W34 2024: Orange Weekly Update

1. Weekly News
Brazil
Orange Prices Remained High Despite Cold Front in São Paulo
Despite a cold front hitting São Paulo, Brazil, the orange market remained resilient, with prices rising amid reduced supply. From August 12 to 16, 2024, the average price of oranges on the tree reached USD 17.97 per 40.8-kilogram boxes (BRL 98.79 per 40.8-kg boxes), a 2.51% week-on-week (WoW) increase. This growth is due to limited supplies and strong pressure from high industrial contract prices.
Brazil Faces Challenges in Orange Supply for 2024/25
As Brazil's 2024/25 orange crop is harvested, major processors operate at full capacity, yet challenges loom. The persistent dry weather and greening disease in primary growing regions have adversely affected fruit maturation, raising concerns about yields. The total orange crop may fall below the historically low Fundecitrus forecast of 232.38 million boxes, potentially marking the lowest production level since the 1988/89 marketing year. Moreover, the demand is expected to exceed supply before the 2025/26 crop becomes available, further stressing the market.
Egypt
Egypt Dominates EU Orange Imports Amid Decline in South African Supplies
According to the Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries, and Food (MAPA), the European Union's (EU) citrus import trends focus on oranges. From Sep-23 to Jul-24, the EU imported 861.7 thousand metric tons (mt) of oranges, a 4.5% year-on-year (YoY) decrease from the previous campaign but a 12% increase over the average. Egypt solidified its position as the top supplier, capturing 57.1% of the market, while South Africa's share dropped to 31% YoY, reflecting a 22.2% YoY decline in supply. The rise in Egypt's exports, particularly to the Netherlands, Spain, and France, led to an overall increase in EU orange imports, even as other suppliers like Zimbabwe, Argentina, and Morocco experienced significant declines.
Honduras
Orange Prices Surge in Honduras Due to Production Decline
In recent months, orange prices in Honduras soared to USD 153.27/1 thousand pieces of oranges (HNL 3,800/1 thousand pieces of oranges), a sharp increase from USD 40.37 to 60.50 (HNL 1,000 to 1,500) a year ago. This price surge is due to a significant drop in production caused by climate change and pests plaguing orange plantations. Sonaguera, the citrus capital of Honduras, is facing a status decline due to reduced yields. While the lower Aguan region previously boasted around 300 trucks transporting oranges annually, this number has dwindled to about 100, with most of the fruit now exported to Guatemala. Managing 117.3 hectares (ha) or 290 acres of orange trees, the Cooperativa de Agricultores de Sonaguera generates USD 1.1 million (HNL 28 million) annually and provides jobs for around 100 people. Initiatives to combat the destructive Huanglongbing (HLB) disease have received government and international support, highlighted by the recent distribution of 13.3 thousand certified citrus plants to enhance production. Despite these measures, many producers are shifting to other crops like African palm and livestock due to ongoing challenges.
Italy
Water Shortages Threaten Sicily's Citrus Production Amid Severe Drought
Responsible for 65% of Italy's orange production, Sicily is facing one of its worst climate crises due to severe drought. Local agricultural associations have issued a joint letter to authorities, urging immediate action to combat water shortages and safeguard the region's citrus industry. The letter emphasizes the need for infrastructure upgrades, including improvements to dams and water reserves, reducing pipe leaks, and streamlining water access for farmers. Additionally, they are calling for economic relief measures such as fee compensation, energy cost discounts, and better crop insurance to mitigate the impact of the drought on orange production. The associations warn that without prompt action, the future of Sicily's citrus industry is at serious risk.
Peru
Adverse Weather Boosts Peruvian Orange Exports Amid Global Supply Disruptions
Adverse weather conditions, including torrential rains and frost, have reduced orange production in major citrus-producing countries such as South Africa, Brazil, and Egypt, significantly impacting global supply. This shortage has benefited Peru, where orange exports surged in Jul-24. Peru exported 4.7 thousand tons of oranges worth USD 4.9 million, marking a 22% YoY increase in volume and a 168% YoY rise in value. The Netherlands led imports, receiving 60.4% of the total export value, followed by the Dominican Republic, the United Kingdom (UK), Sweden, and Colombia. Most exports were of the Valencia variety, with Selva Industrial SA dominating the market at 32% of total exports.
