W5 2025: Apple Weekly Update

In W5 in the apple landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- Several countries, including Brazil, France, and Georgia, are experiencing positive production trends, with Brazil's apple harvest growing by 10%, France adjusting its forecast upward, and Georgia seeing a surge in apple exports.
- Georgia and Poland are increasing their apple exports, with Georgia's exports to Russia significantly rising and Poland planning to export to Indonesia.
- Several regions, including Brazil and Chile, are seeing higher-quality apple production due to favorable weather conditions and better farming techniques, contributing to higher demand and prices.
- In South Korea and India, concerns about lower yields are emerging, with issues like lower flower bud differentiation rates in South Korea and disrupted chilling requirements in India threatening apple productivity.
1. Weekly News
Brazil
Brazil’s Apple Harvest Sees Growth in the 2024/25 Season
The City Hall of Fraiburgo, Brazil officially launched the 2024/25 apple harvest on January 31, 2025, with production expected to reach 915 thousand tons, marking a 10% increase from the previous cycle. This season's apples are of superior quality, featuring larger sizes, vibrant colors, and improved post-harvest conservation, which could increase the fresh fruit supply by 20% year-on-year (YoY).
Apple cultivation remains a primary driver of Brazil's economy, supporting over 120 thousand jobs across 33 thousand hectares (ha) of orchards. With an annual production potential exceeding 1.35 million tons, apples rank as the country’s third most consumed fruit, primarily sourced from local growers.
France
France Revises Apple Production Forecast for 2024/25 Season
France's apple production for the 2024/25 season has been revised down to 1.43 million tons, reflecting a slight adjustment from initial estimates. Although the season started slower than last year, market activity gained momentum on Dec-24, driven by significant inventory reductions, favorable winter weather, and a citrus shortage that boosted apple demand. By Jan-25, sales showed a promising recovery, with stock levels slightly below last year’s but still above the three-year average. With European two-tone apple supplies expected to decline in spring, market conditions remain favorable and industry experts anticipate a stable and balanced season ahead.
Georgia
Georgia’s Apple Exports Surge with Strong Demand from Russia
According to the Ministry of Agriculture, Georgia exported 9.1 thousand tons of apples, generating USD 5.8 million from Aug-24 to mid-Jan-25. This represents a significant increase of 7.6 thousand tons in volume and a six-fold rise in value compared to the previous year. Russia remained the dominant market, receiving 9.02 thousand tons, while smaller shipments were sent to other countries: Kazakhstan with 60 tons, Turkey with 21 tons, and Armenia with 2 tons.
India
Unseasonal Warmth in Himachal Pradesh Threatens Apple Production
In Himachal Pradesh, unusually high January temperatures are raising concerns about their impact on apple orchards. Apple trees require sufficient chilling periods for proper flowering and fruit development, but the recent warm spell could disrupt this process, potentially reducing yields. Growers fear delayed flowering and reduced production if chilling requirements are not met. While an approaching western disturbance is expected to bring rain and snowfall to mid-mountainous districts including Shimla, Solan, Sirmaur, Mandi, Kullu, Chamba, Kinnaur, and Lahaul-Spiti experts warn that the warm temperatures may have lasting effects on apple productivity in the region.
Kenya
Kenya’s Nyandarua County Shifts to Apple Farming to Overcome Climate Challenges
In response to climate-induced declines in plum production, Nyandarua County, Kenya, is shifting to apple farming as a more resilient alternative. Backed by a USD 181.8 thousand (KES 26 million) investment from the county government, farmers are receiving climate-appropriate apple varieties, with grafted specimens showing an 85% success rate. With certified seedlings supplied by the Kenya Plant Health Inspectorate Service, this transition offers economic opportunities and supports environmental conservation. As Nyandarua adapts to changing weather patterns, apple cultivation emerges as a sustainable solution to secure the region’s agricultural future.
Poland
Poland to Begin Apple Exports to Indonesia by Late 2025
Poland is expected to begin apple exports to Indonesia by the end of 2025, marking a key expansion in its agricultural trade with the Southeast Asian market. As one of the world's largest apple producers, with an annual harvest of around 4 million tons, Poland sees strong potential in Indonesia's growing fruit imports, which reached nearly 690 million kilograms (kg) in 2023. Although the initial export volume remains undisclosed, rising demand creates a promising opportunity for Polish apples to establish a foothold and support long-term trade growth.
