W29 2024: Beef Weekly Update
.jpg)
1. Weekly News
Global
Global Beef Production Expected to Drop in the Second Half of 2024
In its Global Beef Quarterly Q2-24 report, Rabobank predicts a contraction in global beef production in the second half of 2024. Although global beef output for Q2-24 is forecasted to be slightly higher than in Q2-23, production for Q3 and Q4 of 2024 is predicted to decline compared to the same periods in 2023. This decline is attributed to expected beef reductions in Europe, the United States (US), and China, which will outweigh the anticipated increases in Brazil and Australia.
Rabobank also notes a two-speed cattle market, with North America experiencing near-record highs due to a contraction in domestic production, while other regions remain more subdued. These regional disparities are beginning to affect international trade flows, with the US increasing import volumes and significant Asian markets maintaining steady import levels.
Global Beef Demand and Exports are Anticipated to Rise in 2024
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) projects global beef demand to reach record levels in 2024, primarily driven by significant changes in the Chinese market. In its latest report, the USDA positively revised its outlook for China's beef imports from an expected decrease to record purchases. Currently, the USDA anticipates that China will import 3.9 million metric tons (mmt) of beef in 2024, an increase of approximately 450 thousand metric tons (mt) compared to the Apr-24 estimate. This positive adjustment suggests that China's beef demand will grow by around 323 thousand mt in 2024 compared to 2023. Notably, the Apr-24 projection was based on an abundant domestic beef supply and a shift among local consumers toward cheaper proteins such as poultry and pork. With the current market outlook, China is expected to account for nearly 36% of global beef trade.
In addition to China's import adjustments, the USDA forecasts an increase in US beef import demand, reaching nearly 1.9 mmt in 2024, more than 20% higher than in the last two to three years. This projection is driven by strong internal demand due to reduced domestic production, which has reached its lowest level since 2018 due to a shrinking cattle herd. The USDA indicates that the expected growth in external purchases by China and the US will increase global demand by more than 500 thousand mt in 2024, representing a significant year-on-year (YoY) increase.
The USDA also expects top global beef exporters to achieve record shipment volumes in 2024. For example, Brazil's beef exports are anticipated to reach 3.3 mmt, an increase of 370 thousand mt compared to the Apr-24 estimate. The realization of this forecast will strengthen Brazil’s position as the world’s leading beef supplier, contributing 25.5% of global trade. Australia's beef exports are forecast to reach 1.79 mmt in 2024, an increase of 85 thousand mt compared to the Apr-24 estimate, contributing 14% of world trade. US beef exports are anticipated to maintain an 8% YoY growth due to subdued domestic consumption despite lower production. Meanwhile, New Zealand's beef shipments are expected to grow in 2024, supported by increased local production and a larger exportable balance.
European Union
EUDR's Administrative Burden on the Beef and Veal Industry
The Central Organization for the Meat Sector (COV), a trade association representing the meat industry in the Netherlands, is concerned that the European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) will impose significant additional administrative burdens on the European and Dutch beef and veal sectors. The EUDR targets products sensitive to deforestation, including soy, palm oil, coffee, cocoa, cattle, and beef. COV argues that the risk of deforestation from Dutch beef and veal production is negligible. However, the regulation requires market participants to prove that their products have not contributed to deforestation, which must be done through a due diligence declaration. This requirement poses substantial administrative challenges for livestock farmers and companies.
COV advocates for a more streamlined and practical approach within the European Union (EU) rules for deforestation-free products, specifically for EU-produced beef, veal and other low-risk products. Additionally, COV is calling for a delay in the EUDR's implementation in the EU and is urging the Netherlands to begin enforcement only if other countries also comply.
Mexico
The New Livestock Traceability System in Mexico Aims to Reduce Health Risk
The new traceability system for the bovine sector in Mexico aims to enhance health actions by tracking data such as the origin, food, medicines, movement, fattening, slaughter, and processing of over 10 million cattle annually, including the movement of 20 million heads. This initiative, led by the National Service for Agri-Food Health, Safety and Quality (SENASICA) and the National Confederation of Livestock Organizations (CNOG), involves using identifiers to minimize health risks. The system includes georeferencing of livestock production units (UPP) to verify the number of animals and ensure data accuracy with the National Livestock Registry (PGN). This will bolster efforts such as eradicating bovine tuberculosis by providing comprehensive data on the cattle herd.
2. Weekly Pricing
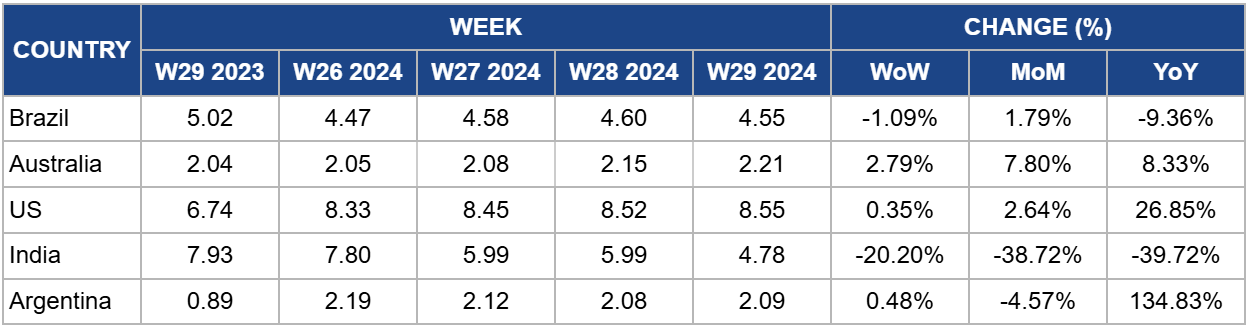
Weekly Beef Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Beef Pricing Important Exporters (W29 2023 to W29 2024)
Brazil
In W29, the wholesale price of boneless rear beef in Brazil averaged USD 4.55 per kilogram (kg), a 1.09% week-over-week (WoW) decrease and a 9.36% YoY decline. Despite this drop in USD, the Brazilian real (BRL) price held steady at BRL 25.00/kg for the seventh consecutive week. This stability in BRL indicates that the decrease in USD was influenced by a weakening real against the US dollar. The substantial YoY decline is primarily due to an abundant beef supply from increased production. According to the Center for Advanced Studies on Applied Economics (CEPEA), beef availability in Brazil's domestic market reached record highs in the first half of 2024, totaling approximately 3.58 mmt, a 14.43% increase compared to the same period in 2023.
