W12 2025: Strawberry Weekly Update

In W12 in the strawberry landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- Unpredictable weather patterns, such as heat waves in Albania and excessive rainfall in Morocco and Spain, are severely affecting strawberry yields and quality. These fluctuations highlight the increasing impact of climate change on production stability.
- Heavy rains in Morocco and Spain have led to reduced marketable supply due to fruit damage and disease outbreaks, such as botrytis, forcing producers to divert crops to freezing or alternative processing methods.
- Weather-related production issues in Morocco and Spain have hindered fresh strawberry exports, causing supply shortages in European markets at a time of strong demand, potentially driving up prices.
- California continues to lead in sustainable strawberry production, focusing on reduced pesticide use, precision irrigation, recyclable packaging, and automation research, demonstrating how innovation can enhance environmental and economic resilience.
1. Weekly News
Albania
Heatwave Disrupts Strawberry Production in Albania
Strawberry farmers in Albania's Myzeqe region are struggling with production and quality issues following an unusual heatwave that pushed temperatures to 29 degrees Celsius (°C) before a sudden cold spell disrupted growing conditions. These extreme weather fluctuations have reduced yields and affected pricing, creating uncertainty for growers. To mitigate losses and prevent waste, farmers highlight the need for strawberry processing lines as a critical solution to enhance product utilization and stabilize the market.
Morocco
Heavy Rains Disrupt Morocco's Strawberry Export Season
Heavy rainfall in early Mar-25 ended a prolonged drought in Morocco, particularly in the Larache region, but severely impacted strawberry production. Prolonged moisture exposure reduced fruit quality, forcing exporters to suspend fresh strawberry shipments for two weeks and divert the entire harvest to freezing. This disruption coincides with strong European demand, which producers are currently unable to meet. Although the season is expected to continue until May, the rains—despite temporarily affecting exports—remain a welcome relief for the drought-stricken region.
Spain
Severe Rains Impacted Strawberry Supply in Spain
Heavy rains in Spain have significantly impacted strawberry production, particularly in Huelva, where excess moisture in cultivation tunnels has led to a 15 to 20% reduction in marketable supply. The spread of botrytis, or gray mold, has further compromised fruit quality, reducing availability in international markets and driving up prices. Additionally, impassable rural roads have hindered farm access, causing delays in harvesting and logistics. While the rainfall has helped replenish water reserves, it has also underscored the need for improved water management and infrastructure to mitigate agricultural losses during extreme weather conditions.
United States
California's Strawberry Industry Drives Sustainability and Economic Mobility
As the world's leading producer of organic strawberries, California plays a vital role in the state's agricultural economy, supporting over 70 thousand jobs. The industry prioritizes sustainability through reduced pesticide use, improved soil health, and recyclable packaging made from post-consumer plastic, while precision irrigation and biological pest control further enhance environmental stewardship. Strawberries also provide a pathway for economic mobility, with 65% of the state's strawberry farmers being Mexican Americans who have transitioned from farmworkers to farm owners. Ongoing research at the California Strawberry Center continues to drive innovation in automation and sustainable farming, reinforcing California’s leadership in responsible strawberry production.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Strawberry Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
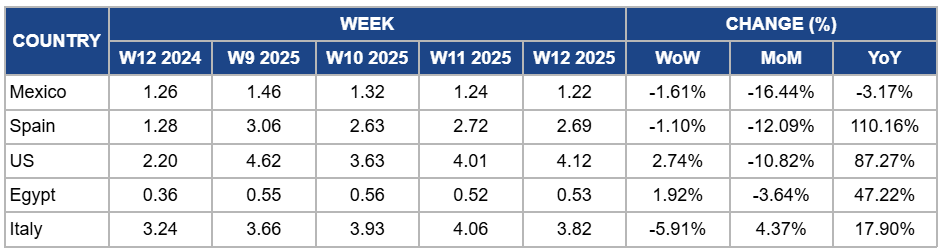
Yearly Change in Strawberry Pricing Important Exporters (W12 2024 to W12 2025)
Mexico
In W12, Mexico's strawberry prices experienced a slight decline of 1.61% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 1.22 per kilogram (kg), marking a 16.44% month-on-month (MoM) decrease and a 3.17% year-on-year (YoY) drop. This price reduction is due to the seasonal increase in supply following the peak harvest period, leading to an oversaturated market and exerting downward pressure on prices. Additionally, intensified competition from other berry-producing regions has further influenced the pricing dynamics. Despite these factors, the overall demand for Mexican strawberries remains robust, particularly in export markets. However, the increased availability has led to adjustments in pricing to balance supply and demand.
Spain
In W12, Spain's strawberry prices declined by 1.10% WoW to USD 2.69/kg, with a 12.09% MoM decrease due to improved weather conditions in Huelva, which facilitated harvesting and increased market supply. However, there is a 110.16% YoY price increase due to the significant production losses experienced in the previous year, when heavy rains and high humidity led to a 15 to 20% reduction in marketable strawberries.
United States
In W12, United States (US) strawberry prices increased slightly by 2.74% WoW to USD 4.12/kg, showing an 87.27% YoY surge due to ongoing supply constraints and adverse weather conditions, including heat waves and drought, which have impacted production volumes. However, MoM prices declined by 10.82% due to the seasonal increase in supply from regions like California, where favorable growing conditions have led to higher yields, temporarily easing market tightness.
Egypt
In W12, Egypt's strawberry prices increased by 1.92% WoW to USD 0.53/kg, with a 47.22% YoY increase. The YoY price surge is due to a significant rise in production costs, including fertilizers, pesticides, and labor, which have doubled compared to previous years. Additionally, adverse climatic conditions, such as high temperatures and successive heat waves, have led to reduced yields and quality in some areas, further contributing to higher prices. However, the MoM price drop of 3.64% can be attributed to increased local production, bolstered by expanded greenhouse cultivation and efficient irrigation methods, leading to a surplus in local markets and exerting downward pressure on prices.
Italy
In W12, Italy's strawberry prices declined by 5.91% WoW to USD 3.82/kg due to increased market supply as production volumes normalized following earlier weather-related delays. However, prices surged by 4.37% MoM and 17.90% YoY, reflecting a broader trend of rising strawberry prices in Italy. This upward trajectory is due to a combination of factors, including increased production costs and a growing consumer demand for strawberries, which have maintained their popularity among Italian households. Despite the recent weekly decline, the overall market dynamics suggest a sustained appreciation in strawberry prices over the longer term.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Enhance Disease Control and Harvest Efficiency
Strawberry growers in Huelva should apply preventive fungicide treatments and improve tunnel ventilation to reduce botrytis spread. Improving drainage systems in cultivation areas can help manage excess moisture, while investing in all-weather farm access roads will minimize harvest delays. Additionally, scheduling staggered plantings can ensure a more consistent supply despite weather disruptions.
Invest in Strawberry Processing to Reduce Losses
Strawberry growers in Myzeqe should establish partnerships with local processors to develop freezing, drying, or jam production facilities. By converting surplus and lower-quality fruit into processed products, farmers can extend shelf life, reduce waste, and create alternative revenue streams. Collaborating with buyers in the food industry can also help stabilize demand and improve market resilience against weather fluctuations.
Sources: Tridge, A2news, California Globe, Freshplaza, MSN