South Korea
Lower Flower Bud Differentiation Rates Raise Concerns for Fuji Apples in South Korea
In South Korea, the Rural Development Administration reported that the flower bud differentiation rate for Fuji apples dropped to 54% YoY in 2025, below the historical average of 62%. Surveys across major apple-producing regions, including Chungcheongbuk-do and Gyeongbuk, showed significant variations, ranging from 44% to 73%, raising concerns about potential yield reductions. Experts caution that rates below 60% may lead to lower harvests and recommend adjusting pruning techniques to stabilize production. Specifically, when differentiation is below this threshold, preserving fruiting branches becomes essential. To ensure a steady yield, farmers are also advised to assess flower bud differentiation before winter pruning.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Apple Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Apple Pricing Important Exporters (W5 2024 to W5 2025)
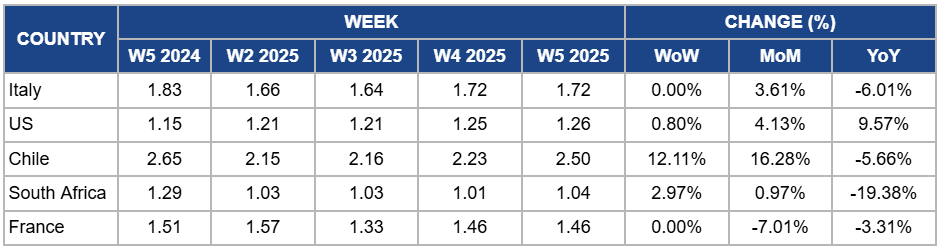
Italy
Italy's apple prices remained steady at USD 1.72/kg in W5, with a 3.61% month-on-month (MoM) increase due to stable demand and a slight tightening of supply following the extended harvest season. However, YoY prices dropped by 6.01% due to the lingering effects of a high supply from last year's extended harvest, which continued to pressure prices. Additionally, competition from other European apple producers and the absence of a significant post-holiday demand spike have contributed to the YoY price decline.
United States
In the United States (US), apple prices rose slightly by 0.80% week-on-week (WoW), marking a 4.13% MoM increase and a 9.57% YoY increase. The price increase is due to strong demand for premium varieties, such as Pink Lady® apples, particularly among affluent, health-conscious consumers. As February marks the peak sales month for Pink Lady® apples, the combination of heightened consumer interest and promotional opportunities related to the winter season and early spring events has contributed to the price uptick. Additionally, the crisp texture, tart-sweet flavor, and premium positioning of the variety have driven sales, supporting higher prices.
Chile
Apple prices in Chile increased by 12.11% WoW to USD 2.50/kg in W5, with a 16.28% MoM increase due to strong export demand and continued supply tightening, particularly for premium apple varieties. The price rise is also due to favorable growing conditions that have resulted in high-quality production, supported by high-density orchards and the use of Geneva rootstock. However, YoY prices dropped by 5.66% due to the normalization of production levels and a return to more balanced supply conditions, following the exceptionally high prices seen last year driven by global supply shortages.
South Africa
In W5, South Africa's apple prices increased by 2.97% WoW to USD 1.04/kg, showing a slight increase of 0.97% MoM due to better-quality production despite the rainy weather in the region. Improved weather conditions have supported higher yields, which have boosted supply. However, YoY prices dropped by 19.38% due to last year’s supply constraints caused by adverse weather events and lower production volumes, which led to higher prices during the same period.
France
France's apple prices remained steady at USD 1.46/kg in W5, with a 7.01% MoM decrease and a 3.31% YoY decline. The price decline is due to a slower start to the season, despite strong destocking and favorable winter weather boosting demand in Dec-24. Increased availability from stock levels, slightly below last year but above the three-year average, has contributed to a price dip. However, with European two-tone apple supplies expected to decline in spring, market conditions are likely to stabilize in the coming weeks, supporting a balanced season ahead.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Adapt Orchard Management to Warmer Winters
Apple growers in Himachal Pradesh should implement adaptive orchard management practices, such as using dormancy-breaking sprays and optimizing irrigation, to counteract reduced chilling hours. Selecting low-chill apple varieties and improving soil moisture retention will help mitigate the impact of rising temperatures. Continuous monitoring of weather patterns and adjusting cultivation techniques accordingly will be crucial to maintaining productivity in changing climatic conditions.
Maintain Steady Supply Amid Market Recovery
Apple growers and exporters in France should maintain consistent supply flows to capitalize on strong winter demand and the expected decline in European two-tone apple availability. Strategic stock management and targeted promotions can help sustain market momentum, ensuring a stable and balanced season.
Optimize Pruning Techniques to Maintain Apple Yields
Apple growers in South Korea should adjust pruning techniques based on flower bud differentiation rates to prevent yield losses. When differentiation falls below 60%, preserving more fruiting branches can help maintain production levels. Farmers should assess bud differentiation before winter pruning and modify thinning strategies to balance tree vigor and fruit quality. Implementing targeted nutrient management and irrigation practices can further support bud development and improve overall orchard resilience.
Sources: Tridge, Agenda, ANPP, Freshplaza, Jakarta Globe, Nation, Nongmin, The News Himachal





