.jpg)
1. Weekly News
Asia
Significant Shifts Expected in Asian Sugar Market in 2025
The Asian sugar market will experience significant shifts in 2025, driven by increased Thai cane output, reduced Indian production, and stable freight rates. Thailand's 2024/25 sugarcane crush is projected at 102 million metric tons (mmt), a 24% increase year-on-year (YoY), supported by higher cane availability and early milling. Despite a 17% drop in initial cane prices to USD 33.74 per metric ton (THB 1,160/mt), many farmers are shifting from cassava to sugarcane due to weaker cassava prices, potentially boosting 2025/26 output to 11.7 mmt. Wet weather in December may temporarily slow crushing but will benefit planting for the next season. Ethanol prices are expected to decline amid lower feedstock costs, while rising electric vehicle adoption reduces gasoline demand.
India's sugar production for 2024/25 is estimated at 27 mmt, 7% lower than the previous year and below the annual consumption of over 29 mmt. Adverse weather, disease impacts, and ethanol diversion have driven this decline. Key states like Maharashtra and Karnataka faced reduced yields by 10 to 15 mt per hectare (ha) due to drought and excessive rainfall, while Uttar Pradesh suffered from red rot disease. This marks the first time production may fall below consumption in eight years, likely eliminating seasonal exports. Limited exports may be allowed only after meeting ethanol needs and supporting global sugar prices.
Dry bulk sugar freight rates have remained steady, with Thailand-Indonesia freight differentials at USD 14/mt. Indonesia plans to import 4.2 mmt of industrial-use sugar in 2025 but has banned imports for consumption. Thai raw sugar was assessed at USD 515.50/mt on a Cost and Freight (CFR) basis to Indonesia on December 19, 2024.. These dynamics highlight evolving market conditions influenced by environmental policies, agricultural trends, and logistical factors.
China
China's Sugar Imports Fall In Oct-24 but Rise in 2024 Year-To-Date, With Brazil Leading Supply
In Oct-24, China's sugar imports totaled 536,900 mt, valued at USD 292 million, marking YoY decreases of 41.95% in volume and 48.40% in value, respectively. However, cumulative sugar imports from Jan-24 to Oct-24 reached 3.43 mmt, valued at USD 1.90 billion, reflecting increases of 12.93% in volume and 10.56% in value compared to the previous year. Brazil remains the leading supplier, with imports amounting to USD 1.63 billion, up 16.35% YoY. Despite a significant drop in Oct-24 imports from Brazil, it accounted for a major share of China's total sugar imports.
Peru
Peruvian Sugar Exports Rise 12.3% in 2024 While Imports Decline by 4.2%
Between Jan-24 and Oct-24, Peruvian sugar exports grew by 12.3% YoY to 104,138 mt. The United States (US) was the primary destination, accounting for 63% of total exports, with 65,135 mt. Ecuador followed with 23%, a total of 23,612 mt. Oct-24 alone saw exports of 30,925 mt. Furthermore, sugar exports during the same period declined by 4.2% to 250,931 mt, with Guatemala (29%) and Nicaragua (24%) as the leading suppliers. In Nov-24, imports totaled 24,322 mt.
Ukraine
Ukraine Approves 2025 Sugar Export Quota to EU Set at 107,240 MT
Ukraine's Cabinet of Ministers has approved a mechanism for distributing the 2025 sugar export quota to the European Union (EU), set at 107,240 mt. The Ministry of Agrarian Policy will allocate the quota among sugar exporters based on actual production volumes from Sep-24 to Dec-24. These production figures must be confirmed through state statistical observation forms (No. 1-P) for the specified months. Exporters must submit their production data and supporting documents to the Ministry of Agrarian Policy by January 20, 2025. This process ensures a fair distribution of the export quota in line with domestic production levels.
United States
US Sugar Production Reaches Record 9.4 MMT in 2023/24, Demand Steady with Global Subsidy Pressures
In the 2023/24 marketing year (MY), US sugar production reached a record 9.4 mmt, with sugarbeets contributing 5.236 mmt. The 2024/25 sugarbeet harvest is expected to yield 5.245 mmt despite some regional yield reductions. Cane sugar production for 2023/24 was 4.133 mmt, the second highest on record. Strong production conditions, particularly in Florida and Louisiana, have supported the sugar supply. Demand remains steady, with the US consuming about 12.4 mmt annually, of which 75% is produced domestically. However, global sugar subsidies, mainly from India, Brazil, and Thailand, are concerned with US prices. In addition, the industry is also seeking a new farm bill to provide a safety net for producers.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Sugar Pricing Important Producers (USD/kg)
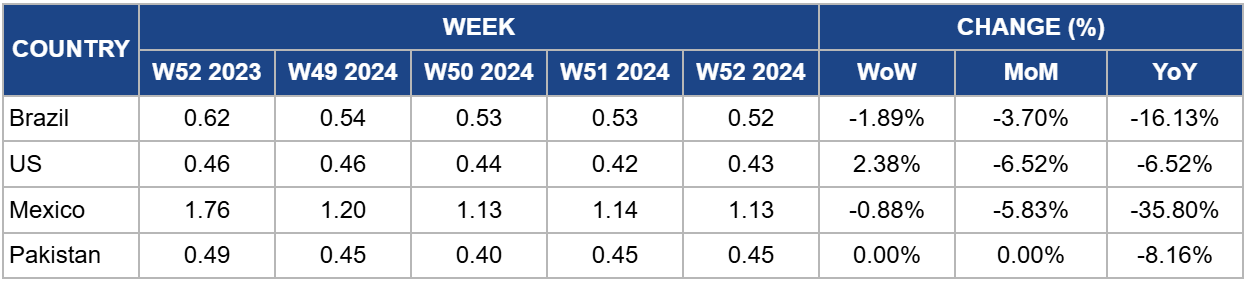
Yearly Change in Sugar Pricing Important Producers (W52 2023 to W52 2024)
.png)
Brazil
Brazil's sugar prices decreased to USD 0.52 per kilogram (kg) in W52, marking a decrease of 1.89% week-on-week (WoW) and a 16.13% YoY. Despite these decreases, Brazil's sugar market faces significant challenges due to adverse weather conditions and production disruptions. In 2024/25, sugar production is estimated at 44 mmt, a reduction from the previous forecast of 46 mmt due to lower sugarcane yields caused by drought and excessive heat. These conditions, particularly in São Paulo, Brazil's largest sugar-producing state, have been compounded by widespread fires, with up to 80,000 ha of sugarcane crops affected. The damage from these fires is expected to result in a loss of approximately 5 mmt of sugarcane.
