W21 2024: Banana Weekly Update

1. Weekly News
Australia
Australia Invests USD 2 Million to Revolutionize Banana Farming with Robotic Automation
Australia's Hort Innovation, Queensland University of Technology (QUT), Future Food Systems, Advanced Robotics for Manufacturing Hub, and BNL Industrial Solutions are investing USD 2 million in a groundbreaking program to revolutionize banana farming. This initiative focuses on developing a robotic arm to automate the labor-intensive and repetitive process of banana de-handing, using advanced computer vision and machine learning technologies. The leading research at QUT underscores the significance of this innovation for the banana industry. A feasibility study indicates strong interest among farmers in adopting robotic solutions for de-handing, which promises to enhance processing efficiency and safety. The project aims to improve processing efficiencies and integrate robotics into the broader agricultural landscape.
Peru
Peruvian Banana Exports Surge 12.3% in Volume and 13.2% in Value in Apr-24
In Apr-24, Peruvian banana exports totaled 14.7 thousand tons, marking a 12.3% year-over-year (YoY) increase in volume and a 13.2% YoY increase in value. Banana exports to the Netherlands totaled 5.5 thousand tons, valued at USD 4.3 million, with an average price of USD 0.78 per kilogram (kg). The United States (US) imported 2.3 thousand tons of Peruvian bananas worth USD 1.7 million at a rate of USD 0.71/kg. Italy received 1.4 thousand tons, valued at USD 1.1 million, priced at USD 0.74/kg, while Panama imported 1.4 thousand tons worth USD 1.0 million, at USD 0.69/kg. South Korea accounted for a 7.4% share, importing 967 tons valued at USD 800 thousand.
Philippines
Philippines Revises Fiscal Incentives for Banana Industry Ahead of South Korea FTA
The Philippine government is updating fiscal incentives for the local banana industry in preparation for the forthcoming free trade agreement (FTA) with South Korea. These adjustments are proactive measures to facilitate a smooth transition once the bilateral trade agreement is in effect. The modifications seek to optimize incentives for banana companies and enhance technical cooperation with South Korea, particularly in mechanical equipment, with support from the South Korean embassy. Ratification of the FTA is anticipated by mid-2024, with progress being made by both parties.
Portugal
Banana Sales Surged by 18.7% YoY in Madeira From Jan-24 to Apr-24
From Jan-24 to Apr-24, Madeira experienced a notable 18.7% YoY rise in banana sales, totaling 6.6 thousand tons. The Regional Directorate of Agriculture and Rural Development (DRADR) noted a significant increase in the sale of extra-category bananas, which saw a 13.1% YoY rise. Despite this growth, the share of extra-category bananas decreased slightly to 78.6% YoY, indicating a shift in consumer preferences. Notably, Apr-24 emerged as the peak sales month, recording 1.9 thousand tons sold, while Feb-24 witnessed the lowest sales at 1.4 thousand tons. Additionally, most bananas were exported to the Mainland, accounting for 80.5% of total sales, a notable increase from the previous year's 78.7%.
Russia
Russia's Q1-24 Banana Imports from China Surge 18-Fold Amid Ecuadorian Supply Issues
In Q1-24, Russia's banana imports from China surged 18-fold, reaching 3.5 thousand tons from Jan-24 to Mar-24, despite a decrease in Ecuadorian banana supply. The Russian Federal Service for Phytosanitary Supervision temporarily revoked the licenses of five Ecuadorian banana exporters due to the discovery of flea flies but restored them after technical consultations.