Australia
In W29, Australia's national young cattle indicator averaged USD 2.21/kg, a 2.79% WoW increase, a 7.80% month-over-month (MoM) growth, and an 8.33% YoY rise. The price increase is attributed to limited supply and heightened market demand. According to Meat and Livestock Australia (MLA), the return of southern processors in Queensland saleyards boosted competition, a situation that supported prices. Additionally, renewed interest from restockers contributed to the price surge. Heavy steers in Victoria also benefited, with notable performances in Shepparton and Leongatha.
United States
The average price of lean beef (92% to 94% lean) in the US stood at USD 8.55/kg in W29, marking a 0.35% WoW increase and a significant 26.85% YoY rise. These price increases are primarily attributed to a reduced beef supply in the market, driven by decreased US beef production due to prolonged drought conditions. According to a CoBank report, US beef production is expected to decline in 2024 due to the prolonged drought experienced in recent years. However, the decline rate is slower than anticipated due to increased slaughter weights of steers and heifers. CoBank notes that feeder cattle have stayed in feedlots longer over the past three months and gained more weight, although these heavier weights are counter-seasonal.
India
The average price of beef (cow) in India stood at USD 4.78/kg in W29, reflecting a 20.20% WoW drop, a 38.72% MoM fall, and a 39.72% YoY decline. These significant price drops highlight the volatility of the Indian beef market, which has been particularly pronounced over the past 12 months. This volatility is primarily driven by domestic and international regulations and fluctuations in the supply within the Indian market.
Argentina
In W29, the average price of beef (steer) in Argentina reached USD 2.09/kg, a 0.48% WoW increase but a 4.57% MoM decline. The WoW price increase suggests a rebound in beef demand in Argentina. However, beef consumption in the country has remained subdued in recent months due to the challenging economic environment, prompting many consumers to opt for more cost-effective options like poultry. According to the Chamber of the Meat and Cattle Industry and Commerce (CICCRA), per capita beef consumption stood at 48.0 kg in Jun-24, a 10.4% YoY decrease. Additionally, the average per capita consumption for the first half of 2024 was 44.7 kg, indicating a 16.7% decline compared to the same period in 2023.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Strategies to Navigate Expected Drop in Global Beef Production and Increased Demand in 2024
To address the expected contraction in global beef production in the second half of 2024, producers and market stakeholders should consider diversifying their supply sources to include countries like Brazil and Australia, which are expected to see increased production. Importers in regions experiencing a decline, such as Europe, the US, and China, should secure contracts early to mitigate the impact of reduced local availability. In addition, investing in technologies and practices that enhance production efficiency and sustainability can help buffer against future supply fluctuations.
Given the USDA's projection of record global beef demand in 2024, exporters should focus on strengthening their supply chains to meet this rising demand. Producers should enhance their marketing strategies and explore new Asian market opportunities, leveraging China's growing consumption. Meanwhile, US producers should optimize their production processes to balance domestic and export demands, ensuring they can meet internal needs despite a shrinking cattle herd. Diversifying export markets can also mitigate risks associated with over-reliance on any single market.
Ensuring Effective Implementation of the EUDR Law
To navigate the EUDR effectively, the EU beef and veal industry should prioritize the development of streamlined, cost-efficient compliance processes. Engaging with industry stakeholders, including producers and regulators, is crucial to advocate for a practical implementation timeline and the adoption of less complicated administrative procedures. This could involve leveraging digital technologies to automate the due diligence declarations required for proving deforestation-free practices. Additionally, the industry should invest in educating all levels of the supply chain, from farmers to distributors, about the importance and methods of compliance. By fostering collaboration with European counterparts, the Dutch beef and veal sector can push for a unified approach to the regulation. This move will ensure that the rules are enforced consistently across the EU, preventing market distortions and competitive disadvantages.
Implementing Mexico's Livestock Traceability System
Considering Mexico’s new livestock traceability system, producers should invest in training and technology to implement the new tracking requirements efficiently. The system's georeferencing capabilities should be fully utilized to ensure accurate data collection, aiding health initiatives like eradicating bovine tuberculosis. Engaging with industry bodies like SENASICA and CNOG will be crucial for smooth integration into the national registry. Participating in discussion forums can also help identify and address region-specific challenges. Additionally, promoting the benefits of traceability to producers can encourage widespread adoption and compliance.
Sources: The Cattle Site, On24, Chacra Magazine, Nieuwe Oogst, Agromeat


