W23 2025: Beef Weekly Update
.jpg)
In W23 in the beef landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- Global beef production is expected to fall by 2% YoY in 2025, driven by declines in Brazil and New Zealand, while trade tensions and animal health issues, like the bluetongue virus and screwworm outbreaks, further strain already tight supplies.
- EU farmers warn of domestic market disruption from incoming beef under new trade deals with Mercosur and Ukraine.
- Brazil, Bolivia, and Uruguay are ramping up beef exports. Brazil is aiming for record live cattle shipments, while Bolivia is resuming trade with new quotas and Uruguay is gaining from shifting global demand.
- In the US, beef prices are rising sharply due to limited supply and strong demand.
1. Weekly News
Global
Trade Tensions and Animal Health Issues Drive Global Beef Market Volatility in 2025
Rabobank forecast global beef production to shrink by 2% year-on-year (YoY) in 2025, following a record output in 2024. This production is expected to be led by a 5% YoY contraction in Brazil and 4% YoY in New Zealand, with further declines anticipated in the United States (US), China, and Europe, while Australia stands apart with modest growth. Rabobank highlights that this production downturn is compounded by challenges such as trade uncertainties following changes in US revised trade agreements, as well as animal health issues like the bluetongue virus in Europe and the New World screwworm affecting US-Mexico cattle trade. Despite shrinking supply, global demand for beef continues to rise, particularly in China, which plans to increase imports by 5% YoY.
Trade tensions, tariffs, and shifting supplier dynamics are altering global beef trade patterns, with South American producers redirecting exports towards foreign markets. While beef markets are currently stable, further escalation in trade conflicts, especially between the US, China, and Europe, could disrupt this balance. Overall, the evolving market environment underscores the complexity of global beef supply and demand, with price increases driven by tightening supplies and ongoing health threats to cattle populations.
European Union
EU Farmers Warn of Market Disruption from Mercosur and Ukraine Deals
Farmers in France and Spain have raised serious concerns about upcoming European Union (EU) trade agreements with the Mercosur bloc and Ukraine. They warn that increased imports, particularly of beef, threaten the viability of European agriculture. Stakeholders argue that the planned 99-thousand metric ton (mt) beef quota from Mercosur, subject to a reduced 7.5% tariff, and the 12-thousand mt beef quota from Ukraine under the updated trade regime, will flood the market with cheaper products produced under different standards. Farmers fear this could undermine food sovereignty, weaken local industries, and intensify already existing pressures related to low farm incomes and rising costs. Calls have been made for reciprocal standards, improved traceability, and clearer labelling to ensure fairer competition. The EU’s efforts to phase in Ukrainian quotas aim to balance support for Ukraine with market stability, but discontent continues to grow among European producers who view these agreements as economically and structurally damaging.
Bolivia
Bolivia Resumes Beef Exports with New Quota and Advances Toward Halal Market Access
Bolivia has resumed beef and beef derivative exports after more than 100 days of suspension, following a new agreement between the government, producers, and exporters. This pact includes commitments to boost domestic supply, conduct biweekly market evaluations, and strengthen anti-smuggling measures. A new export quota of 44 thousand mt, up from the previous 35 thousand mt, is expected to generate over USD 100 million in foreign currency, capitalizing on the national production surplus of 351.23 thousand mt. Meanwhile, Bolivia is also advancing efforts to diversify export markets, with ongoing negotiations to secure Halal certification for exports to Egypt. Technical and sanitary inspections have yielded positive results, moving Bolivia closer to accessing new markets in Africa and the Middle East. Despite the temporary halt in exports due to rising local beef prices, the government sees this reopening as a strategic opportunity to stabilize the domestic market while boosting foreign currency inflow.
Brazil
Brazil’s Live Cattle Exports Projected to Hit Historic High in 2025
Brazil is expected to export 1.5 million live cattle by the end of 2025, potentially marking one of the highest volumes in its history, according to Scot Consultoria, a Brazil-based agribusiness advisory firm. From Jan-25 to Apr-25, exports reached 300,000 heads, more than double the same period in 2024, with revenue rising to USD 286 million. Key markets include Iraq, Türkiye, and Egypt, with new access granted to Indonesia, which raised its 2025 import quota to 534,000 heads. Brazil’s recognition as free from foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) is expected to support access to high-value markets like South Korea and Japan. The country also maintains its commitment to strict environmental standards in trade negotiations, while asserting the need to protect its national sovereignty.
Uruguay
Uruguay's Beef Exports Surge in May as Market Dynamics Shift
Uruguayan beef exports reached 36 thousand mt in May-25, marking a 36% YoY increase. China led in volume with 13 thousand mt imported, though it slipped to third place in value terms with purchases worth USD 32 million, despite a 23% YoY increase. The US followed with 11 thousand mt, but remained Uruguay’s top market in value at USD 83 million, a significant 45% YoY rise and accounting for 32% of total export revenue. The EU ranked third in volume with 7 thousand mt, but second in value at USD 75 million, reflecting a significant 78% YoY increase. These shifts highlight changing dynamics in Uruguay’s beef export markets, with the US and the EU showing stronger growth momentum than China in value terms.
