W7 2025: Beef Weekly Update
.jpg)
In W7 in the beef landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- FAO projects a 12% increase in global meat production by 2033, reaching 388 mmt. Beef production is expected to reach 81.2 mmt, driven by improved genetics and efficient management.
- The Chile-EU ITA expands tariff cuts to 99.6% of Chilean products, enhancing the competitiveness of Chilean beef, pork, poultry, and sheep meat in Europe.
- South Korean beef sales declined after the LNY 2025 holidays due to cold weather and weak restaurant demand.
- Germany has contained an FMD outbreak in Brandenburg, leading to lifting of animal movement restrictions.
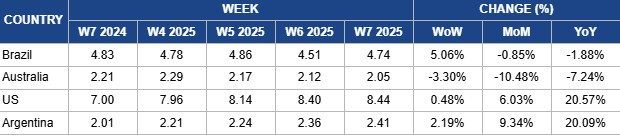
- Brazil, the US, and Argentina experienced weekly price increases driven by higher demand and supply concerns, while Australia saw a price drop due to the impact of hot and dry weather in previous weeks.
1. Weekly News
Global
FAO Forecasts 12% Growth in Global Meat Production by 2033
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) projects a 12% increase in global meat production over the next decade, reaching 388 million metric tons (mmt) by 2033, an increase of 41 mmt from the period between 2018 and 2020. Poultry is expected to lead this growth, with production rising from 141.3 mmt in 2024 to nearly 160 mmt in 2033, driven by demand in developing countries due to low costs and high efficiency. Pork production will also expand, reaching 131.1 mmt by 2033, with Asia leading the recovery from African swine fever (ASF).
Beef production is expected to hit 81.2 mmt, supported by improved genetics and efficient management, with China, India, the United States (US), Brazil, and Australia as key contributors. Sheep meat will grow to 19.3 mmt, with China contributing 16% of this increase. Meat exports are forecast to exceed 40 mmt by 2033, with the US and Brazil dominating at 40% of global exports, while the European Union’s (EU) share will decline to 15%. Africa is expected to drive demand, accounting for 73% of import growth, but must address health and sustainability challenges in its meat industry.
Chile
Tariff Cuts Under Chile-EU Trade Pact to Strengthen Chilean Meat Industry
The Interim Trade Agreement (ITA) between Chile and the EU came into effect on February 1, 2025. This agreement enhances trade provisions, including significant benefits for Chilean meat exports. Notably, the EU has expanded tariff reductions to cover 99.6% of Chilean products, up from the previous 94.7%, encompassing almost all Chilean exports to the EU market. This expansion covers products such as beef, sheep, poultry, and pork, and other products like olive oil, seafood, and food preparations, which will now face reduced tariffs, improving their competitiveness in the European market. Additionally, the ITA ensures mutual recognition of geographical indications and designations of origin, granting exclusivity to these products in their respective markets. This mutual recognition aims to protect and promote regional meat specialties, enhancing their market appeal and authenticity.
Germany
Germany Contains FMD Outbreak
Germany has successfully contained a foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) outbreak in a water buffalo herd in Brandenburg, preventing further spread. As a result, the German Ministry of Agriculture lifted animal movement restrictions, while the European Commission (EC) reclassified the affected area from a 3-kilometer (km) protection zone to an observation zone. The outbreak remained an isolated incident with no evidence of transmission to other species, though its origin is still undetermined. The Agriculture Minister announced that Germany will seek to regain its FMD-free status from the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH) , provided no new cases emerge over the next three months.
South Korea
South Korean Beef Sales Struggle After Lunar New Year
After the Lunar New Year (LNY) 2025 holidays, demand for Korean beef has sharply declined, prompting distributors to reduce processing to manage inventory. Large discount stores, small marts, and butcher shops have all seen a drop in grilled meat sales, worsened by severe cold weather. While slaughterhouse closures during the holiday helped ease backlog concerns, wholesale prices fluctuated, rising from USD 12.24 per kilogram (kg) (KRW 17,650/kg) before Lunar New Year to USD 13.36/kg (KRW 19,266/kg) on February 6. Despite steady demand for ribs, restaurant sales of premium cuts like sirloin, tenderloin, and ribeye remain weak, keeping overall Korean beef prices stagnant.
Uruguay
Uruguay Strengthens Presence in Japan’s Growing Meat Market
Uruguay is strengthening its position in the Japanese meat market through strategic participation in trade fairs, promotional activities, and collaborations with importers. At the Food Fair in Chiba, Japan, the National Meat Institute (INAC) showcased Uruguayan meat, offering tastings to reinforce brand recognition. Japan has become a key market, with Uruguayan meat exports increasing by 26% year-on-year (YoY) in 2024, reaching 10 thousand metric tons (mt).
