W23 2024: Tomato Weekly Update

1. Weekly News
Brazil
Late Blight Threatens Brazilian Tomato Crops, Potentially Reducing Yields by Up to 70%
In Brazil, late blight, caused bypotato late blight fungus (Phytophthora infestans), proliferates rapidly in tomato crops under climatic conditions with temperatures between 12°C and 18°C and relative humidity above 90%. This fungal disease spreads more quickly in densely planted areas, and a single outbreak can devastate an entire plantation, causing significant losses in quality and quantity. According to data from the Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation (Embrapa), productivity reductions in tomato cultivation can be between 20% and 70%.
Tomatoes Thrive in Paraná, Brazil
Potatoes and tomatoes are among the main crops in Paraná, Brazil. First-crop tomatoes are expected to increase slightly, with an expected harvest of 146 thousand metric tons (mt), up 1% year-on-year (YoY) from the 145 thousand mt harvested in 2023. The harvest for the first crop is nearly complete. The second tomato harvest is projected to yield 109 thousand mt, meeting expectations, with 66% of the 1,600 hectares (ha) already harvested.
Italy
Italian 2024 Tomato Campaign: Market Flooded, Prices Plummet
The Italian 2024 tomato campaign is in full swing, leading to an influx of high quantities into the markets and causing a significant price drop. Demand has dropped considerably with the arrival of high temperatures. Prices are low, particularly for cherry tomatoes and datterini tomatoes, which have seen reductions of up to 60% YoY in W23.
Kazakhstan
Phytosanitary Challenges and Returns of Tomato Products in Kazakhstan
The Turkestan region of Kazakhstan imported 15,637.802 mt of tomato products through phytosanitary control posts in 2024. However, due to violations of phytosanitary requirements, such as lacking phytosanitary certificates and proper labeling, regulated tomato products totaling 29.522 tons were returned to their exporting countries. The Committee of State Inspection in the Agro-Industrial Complex of the Ministry of Agriculture of Kazakhstan oversaw quarantine phytosanitary examinations (PCR) on each batch of imported tomatoes, eggplants, and sweet peppers to detect hidden contamination. As a result, the "tomato brown wrinkle virus" (ToBRFV) presence was identified in some batches. Specifically, contaminated products returned amounted to 56.1 mt to the Republic of Turkmenistan and 4.2 mt to the Republic of Uzbekistan.
Morocco
Moroccan Greenhouse Tomatoes Exports to Germany Doubled in Q1-2024
From Jan-24 to Mar-24, direct deliveries of fresh and frozen vegetables and fruits from Morocco to Germany reached a record high. During this period, Morocco exported nearly 35 thousand mt of these products to Germany, marking a 40% YoY increase and double the average for the same period over the past five years. Direct supplies of greenhouse tomatoes from Morocco to Germany during this period almost doubled to 13 thousand mt.
2. Weekly Pricing
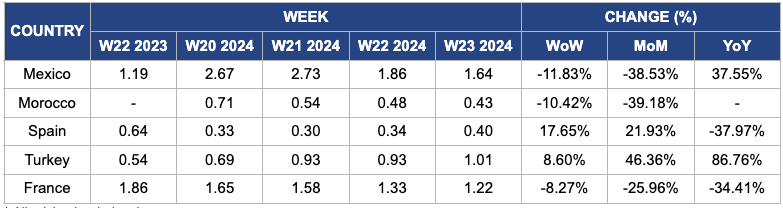
Weekly Tomato Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Tomato Pricing Important Exporters (W23 2023 to W23 2024)
Mexico
In Mexico, tomato prices dropped to USD 1.64 per kilogram (kg), reflecting a significant 11.83% decrease week-on-week (WoW) and a substantial 38.53% decline month-on-month (MoM). This decline can be due to several factors, including the rebound in Mexico's headline inflation, which rose to 4.9% YoY. Additionally, tomato production in northern Mexico is in full swing, with the spring season starting in mid-April and expected to continue until mid-July. As warmer temperatures in Sonora contribute to increased production, prices are forecasted to stabilize soon.
Morocco
In Morocco, tomato prices saw a notable decline of 10.42% WoW and a significant 39.18% MoM to USD 0.43/kg in W23. The Moroccan tomato season has concluded for most varieties, except for late varieties exported during the summer. As the season progressed, volumes increased substantially due to exceptionally warm weather conditions. Consequently, the increased supply led to a significant drop in prices. Growers noted that prices fell by an average of 30%, impacting incomes negatively. Despite the price drop, Moroccan exporters maintained stable market shares in Europe, with steady growth in export volumes.
Spain
In W23, Spanish tomato prices experienced a notable increase of 17.65% WoW and a significant rise of 21.93% MoM to USD 0.40/kg. This increase is likely due to decreased tomato cultivation across Europe, leading to tighter supply and higher prices. The greenhouse campaign in Almería, Spain is ending.
Turkey
In W23, tomato prices in Turkey increased 8.6% WoW to USD 1.01/kg, stabilizing after previous fluctuations as the 2024 harvest progressed. This is due to fewer local greenhouse tomatoes being planted in the autumn due to high fuel prices.
France
French tomato prices decreased by 8.27% WoW and 34.41% YoY to USD 1.22 per kilogram (kg). The decline is due to a downturn in global tomato markets, characterized by lowered consumer demand and increased supply. This trend is evident in France, where prices have dropped significantly. The price decrease in France is further exacerbated by tomato imports from Spain, Turkey, and Morocco, leading to an oversupply and decreasing demand in the market.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Enhancing Tomato Crop Management Against Late Blight in Brazil
Given the threat of late blight in Brazilian tomato crops, farmers must implement proactive disease management strategies. This includes regular monitoring for early signs of infection, timely application of fungicides approved for late blight control, and adoption of crop rotation practices to reduce disease pressure in fields. Embracing integrated pest management (IPM) approaches that combine biological controls and cultural practices can also enhance resilience against late blight outbreaks. Government agencies such as Embrapa can play a pivotal role by providing training programs and disseminating updated disease management guidelines to farmers.
Strengthening Market Resilience for Paraná's Tomato Producers
Efforts should focus on improving market access and resilience To support tomato producers in Paraná, Brazil. This includes enhancing infrastructure for post-harvest handling and storage facilities to minimize losses and maintain product quality. Establishing cooperative marketing arrangements among farmers can enable collective bargaining power and improve market competitiveness. Furthermore, investing in research and development for high-yield tomato varieties adapted to local climatic conditions can bolster productivity and meet fluctuating market demands effectively.
Sources: NoticiasAgricolas, Opresenterural, Fresh Point Magazine, Eastfruit






