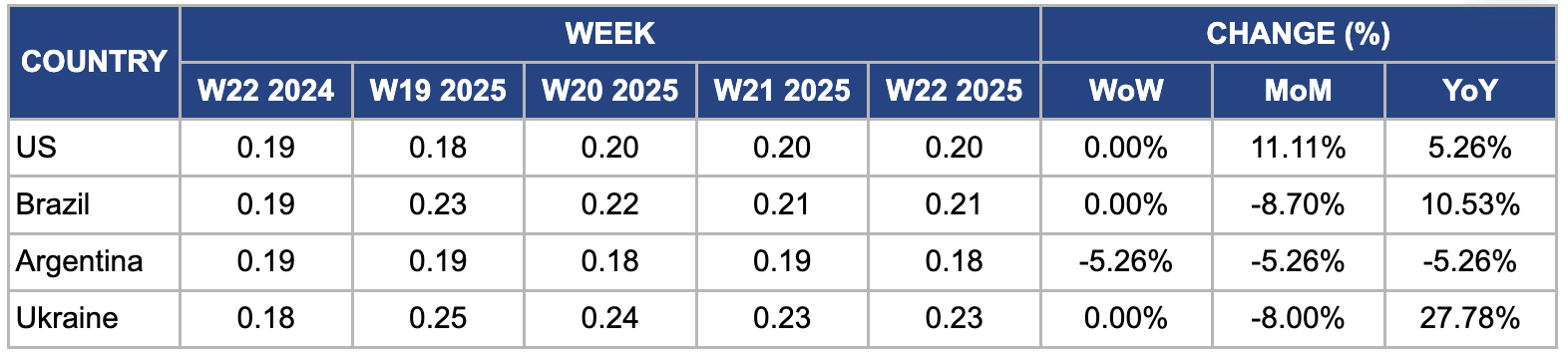
Weekly Maize Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Maize Pricing Important Exporters (W22 2024 to W22 2025)
United States
In W22, US corn prices held steady WoW at USD 0.20 per kilogram (kg) but rose 11.11% month-on-month (MoM) and 5.26% YoY. The price increase was due to supply constraints as planting neared completion in key production states. Despite the supply constraints, planting crop conditions were positive. In Iowa, corn planting reached 97% completion with 87% emergence, ahead of both 2024 and the five-year average, and 84% of the crop was rated good to excellent despite some dryness in topsoil and subsoil. Minnesota’s corn crop also strongly recovered after earlier weather challenges, with 76% rated good to excellent. However, heavy rainfall caused planting delays in Southern Illinois.
Brazil
In W22, Brazil’s wholesale maize prices held steady WoW but fell 8.70% MoM to USD 0.21/kg. Favorable weather conditions in key maize-producing states such as Mato Grosso and Paraná eased earlier concerns about yield losses, enabling faster harvesting and increasing the 2024/25 Safrinha crop supply. Meanwhile, demand from the livestock and ethanol sectors weakened as economic challenges forced these industries to reduce consumption. The combination of higher supply and softer demand put significant downward pressure on Brazilian maize prices.
Argentina
In W22, Argentine maize prices declined 5.26% WoW and MoM to USD 0.18/kg, mainly due to improved weather conditions across key growing regions such as Buenos Aires and Córdoba, which enhanced crop development and boosted production prospects. The Buenos Aires Grain Exchange (BAGE) projected Argentina’s 2025 maize production to reach approximately 54 mmt, up slightly from 52.5 mmt in 2024, driven by favorable rainfall and soil moisture levels. Moreover, increased global maize supply from competitors like Brazil and the US and logistical challenges affecting Argentine exports through key ports dampened export demand and further pressured prices downward.
Ukraine
In W22, Ukrainian wholesale maize prices remained steady WoW but declined 8% MoM, falling to USD 0.23/kg from USD 0.25/kg in W19. Improved weather conditions in key producing regions boosted crop development and eased earlier concerns about yield losses. Recent agricultural reports project Ukraine’s 2025 maize harvest area to increase by approximately 2% YoY, raising production forecasts to around 39 mmt. Furthermore, stabilized export logistics and increased throughput at Black Sea ports have enabled higher shipment volumes, enhancing domestic supply availability.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Accelerate Harvest and Storage Logistics in Brazil’s Center-South Region
Given the slow harvest progress in Brazil’s key corn-producing center-south region due to rain and low temperatures, local authorities and agribusinesses should focus on improving harvest logistics and storage capacity. Investing in better drainage systems, efficient grain drying and storage facilities, and timely transportation can help minimize harvest delays and post-harvest losses. This will allow Brazil to capitalize on the favorable Safrinha crop yields and maintain export competitiveness despite weather challenges.
Support Smallholder Farmers in Nigeria with Climate-Resilient Practices and Input Subsidies
The price surge of corn in Enugu, Nigeria, driven by climate change impacts and rising input costs, calls for targeted support to smallholder farmers. Programs should promote climate-smart agriculture techniques, including drought-tolerant seed varieties such as TMV 1, SAMMAZ 14, and EV-268, and encourage water conservation methods like mulching, rainwater harvesting, and drip irrigation. Moreover, they should provide subsidies or credit access for inputs like labor, transportation, and packaging materials. These varieties can withstand prolonged dry spells and erratic rainfall by maintaining yield and reducing crop failure risks. This approach would help stabilize local production, reduce supply shortages, and curb rapid price inflation, making corn more affordable for consumers.
Monitor Weather and Market Conditions Closely to Optimize US Corn Planting and Marketing Strategies
With US corn planting nearly complete and crop conditions rated mostly good to excellent, farmers and traders should closely monitor weather forecasts, especially regarding the critical pollination period and evolving market dynamics, including input costs and export demand. This data-driven approach can inform decisions on fertilizer application timing, crop insurance purchases, and optimal marketing strategies (e.g., forward contracting) to maximize yield and price realization, especially in regions like Southern Illinois, where late planting and weather variability pose risks.
Sources: Tridge, Brownfield Ag News, KTVO, Punch Ng, Ukr AgroConsult, WSILTV