United States
Tight Supply and Strong Demand Drive Up US Beef Prices
According to the United States Department Agriculture (USDA), beef prices in the US are expected to continue rising in 2025 due to supply constraints driven by a prolonged dry season and the impact of the screwworm outbreak in Mexico. Retail beef prices rose 0.7% between Mar-25 and Apr-25, marking an 8.5% YoY increase, while producer and wholesale prices also saw significant hikes. The USDA projects annual increases of 12.6% for producer prices and 5.7% for wholesale prices. As beef becomes more expensive, poultry prices are also rising due to a substitution effect, with chicken costs up 0.9% month-on-month (MoM) in Apr-25 and expected to increase by 2.1% YoY for the year. Conversely, pork prices dropped 1.3% MoM in Apr-25 and are forecast to decline slightly by 0.2% YoY in 2025, reflecting growth in pork production.
2. Weekly Pricing
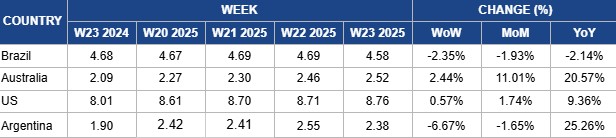
Weekly Beef Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Beef Pricing Important Exporters (W23 2024 to W23 2025)
Brazil
In W23, Brazil’s wholesale price for boneless rear beef fell by 2.35% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 4.58 per kilogram (kg), marking a 1.93% MoM decline and a 2.14% YoY drop. This weekly decline could be linked to increased domestic chicken supply, an alternative protein, after bird flu was confirmed at a commercial farm in Montenegro in mid-May-25, prompting export restrictions. It is worth noting that consumers currently tend to opt for more affordable proteins like chicken, sausages, and eggs, a situation which could have dampened the demand for beef. Despite the recent price dip, Safras and Mercado report that the wholesale beef market remains stable, with short-term price increases still possible as wage inflows support demand. Additionally, the physical cattle market saw rising prices throughout the week, and analysts expect this upward trend to continue, supported by current slaughter scale dynamics.
Australia
Australia’s National Young Cattle Indicator (NYCI) averaged USD 2.52/kg in W23, rising 2.44% WoW, 11.01% MoM, and 20.57% YoY. Meat and Livestock Australia (MLA) reported an 8.35 thousand head increase in cattle yardings, reaching 72.05 thousand heads, up 13% WoW, indicating consistent supply. Prices held firm overall, with most indicators trending upward, except for the restocker yearling steer indicator, which declined slightly. In contrast, the restocker yearling heifer indicator rebounded to Apr-25 levels. Premiums for restocker, feeder, and heavy steers continue to reflect strong market confidence, especially in southern states, where finished steers are trading at higher prices than restockers.
United States
In W23, US lean beef (92% to 94% lean) averaged USD 8.76/kg, up 0.57% WoW and 1.74% MoM, likely driven by rising summer demand linked to grilling and outdoor gatherings. Prices also rose 9.36% YoY, supported by tightening domestic supply. As of January 1, 2025, the US cattle herd declined to 86.7 million heads, with beef cow numbers falling to a 74-year low of 28 million. Supply constraints are expected to worsen following the suspension of live cattle imports from Mexico due to a screwworm outbreak, likely pushing prices higher during peak summer demand.
Argentina
Argentina’s average steer beef price fell 6.67% WoW to USD 2.38/kg in W23, down 1.65% MoM but up 25.26% YoY. The weekly decline likely reflects a post-holiday dip in demand following heightened consumption during the First National Government celebrations. However, the strong YoY growth signals a rebound in domestic demand after 2024’s economic difficulties. In 2025, rising local consumption is increasingly competing with exports, which face challenges such as extended payment terms and a 6.75% withholding tax. Analysts expect per capita domestic beef consumption to rise to between 48 kg and 49 kg in H1-2025, up from 43 kg in 2024, further shifting market dynamics in favor of the internal market.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Enhance Supply Chain Resilience through Diversified Sourcing and Strategic Reserves
In light of the forecasted global beef production contraction and increasing volatility from animal health issues and trade disruptions, stakeholders, particularly import-reliant countries like China and the EU, should invest in diversified sourcing strategies. Establishing long-term contracts with stable exporters like Australia, building strategic beef reserves, and enhancing cold-chain infrastructure will mitigate the risks of supply shocks and price spikes. Governments can further support the sector by providing incentives for domestic production and facilitating bilateral agreements with emerging exporters such as Bolivia.
Support Fair Trade Mechanisms and Standards Harmonization in the EU
In response to growing farmer concerns about Mercosur and Ukraine trade deals, the EU should prioritize reciprocal production and sustainability standards. Implementing mandatory origin labeling, stricter import audits, and phased quota introductions with real-time market monitoring will help protect local producers from abrupt competition. Additionally, transition support programs, such as income stabilization and innovation grants, can aid European farmers in adjusting to heightened competition while promoting sustainable practices.
Capitalize on Market Opportunities by Expanding into Regions with High Demand
Exporters like Bolivia, Uruguay, and Brazil should intensify efforts to access and expand in high-potential markets in Africa, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia. Bolivia’s push for Halal certification and Brazil’s entry into Indonesia illustrate strategic market entry that meets both religious and commercial demands. Governments and exporters should collaborate on trade missions, multilingual marketing, and the alignment of export products with specific market standards like Halal, organic, grass-fed, and Kosher to increase market penetration.
Sources: Tridge, agromeat, Agrosektor, Canal Rural, Euromeat, Hellenic Shipping News, UkrAgroConsult