South Africa
Prices of South African Cambria Oranges Surged in the Chinese Market Despite Low Volumes
In W34, South African Cambria oranges have experienced an increase in arrivals in the Chinese market compared to the beginning of Aug-24, although overall volumes remain low. The current batch has green stems and is adequately hydrated but not yet fully sweet, leading to 20% to 30% higher prices than in 2023. In contrast, Australian oranges have disappointed consumers with their low quality, resulting in a decrease in selling prices.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Orange Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
* Varieties: Spain, South Africa, and the US (Navel), Italy (Tarocco), and Egypt (overall orange average)
Yearly Change in Orange Pricing Important Exporters (W34 2023 to W34 2024)
* Varieties: Spain, South Africa, and the US (Navel), Italy (Tarocco), and Egypt (overall orange)
* Blank spaces on the graph signify data unavailability stemming from factors like missing data, supply unavailability, or seasonality
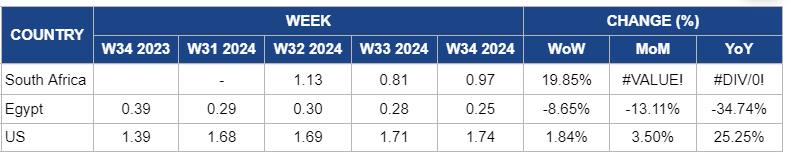
South Africa
Orange prices in South Africa surged by 19.85% WoW to USD 0.97/kg in W34. This is due to a significant drop in the quantity and quality of citrus fruits caused by inclement weather, including frost and hail storms. The shorter-than-usual orange campaign and port issues related to Citrus Black Spot (CBS) prevention measures have further constrained supply. As a result, the reduced availability of high-quality oranges has led to a substantial price increase.
Egypt
Orange prices in Egypt decreased by 8.65% WoW to USD 0.25/kg in W34, compared to last week's price of USD 0.28/kg. There is also a 12.11% month-on-month (MoM) decrease and a 34.74% YoY reduction from USD 1.39/kg last year. The recent price drop is mainly due to an oversupply in the market, which has been exacerbated by a huge harvest this season. Despite this, Egypt's strengthened export position and increased market share in the EU could exert upward pressure on prices in the near future. As Egypt continues to dominate the EU market and other suppliers face constraints, prices are expected to stabilize or potentially increase, reflecting robust demand for Egyptian oranges and reduced competition from different sources.
United States
In W34, the orange prices in the United States (US) increased by 1.84% WoW to USD 1.74/kg, compared to the previous price of USD 1.71/kg in W33. There is also a 3.5% MoM and a 35.25% YoY increase. This continued price rise is primarily due to ongoing supply constraints resulting from a reduced production forecast for oranges in Florida. Moreover, the persistent challenges, including citrus-greening disease and damage from recent hurricanes, have significantly impacted production. These factors have not only constrained supply but also driven up production costs. Additionally, the price increase reflects a broader recovery trend from past low outputs and elevated production expenses. The price adjustments also account for the higher costs associated with the diminished supply and the need to address the overall market imbalance caused by the reduced Florida harvest. As these issues persist, prices will continue to rise in the short term.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Enhance Promotion and Quality Assurance for Cambria Oranges
Despite low volumes, South African exporters should enhance promotional efforts and invest in quality assurance to capitalize on the increased prices of South African Cambria oranges in the Chinese market. This includes launching targeted marketing campaigns to highlight the distinctive qualities of Cambria oranges and attract new buyers. Additionally, they should focus on improving the sweetness and overall quality of the oranges through better post-harvest handling and quality control measures. These combined efforts will help justify the higher prices, boost market demand, and maintain a competitive edge.
Implement Infrastructure Upgrades and Economic Relief for Sicilian Orange Industry
To address the severe drought impacting Sicily's orange production, local agricultural associations in Italy should prioritize implementing infrastructure upgrades and securing economic relief measures. This involves working with authorities to enhance water management infrastructure, including upgrading dams, repairing pipe leaks, and improving water access for farmers. Additionally, the associations should advocate for economic support such as compensation for fees, discounts on energy costs, and enhanced crop insurance. These actions are essential to mitigating the drought's impact and safeguarding the region's citrus industry.
Strengthen Citrus Export Strategies to Maintain Market Share
South African citrus exporters should develop and implement strategic measures to counter the decline in market share and improve competitiveness in the EU market. This involves enhancing product quality and reliability to meet the high standards demanded by EU consumers. Exporters should also target marketing efforts to emphasize the superior attributes of South African oranges and leverage promotional campaigns to attract new buyers. Additionally, establishing or strengthening trade partnerships with EU importers and exploring opportunities for expanding into emerging markets will help boost market presence and recover lost share. Improving supply chain efficiency ensures consistent product delivery and supports market growth.
Sources: Tridge, Portaldelcampo, Comitedecitricos, Portal Do Agronegocio, Agronews, Mintecglobal, Freshplaza