However, a 38.5% tariff remains a major challenge, limiting competitiveness against Australia and the US, which dominate 80% of the market. Uruguay is boosting its presence with initiatives like Expo Osaka, an event held in April-May. A significant breakthrough was the introduction of beef tongue in Nov-22, a highly valued cut in Japan. While Australia competes with Uruguay in grass-fed beef, the US focuses on grain-finished meat. Despite the tariff barrier, Uruguay aims to further consolidate its market presence and expand exports.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Beef Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Beef Pricing Important Exporters (W7 2024 to W7 2025)
Brazil
In W7, Brazil's wholesale price for boneless rear beef increased by 5.06% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 4.74/kg. Despite this weekly rise, prices remained 0.85% lower month-on-month (MoM) and 1.88% lower YoY. In the local currency, prices rose 3.85% WoW to BRL 27/kg, reflecting a smaller change due to exchange rate fluctuations. According to Safras and Mercado, the wholesale market is still operating at relatively stable price levels. However, a moderate price increase was expected in the first half of the month, driven by salary inflows that stimulate the replenishment of wholesale and retail stocks. Despite this, demand is expected to be slow in the second half of the month, which could pressure prices downward. The decline has been more pronounced in specific cuts like picanha, alcatra, and striploin, aligning with the trend of consumers opting for more affordable protein options.
Australia
Australia’s National Young Cattle Indicator averaged USD 2.05/kg in W7, reflecting a 3.03% WoW decline, a 10.48% MoM drop, and a 7.24% YoY decrease. The decline was largely due to hot, dry conditions affecting stock quality in the previous week. Despite this, the Meat and Livestock Australia (MLA) reported that widespread rainfall in Queensland boosted confidence in both Queensland and New South Wales markets, lifting the Restocker Heifer Indicator and contributing to a rise in the National Indicator. Meanwhile, the feeder and heavy steer market showed WoW growth, driven by strong demand in northern markets. However, the trend was reversed in South Australia and Victoria, where finished stock commanded higher prices than feeders.
United States
In W7, US lean beef (92% to 94%) averaged USD 8.44/kg, rising 0.48% WoW for the sixth straight week and reaching its highest level since W39 2024. Prices also increased 6.03% MoM and surged 20.57% YoY, driven by tightening domestic supply due to a shrinking cow herd. According to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), total cattle and calf inventory stood at 86.7 million heads as of January 1, 2025, marking a 0.6% YoY decline and the sixth consecutive year of contraction. As a result, US beef production in 2025 is projected to fall by 4.4% YoY, with per capita beef consumption expected to decline by 2.68% to 58 pounds (lbs) per person.
Argentina
Argentina's average steer beef price climbed to USD 2.41/kg in W7, reflecting a 2.19% WoW increase, a 9.348% MoM rise, and a significant 20.09% YoY surge. The sharp YoY increase reflects weak beef consumption in 2024 due to economic challenges, while the WoW rise is linked to supply concerns. According to the Argentine Meat Exporters Consortium (ABC), cattle slaughter in Jan-25 totaled 1.14 million heads, down 8.1% MoM and 2% YoY. Beef production fell to 263.9 thousand mt, marking a 6% MoM drop and 1.5% YoY decline. The availability of light cattle categories decreased in Jan-25 compared to Dec-24, while steer and cow supply increased.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Expand Market Reach Through Diversified Trade Agreements
Given the global increase in meat production, Chile should leverage its expanded tariff reductions under the ITA to enhance its competitiveness in the European market. This can be through increasing production efficiency and enhancing product differentiation through branding and quality assurance. Expanding premium meat offerings, such as grass-fed and organic beef, will appeal to European consumers who prioritize sustainability. Additionally, Chilean exporters should maximize the benefits of geographical indication recognition by marketing regional specialties and collaborating with EU distributors to improve market penetration.
Boost Domestic Demand for South Korean Beef
With declining beef sales post-holidays, South Korea should introduce targeted consumer promotions, such as discounts on premium cuts and bundled deals with complementary ingredients. Expanding into ready-to-cook meal kits and promoting Korean beef in convenience foods could help stimulate demand beyond traditional restaurant consumption. Also, encouraging at-home grilling trends through recipe partnerships and social media engagement can stimulate demand. Collaboration with restaurants to introduce seasonal beef dishes may help stabilize prices and drive consumption.
Strengthen Uruguay’s Market Share in Japan
To compete with Australia and the US in Japan’s high-tariff meat market, Uruguay should engage in trade negotiations to secure preferential tariff reductions. This can be through bilateral agreements or regional trade blocs. Uruguay should focus on branding Uruguayan beef as a premium, grass-fed alternative. Strengthening partnerships with Japanese importers, increasing participation in trade expos, and negotiating trade concessions can also enhance market penetration. Additionally, emphasizing lesser-known but highly valued cuts, like beef tongue, can provide an edge over competitors.
Sources: Tridge, Agromeat, Aflnews, Bichos de campo, NoticiasAgricolas


