W47 2024: Mango Weekly Update

1. Weekly News
Brazil
Brazil's Mango Exports Declined Amid Seasonal Challenges but Show Recovery Potential
Brazil's mango exports decreased by 17% year-on-year (YoY) to 29.7 thousand tons, with revenue dropping by 9% to just over USD 38 million. This decline reflects a return to normalcy after an unusually strong 2023 season, which benefited from crop losses in competing exporters like Peru and Ecuador. Moreover, the 2024 mango season challenges include stricter United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) certification requirements affecting shipments from the São Francisco Valley region and logistical disruptions caused by United States (US) port strikes. Despite these challenges, Brazil's mango exports are expected to recover in the coming months as reduced supply from Peru and Ecuador presents an opportunity to regain market strength.
Egypt
Egypt’s Mango Season Ends with Strong Export Performance
Concluded in early Nov-24, Egypt’s mango season yielded an estimated 2 million metric tons (mmt) across 100 thousand hectares (ha). Despite a 15% price drop early in the season due to overproduction, exports finished strong with robust demand from Russia, the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), and Europe. Average free-on-board (FOB) prices ranged between USD 700 and USD 1,400 per metric ton (mt), matching last year’s levels. Russia emerged as a primary buyer late in the season, while Gulf markets like Saudi Arabia sustained high summer demand. Favorable weather, early flowering, and improved crop quality contributed to increased production, solidifying Egypt’s position in major and smaller markets such as Morocco, surpassing Senegalese exports.
Mexico
Mexico Strengthens Mango Exports Despite Climate Challenges
In 2024, Mexico exported 80 million boxes of mangoes, with 90% going to the US, reinforcing its position as a leading global supplier. Despite climate challenges like droughts in the north affecting quality, favorable rainfall in central and southern regions signals a recovery, with export volumes projected to grow by 10 to 15% in 2025. Strong US demand and Mexico’s logistical advantage support its dominance, though rising production and logistics costs pose challenges. Smaller markets like Japan and Australia remain limited by certification requirements, while competition with Peru persists. The sector generated USD 600 million in 2024, aiming to capitalize on global mango shortages for future growth.
Spain
Spain's Axarquía Mango Harvest Surpasses Expectations Despite Drought
Producing over 90% of Europe's mangoes, Spain's Axarquía region harvested over 15 thousand mt this year, exceeding expectations by 25% despite a five-year drought. The season, led by the Keitt and Osteen varieties, lasted longer than usual, increasing availability in major supermarkets nationwide. Average prices remained favorable, with Keitt priced at USD 1.08 per kilogram (EUR 1.2/kg) and Osteen at USD 1.58/kg (EUR 1.5/kg). The Spanish Tropical Fruit Association (AET) highlighted the appeal of Malaga's mangoes for their sustainable production, organic certifications, and minimal carbon footprint. These mangoes compete effectively with imports, offering superior ripeness and meeting European Union (EU) standards, positioning them as a premium market choice.
Peru
Peru’s Mango Exports Surged Despite Ongoing Challenges
Between W35 and W42, Peru exported 3.5 thousand tons of fresh mangoes, generating USD 8.2 million in revenue, a 239% YoY increase in volume, and a 162% YoY rise in value due to an earlier export window. However, the average price dropped 22% to USD 2.32/kg, marking the third consecutive year of low prices. There is a strong demand for primary markets such as Canada, Chile, and Spain, with Canadian imports surging by 310%. Despite this growth, ongoing challenges like poor water management, logistical constraints, and low profitability continue to affect farmers, many of whom are struggling after three years of financial losses. The sector urgently needs innovative and sustainable solutions to stabilize its value chain and ensure long-term growth.
2. Weekly Pricing
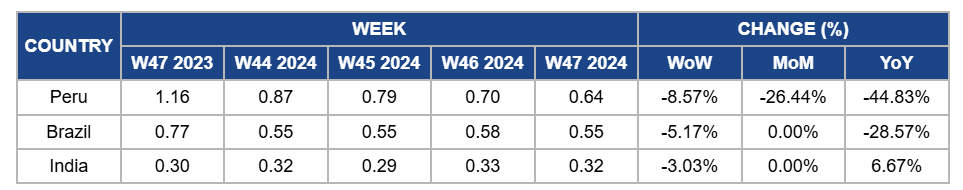
Weekly Mango Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Mango Pricing Important Exporters (W47 2023 to W47 2024)
Peru
Peru's mango prices decreased by 8.57% week-on-week (WoW) in W47, with a 26.44% month-on-month (MoM) decline and a 44.83% YoY drop due to ongoing market saturation caused by peak harvest periods in competing countries such as Colombia and Ecuador. The high supply from these regions continues to flood the market, intensifying competition and exerting downward pressure on prices. Additionally, logistical bottlenecks, including limited freezing and processing capacities, have compounded the oversupply issue, leaving growers constrained export opportunities. Despite Piura's mangoes' high quality and superior flavor, these factors have overshadowed efforts to stabilize prices.
Brazil
In W47, mango prices decreased by 5.17% WoW to USD 0.55/kg, with no MoM change. There is also a 28.57% YoY decrease due to persistent market saturation from peak harvests in the São Francisco Valley, which kept supply levels high. Additionally, reduced export demand from the US, influenced by stricter USDA certification requirements and logistical disruptions such as port strikes, has limited Brazil's ability to alleviate domestic oversupply. The 17% YoY decline in export volumes further highlights these challenges. While domestic demand remains stable, it has not been sufficient to offset the downward price pressures caused by abundant supply and export market difficulties.
India
In India, mango prices decreased by 3.03% WoW to USD 0.32/kg in W47 due to stabilizing market conditions as harvesting activities gained momentum, particularly for late-season varieties. Supported by favorable weather, the consistent supply has eased upward price pressures seen in previous weeks. There is a 6.67% YoY increase due to strong demand this season for improved-quality produce and the steady recovery in export activities, which supported market dynamics compared to last year.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Leverage Sustainability and Quality to Expand Premium Market Reach
Mango producers should emphasize sustainable production practices, organic certifications, and minimal carbon footprints in their cultivation processes to appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. They can achieve this by adopting water-efficient irrigation techniques, reducing pesticide use, and utilizing renewable energy sources. Certification from recognized organic and sustainability standards can further enhance their reputation. Additionally, producers should showcase the environmental benefits of their farming practices, highlighting their commitment to reducing carbon emissions and preserving biodiversity. To improve competitiveness in premium markets, they should also emphasize the superior ripeness and quality of their Keitt and Osteen varieties, ensuring they meet EU standards for freshness and taste. Producers across regions should collaborate with supermarkets and premium retailers to strategically position their products as high-quality, eco-friendly alternatives to imports, boosting both demand and profitability.
Focus on Strategic Export Partnerships for Late-Season Mangoes
Egyptian mango exporters should strengthen partnerships with key markets like Russia, the GCC, and Europe to capitalize on late-season demand. Emphasizing Egypt's high-quality crop and competitive FOB pricing will help sustain exports and mitigate early-season price drops caused by overproduction. Exporters should also explore promotional campaigns highlighting early flowering and favorable weather conditions to attract premium buyers in emerging markets, further solidifying Egypt's leadership in the international mango trade.
Sources: Tridge, Citrus Agro, Freshfruitportal, Freshplaza, Hfbrasil, Surinenglish