Despite these setbacks, Brazil remains a major player in the global sugar market. However, the combination of a weakened Brazilian real and the uncertainty around production levels exerts downward pressure on global sugar prices, encouraging export selling. These developments, alongside Brazil's increased sugar exports, continue to shape the dynamics of the global sugar market for 2025.
United States
In W52, US sugar prices rose to USD 0.43/kg, reflecting a 2.38% WoW increase but a 6.52% YoY decline. This price shift comes as the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) adjusted its 2024/25 sugar production forecast downward by 45,359.25 mt, citing reduced sugar extraction from beet molasses. This marks the second consecutive reduction, suggesting that domestic sugar output will fall short of 2023 levels. To address the shortfall, the USDA raised its import projection by 272,155.5 mt, with imports from Mexico increasing significantly.
Despite these adjustments, the US sugar supply remains adequate, with a projected stocks-to-use ratio of 13.5%. However, this reliance on imports, combined with potential shifts in trade policies or global market conditions, introduces risks of supply disruptions. Such factors could contribute to upward price pressures in 2025, particularly if tariffs or global market dynamics impact the flow of imported sugar.
Mexico
In W52, Mexico's sugar prices decreased to USD 1.13/kg, reflecting a slight 0.88% WoW decline. Mexico's sugar industry benefits from a profitable sugar cane harvest, with local producers achieving excellent returns. A single ha of sugar cane can yield up to 25 mt per cut, contributing to strong regional economic activity. This profitability is especially notable in areas such as Mocorito, where sugar cane cultivation is vital in producing traditional sweet products. Additionally, the region's commitment to organic practices—avoiding agrochemicals—further enhances the appeal of its products.
Sugarcane cultivation contributes significantly to Mexico's economy. The country ranked eighth in global production in 2023 with 55.6 mmt. The stability of Mexico's 2025 sugar prices will likely depend on factors such as global demand, domestic production conditions, and potential shifts in trade policies. However, as local harvests remain strong and organic appeal grows, price stability could be supported in the short term.
Pakistan
In W52, Pakistan's sugar prices remained stable at USD 0.45/kg but saw an 8.16% YoY decrease. Pakistan's sugar industry faces challenges due to the lack of government-set minimum prices for sugarcane. This issue persists despite an agreement with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to promote a free-market economy, leading to tensions among producers. The Punjab government's decision to allow sugar mills to set buying prices—ranging from USD 1.08 to 1.17 per maund (PKR 300 to 325/maund), while some mills announce USD 1.44 (PKR 400/maund)—has sparked protests. Additionally, increased input costs, such as surging electricity bills and irrigation water rates, exacerbate the financial pressure on sugarcane producers. These ongoing issues could result in supply disruptions if farmers' demands are not addressed, potentially leading to upward pressure on sugar prices. If the government fails to implement changes, including setting appropriate support prices and curbing rising input costs, future price stability could be at risk.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Diversify Sugar Sourcing Strategies
To mitigate the impact of global supply disruptions and price fluctuations in the sugar market, businesses should diversify their sugar-sourcing strategies by establishing relationships with producers from regions with fluctuating output levels. For instance, with Thailand's projected increase in sugarcane production, stakeholders could consider sourcing more from Thailand to capitalize on its growing supply. Additionally, expanding sourcing from markets like Peru, where exports have increased, or Mexico, with its stable production and profitable harvest, can reduce reliance on high-risk markets like Brazil and India, which face production challenges due to adverse weather and disease. This diversification will help ensure a more stable supply chain and better price control in volatile market conditions.
Monitor and Adjust to Changing Import Regulations
Given the shifting dynamics in global sugar markets, such as Indonesia's ban on sugar imports for consumption and the EU's export quota mechanism, businesses must stay informed about regulatory changes that could affect sugar trade flows. Companies should invest in monitoring import/export policies, especially in key markets like China, which has seen fluctuating imports, and adapt their supply chains accordingly. Proactively adjusting import strategies to align with changing trade policies can help prevent disruptions and avoid potential cost increases. Long-term contracts with key suppliers in stable regulatory environments will also stabilize pricing.
Enhance Production Resilience through Investment in Local Agriculture
To minimize the risks associated with global sugar supply volatility, businesses should consider supporting local sugarcane farming initiatives, especially in regions like Mexico, where sugarcane cultivation is profitable and growing. Financial support or incentives for sustainable agricultural practices, such as organic farming or improved irrigation techniques, can improve domestic production capacity and reduce import dependence. By partnering with local farmers and supporting adopting advanced farming practices, businesses can enhance supply chain resilience, stabilize costs, and contribute to long-term agricultural sustainability.
Sources: Tridge, Hellenic Shipping News, Agraria, Agro Portal, PGP of Minnesota & South Dakota, News Foodmate, Noticias Agricolas, Nasdaq



