W6 2025: Sugar Weekly Update

In W6 in the sugar landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- Global sugar consumption is rising, creating a 2.5 mmt deficit in 2024/25. India's output is expected to drop 14.4% due to lower cane supply and ethanol use, with a rebound expected in 2025/26. EU production is growing despite sharp price declines, especially in Spain.
- Brazil’s sugar exports fell 30.1% YoY, impacting revenues and future production. Myanmar faces export hurdles, while Ukraine shifts trade outside the EU but regains access in 2025.
- Pakistan's sugar prices surged 97.78% WoW due to shortages, triggering government action.
- Weather challenges in key regions, particularly Mexico and India, are affecting yields and future price stability. Government policies continue to shape domestic and international sugar markets.
1. Weekly News
Global
Global Sugar Consumption Rises as Production Declines
Global sugar consumption is rising in line with population growth, with trade shaped by supply, demand, and climate rather than geopolitical factors, according to the executive director of the International Sugar Organization (ISO). The executive director stated that United States (US) tariff threats have had little to no impact on the sugar market. In the 2024/25 season, global sugar production fell 1.25% to 179.07 million metric tons (mmt), while consumption increased 0.85% to 181.58 mmt, resulting in a 2.5 mmt deficit. US sugar prices have reached record highs, boosting imports from Guatemala, Colombia, and Brazil. Latin American sugar remains largely within the region due to strong demand. European Union (EU) production is rising despite a sharp price decline, particularly in Spain, where prices dropped nearly 30% in 2024. Global sugar consumption is expected to grow annually by 1.8 to 2.1%, driven by markets such as Mexico and India.
India
India's Sugar Production to Drop 14.4% in 2024/25, Rebound Expected in 2025/26
India's sugar production is expected to decline by 14.4% to 27.4 mmt in the marketing year (MY) 2024/25 due to reduced sugarcane output and increased ethanol diversion, according to the Investment Information and Credit Rating Agency of India Limited (ICRA) Research. Despite this, domestic supply will be sufficient to meet consumption needs. Around 4 mmt will be used for ethanol, while ending stocks are projected at 6.1 mmt, down from 7.7 mmt the previous year. Production as of December 31, 2024, stood at 9.54 mmt, compared to 11.3 mmt a year earlier. Covrig Analytics, a market research firm specializing in global sugar and ethanol markets, forecasts a 19.5% production increase in MY 2025/26 to 33.1 mmt, driven by expanded sugarcane cultivation and favorable weather, with ethanol use rising to 5.5 mmt.
Myanmar
Myanmar's Sugar Exports Set to Decline 30% Due to Pricing Disputes and Market Shifts
Myanmar has yet to export sugar to new markets like Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Singapore due to pricing disagreements, according to the vice chairman of the Myanmar Sugar and Sugarcane Products Entrepreneurs' Association (MASCEPA). With export prices at around USD 600 per metric ton (mt)—lower than domestic rates—sugar exports are expected to decline by 30% this fiscal year (FY). Vietnam remains the primary export destination, while molasses exports to China have been suspended. Domestic sugar prices exceed USD 2.38 per bag (MMK 5,000/bag), supporting higher sugarcane prices at USD 85.67/mt (MMK 180,000/mt). Despite operational challenges, Myanmar is projected to produce 500,000 mt of sugar this season.
Ukraine
Ukraine's Sugar Exports Rise 17% in 2024/25, With Shipments Shifting Outside EU
Ukraine exported over 352,000 mt of sugar in the first five months of MY 2024/25, a 17% increase from the previous season, according to the National Association of Sugar Producers of Ukraine (Ukrsugar). All shipments were directed outside the EU, a shift driven by EU trade restrictions. Major importers included Türkiye with 19% of total exports, Libya, Somalia, Sri Lanka, and North Macedonia. From January 1, 2025, Ukraine will regain access to the EU market, with a quota allowing the export of 107,300 mt by June 1, 2025.