South Korea
Record-High Banana Imports Drive All-Out Effort to Control Fruit Prices in Korea
According to the Korea Customs Service, banana imports in Korea hit an all-time high in Apr-24, reaching USD 46.296 million, a 58.5% YoY increase. This surge is part of an all-out effort to control fruit prices, with pineapple imports also reaching record levels.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Banana Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
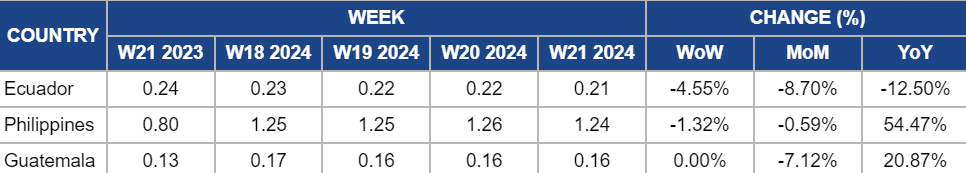
Yearly Change in Banana Pricing Important Exporters (W21 2023 to W21 2024)
.png)
* Blank spaces on the graph signify data unavailability stemming from factors like missing data, supply unavailability, or seasonality
Ecuador
In W21, the wholesale price of bananas in Ecuador decreased by 4.55% week-over-week (WoW) to USD 0.21/kg. Despite a decrease in production, prices declined due to short-term market dynamics, seasonal factors, and long-term trends. Immediate market fluctuations and supply-demand imbalances contributed to the 4.55% WoW decrease. Moreover, the seasonal changes in banana production led to an 8.70% month-on-month (MoM) decrease, while long-term trends, such as changes in production costs or shifts in global trade patterns, resulted in a 12.5% YoY decrease. These factors combined influenced the decline in banana prices in Ecuador.
Philippines
Banana wholesale prices in the Philippines decreased slightly in W21, dropping by 1.32% WoW to USD 1.24/kg compared to the previous price of USD 1.26/kg in W20. On a YoY basis, banana prices have significantly increased by 54.47%, rising from USD 0.80/kg in W21 2023. This substantial increase can be attributed to various factors, including the impact of El Niño-induced drought, which affected agricultural production and led to production losses across various crops, including high-value crops like bananas. Other factors, such as inflation, changes in consumer preferences, and global market trends, may have also contributed to the YoY increase in banana prices.
Guatemala
Banana prices in Guatemala remained stable at USD 0.16/kg in W21 and for the past weeks due to a consistent supply and steady demand. Favorable weather conditions ensured a regular harvest, while demand from key export markets remained strong and predictable. Additionally, no significant transportation or production disruptions contributed to the price stability.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Leveraging Robotic Automation for Sustainable Banana Farming
Revolutionizing banana farming with robotic automation presents a significant opportunity for Australian banana producers. To leverage this technology effectively, farmers should consider collaborating with research institutions and industry partners to pilot and adopt these robotic solutions. Participating in training programs to familiarize themselves with the technology and its integration into existing farm operations is crucial. Additionally, exploring funding opportunities and incentives for adopting automation can help offset initial investment costs and drive long-term efficiency gains in banana farming.
Strengthening Competitiveness for the South Korea FTA
Ahead of the FTA with South Korea, the Philippine banana industry should prioritize enhancing productivity and competitiveness. This includes investing in research and development to improve cultivation techniques, disease management, and post-harvest practices. Strengthening market linkages and value chains can help ensure smooth access to the South Korean market. Additionally, leveraging fiscal incentives and technical cooperation with South Korea can support the industry's growth and sustainability in the long term.
Managing Import Risks and Ensuring Quality in Banana Imports
With the surge in banana imports from China, Russian banana distributors should ensure compliance with phytosanitary regulations and quality standards. They should closely monitor supply chains to prevent the entry of pests and diseases that could impact local banana production. Collaborating with reputable suppliers and implementing rigorous quality control measures can help maintain consumer confidence in Russian banana imports. Additionally, diversifying import sources and exploring alternative suppliers can mitigate risks associated with overdependence on a single market.
Balancing Banana Imports with Sustainable Domestic Production
To manage the impact of record-high banana imports on fruit prices, South Korea should focus on enhancing domestic fruit production. This includes supporting local farmers through subsidies, technical assistance, and access to modern farming practices. Strengthening agricultural infrastructure and promoting sustainable farming practices can help increase domestic fruit supply and reduce reliance on imports. Additionally, implementing measures to reduce post-harvest losses and improve distribution networks can ensure consumers' stable supply of affordable fruits.
Sources: Tridge, Manila Standard, Fresh Plaza, Portal Fruticola





