
1. Weekly News
Brazil
Slow Sales and Price Drop for Fuji Apples in Southern Brazil
In W23, the sales for Fuji apples in Southern Brazil's classification regions was slow. Experts from Hortifrúti/Cepea attribute this to several factors such as lower temperatures in major consumer centers, which reduce overall fruit demand, a high volume of inferior quality Fuji apples on the market, and competition from imports. On average, the Fuji 110 Cat 3 apple sold for USD 20.07 per 18 kilogram (kg) box (BRL 109.44/18 kg box), representing a 5% week-over-week (WoW) decline.
India
Apple Production and Prices in Rohru, Shimla Impacted by Climate Change
Climate change is causing a significant decline in apple production in Rohru, Shimla, along with a three-fold increase in production costs. The shift in the apple belt and the requirement for crops to experience 1.2 thousand to 1.5 thousand hours at 7 degrees Celsius (°C) are significant factors affecting production. Additionally, altered snowfall patterns are impacting tourism during Christmas and New Year. Climate change also affects apricots, plums, and cherries, with consumers increasingly preferring imported fruit varieties. Despite a slight increase in overall fruit production from 107 million tons in 2021/22 to 108 million tons in 2022/23, transport and storage infrastructure challenges remain. Addressing these issues could help mitigate hunger and malnutrition while reducing carbon emissions.
New Zealand
Decline in New Zealand Apple Exports Due to Size Variations
New Zealand Apples and Pears (NZAPI) reported an 11% decrease in total carton equivalents (TCEs) for export in 2024, attributed to varying fruit sizes across growing regions. Despite this, exceptional summer conditions have produced apples with excellent eating quality and color. Smaller fruit sizes are linked to last year's Cyclone Gabrielle and spring weather conditions. However, this year's crop is praised for its outstanding flavor profile, with trees recovering better than expected from the cyclone's impact. The export cartons contain New Zealand's best apples, which are highly regarded in global markets.
Russia
Spring Frosts and Hail Devastate Apple Crops in Russia and Belarus
Spring frosts and hail have severely damaged apple orchards in Russia and Belarus, leading to significant crop losses and a 30% to 35% decrease in production. As a result, apple prices in these countries are expected to reach record highs by spring 2025. Russia's ban on importing apples from European Union (EU) countries, Moldova and Ukraine has also led to complex and costly import schemes. While Russia sources apples from Serbia, these supplies are dwindling due to market diversification. Imports from Turkey, Iran, and Azerbaijan have increased but remain expensive due to high transport costs and quality issues. Finding affordable apples will be challenging, with the European apple harvest likely lower this 2024.
Ukraine
Hailstorms Damage 5 to 10% of Apple Orchards in Ukraine
Hailstorms damaged 5 to 10% of apple orchards in Ukraine, while blueberry-growing enterprises experienced more minor losses. Agronomists reported crop damage in neighboring villages. Anti-hail nets saved many businesses, with investments in them already paying off. The threat of hailstorms in Ukraine will persist until the end of June, with additional risks of increased losses due to the abnormally early ripening season of blueberries and raspberries in 2024.
United States
US Apple Holdings Surge in 2024
Apple holdings in the United States (US) have increased by about a third, with 57 million bushels in storage on June 1, marking a 36% rise from last June's total and a 34% increase over the 5-year average. Fresh apple holdings reached 40 million bushels, up 38% from last June's inventories, while processing holdings hit 17 million bushels, 32% higher than last year and 19% above the previous year's value. Processor movement reached 6.2 million bushels, 50% higher than last May's figure. Only Michigan and Virginia reported storage declines, while Washington's storage rose from 34 million to 47 million bushels. The top 15 varieties in storage include Red Delicious, Honeycrisp, Granny Smith, Gala, Fuji, Cosmic Crisp, Pink Lady/Cripps Pink, Golden Delicious, Ambrosia, Rome, Idared, York, McIntosh, Envy, and Empire.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Apple Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
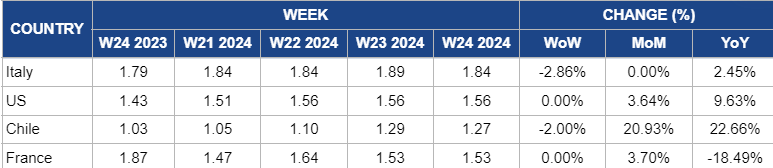
* Varieties: US and Italy (Gala), Chile, South Africa, and France (Granny Smith)
Yearly Change in Apple Pricing Important Exporters (W24 2023 to W24 2024)
* Varieties: US and Italy (Gala), Chile, South Africa, and France (Granny Smith)
* Blank spaces on the graph signify data unavailability stemming from factors like missing data, supply unavailability, or seasonality
Italy
The 2.86% WoW decrease in apple prices in Italy to USD 1.84/kg in W24 is due to reduced demand as summer fruits gain popularity, causing a shift in consumer preferences. Economic challenges and import restrictions in key markets like India and Egypt have also impacted export volumes. Despite steady domestic sales earlier, the onset of summer has led to quality-related discounts, particularly for Red Delicious apples. This overall shift in market dynamics has contributed to the decline in orange prices.
United States
In W24, apple prices decreased by 2.86% WoW to USD 1.84/kg in W24. The price decline is due to a seasonal shift in consumer preferences towards summer fruits, reducing demand for apples. Economic challenges and import restrictions in key markets like India and Egypt have also impacted export volumes. Despite no month-on-month (MoM) change, the 2.45% year-over-year (YoY) increase reflects ongoing inflationary pressures, higher production costs, and weather-related impacts on crop yields. This complex interplay of factors contributes to the fluctuating orange prices.
Chile
There is a 2% WoW decrease in apple prices to USD 1.27/kg in W24 in Chile. This is due to short-term market fluctuations, such as supply or consumer demand changes. However, the significant 20.93% MoM increase and 22.66% YoY increase suggest broader trends influencing higher prices over time, such as inflation, increased production costs, or changes in market dynamics. These contrasting short-term and long-term factors contribute to the overall price trends observed in the apple market.
France
In W24, apple prices in France held steady at USD 1.53/kg, with a 3.7% MoM increase but an 18.49% YoY decrease. The stable prices suggest a balanced market, while the MoM increase may reflect short-term adjustments. The YoY decrease likely stems from broader market trends or changes in production costs.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Enhancing New Zealand Apple Export Strategies
To address the decrease in export volumes due to varying fruit sizes, NZAPI should implement the following strategies. Enhance orchard management practices to ensure consistent fruit sizes across growing regions. Invest in research and development to mitigate the impact of adverse weather conditions on fruit size. Focus on marketing New Zealand apples' exceptional eating quality and flavor profile to maintain their premium position in global markets.
Mitigating Hail Damage in Ukrainian Orchards
To protect orchards from hail damage in Ukraine, orchard owners should invest in anti-hail nets and consider insurance options to minimize financial risks. Diversifying crops and planting resilient varieties can also help reduce the impact of hail damage. Collaborating with local experts can provide valuable support in implementing these strategies effectively.
Addressing Climate Change Challenges in Apple Production in Rohru, Shimla
To tackle the impact of climate change on apple production in Rohru, Shimla, farmers can implement several key strategies. Firstly, they should consider shifting to more resilient apple varieties that require fewer chilling hours. Improved irrigation and water management practices can help manage erratic rainfall patterns. Collaborating with experts to adopt sustainable farming practices and investing in greenhouse cultivation can enhance production resilience. Diversifying crops to include less climate-sensitive varieties and improving transport and storage infrastructure will also be crucial.