2. Weekly Pricing
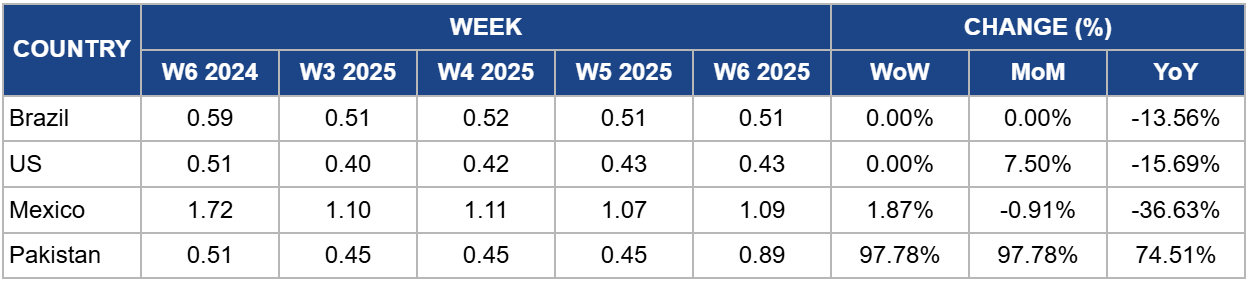
Weekly Sugar Pricing Important Producers (USD/kg)
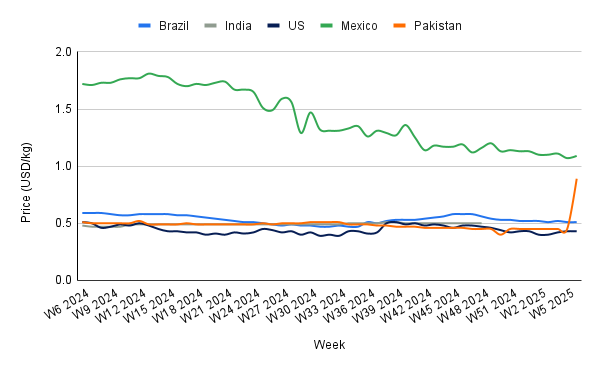
Yearly Change in Sugar Pricing Important Producers (W6 2024 to W6 2025)
Brazil
In W6, Brazil's sugar prices remained unchanged at USD 0.51 per kilogram (kg) but declined by 13.56% year-on-year (YoY), reflecting a broader downturn in the market. The sharp 30.1% drop in sugar and molasses exports in Jan-25 contributed to a 37.1% decline in export revenue. If this trend continues, reduced export earnings may dampen production incentives, potentially tightening future supply. This could initially exert downward pressure on global prices due to lower Brazilian exports, but in the long term, supply adjustments might lead to price stabilization or even increases, particularly if demand remains strong in key import markets.
United States
In W6, US sugar prices remained stable at USD 0.43/kg but experienced a monthly increase of 7.50% month-on-month (MoM) and 15.69% YoY, driven by government support for domestic producers. Federal subsidies and import restrictions keep US sugar prices nearly double global levels, benefiting major producers while raising costs for consumers and food manufacturers. High domestic prices have pushed some confectionery production offshore and increased reliance on high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS), which faces health concerns. If subsidies or trade policies change, US sugar prices could decline, increasing imports and reshaping domestic production. However, entrenched lobbying may limit policy shifts, maintaining current price trends.
Mexico
Mexico's sugar prices rose to USD 1.09/kg in W6, up 1.87% WoW but down 36.63% YoY. Veracruz, the country’s top sugarcane-producing state, faces challenges from climate variability, including droughts and floods, which impact yields and disrupt planting and harvesting cycles. With 40% of Mexico’s sugarcane processed in Veracruz, these environmental risks could reduce future output and contribute to price volatility. Sustained production challenges may tighten domestic supply, supporting higher prices, while potential disruptions could also affect export availability, influencing regional sugar markets.
Pakistan
Pakistan's sugar prices surged to USD 0.89/kg in W6, nearly doubling WoW and MoM by 97.78% due to an artificial shortage linked to exports. The government is taking measures to control inflation, including collaboration with provincial authorities and potential price caps. With Ramadan approaching, further price hikes are expected unless supply constraints are addressed. If the government intervenes by restricting exports or imposing price controls, domestic prices could stabilize, but global availability may tighten, potentially influencing regional sugar markets.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Diversify Supply Sources and Strengthen Trade Partnerships
With global sugar consumption outpacing production, importers should diversify supply sources to mitigate risks from production declines in India and Brazil. Strengthening trade partnerships with alternative suppliers, such as Ukraine and Latin American producers, can ensure stable access to sugar while minimizing price volatility.
Invest in Climate-Resilient Sugar Production
With climate challenges affecting sugarcane yields in Mexico, India, and other key producing regions, stakeholders should invest in sustainable and climate-resilient agricultural practices. Supporting drought-resistant sugarcane varieties, precision irrigation, and regenerative farming can enhance long-term production stability and reduce environmental risks.
Adapt Pricing Strategies and Inventory Management
Given fluctuating sugar prices in key markets like the US, Mexico, and Pakistan, businesses should implement dynamic pricing strategies and optimize inventory management to navigate market shifts. Hedging strategies, futures contracts, and stockpiling during low-price periods can help stabilize costs and protect against supply disruptions.
Sources: Tridge, Grain Trade, News Foodmate, UkrAgroConsult, EFE: Agro, Heritage, Notiver, ChiniMandi




