W34 2025: Beef Weekly Update
.jpg)
In W34 in the beef landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- The EU protected its beef sector in the latest US trade deal, excluding it from tariff concessions while granting access to other American farm products.
- Argentina’s beef exports rebounded to 76 thousand mt in Jul-25, supported by higher international prices and currency devaluation.
- Nicaragua expanded beef exports to China with its 36th shipment, highlighting the sector’s economic role and improved sanitary controls.
- South Korean beef retains cultural and economic importance through premium Hanwoo sets and record auctions, while trade liberalization debates reveal political sensitivities.
- Ukraine saw a surge in live cattle and beef exports in Jul-25, capitalizing on tighter global supplies and stronger demand, boosting revenues.
1. Weekly News
European Union
EU Shields Beef Sector in Trade Deal with the US
The European Union (EU)–United States (US) trade agreement sought to ease tensions over threatened tariffs, but beef was deliberately excluded from the EU’s tariff concessions, reflecting its status as a highly sensitive sector. While the EU agreed to lower barriers for several US agricultural products, including nuts, dairy, pork, and bison meat, it maintained protections on beef alongside poultry, sugar, rice, and ethanol, to shield European farmers from competitive pressure. This decision highlights the EU’s cautious approach, prioritizing market access for products its industries need while safeguarding sectors like beef that are central to rural economies and politically sensitive. Nonetheless, farm representatives warn that even with beef excluded, the deal indirectly disadvantages producers by making US agricultural imports cheaper and raising costs for EU exports to the US, potentially eroding overall competitiveness in the livestock sector.
Argentina
Argentina’s Beef Exports Rebound in Jul-25 amid Price Gains and Currency Shift
In Jul-25, Argentina’s beef exports reached 76 thousand metric tons (mt), the highest monthly volume of the year, marking a 10% year-on-year (YoY) rise and 7% month-on-month (MoM) increase. This growth was largely driven by improved international prices and currency devaluation that boosted competitiveness. Despite this rebound, total shipments between Jan-25 and Jul-25 were still 15% below 2024 levels due to a weak start to the year. Government measures also influenced sentiment, including a modest cut in export duties on steer beef from 6.75% to 5%. However, producers had anticipated significant reductions.
Meanwhile, domestic beef consumption remained strong at around 53 kilograms (kg) per capita annually. This was supported by high slaughter rates and feedlot supply, even as exports to China benefited from preferential conditions without withholdings. However, structural challenges persist as ranchers continue to demand modernization of the foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) vaccination plan to secure long-term competitiveness. On the other hand, economists warn that fiscal pressures limit the scope for further tax relief.
Nicaragua
Nicaragua Expands Beef Exports to China with New Shipment
One of the leading Nicaraguan meat producers, Industrial Comercial San Martín, recently launched beef exports to China, beginning with a shipment of over 21 mt through the Port of Shanghai. This marked the 36th batch of Nicaraguan beef exported since bilateral trade opened. This expansion reflects strengthened cooperation between the two countries’ health agencies and a shared commitment to ensuring food safety and trade facilitation. Supported by regular sanitary inspections and audits by the Institute for Agricultural Protection and Health (IPSA), Nicaragua has consolidated its position as a major beef exporter in Central America, where the sector is the second-largest contributor to the economy and employment. In 2024, beef production surpassed 162 thousand mt, highlighting the industry’s expansion potential. With China offering a key growth market, Nicaragua is targeting beef as a priority export and is also developing policies to enhance livestock efficiency among family farmers, reinforcing the sector’s role in national production and trade.
South Korea
Hanwoo Competitions and Gift Sets Highlight South Korean Beef Strength
Ahead of the 2025 Chuseok holiday, South Korean supermarkets launched early pre-orders for gift sets, with strong emphasis on value-for-money options amid rising living costs. Alongside fruit and seafood, premium Korean beef gift sets remain central, offering consumers affordable yet high-quality choices. At the same time, regional competitions such as the Gyeongnam and Chungnam Hanwoo Premium Beef contests showcased the excellence of local cattle, with record auction prices highlighting strong consumer demand for premium Hanwoo. These events encourage farmers to improve quality through better feeding and breeding practices and aim to strengthen the global competitiveness of Korean beef. Meanwhile, political debates around the South Korea-US summit underscored concerns about protecting sensitive agricultural markets, particularly beef, from further liberalization or quarantine easing. These developments reflect both the cultural and economic significance of beef in Korea, balancing consumer accessibility, farmer competitiveness, and trade policy challenges.
Ukraine
Ukraine’s Beef Exports Surge as Live Cattle and Frozen Shipments Drive Trade Balance
In Jul-25, Ukraine increased its beef and live cattle exports, taking advantage of tightening global supplies and rising prices for red meat. Live cattle exports reached 1.98 thousand mt, up 62% from Jun-25 and 14% above Jul-24. This has contributed to a total of 11.71 thousand mt, valued at USD 25.65 million in the first seven months of 2025, more than double last year’s revenue. Fresh and chilled beef exports also surged, with 35 mt shipped abroad in Jul-25, 70 times more than in Jun-25 and 50 times higher YoY, amounting to USD 165 thousand. However, cumulative exports of fresh and chilled beef for the year remain 89% lower than in 2024. Frozen beef exports totaled 1.68 thousand mt, slightly above Jun-25 but just below last year, while Jan-25 toJul-25 shipments rose 21% YoY to 11.27 thousand mt, generating USD 45.14 million in revenue. The export growth was driven by reduced global availability of cows and red meat, higher international prices, and the reallocation of major suppliers like Brazil and Australia to the US and Chinese markets, alongside stronger demand from the United Kingdom (UK). On the import side, live cattle purchases grew 36% over the seven-month period, though chilled beef imports were flat and frozen beef imports fell sharply.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Beef Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
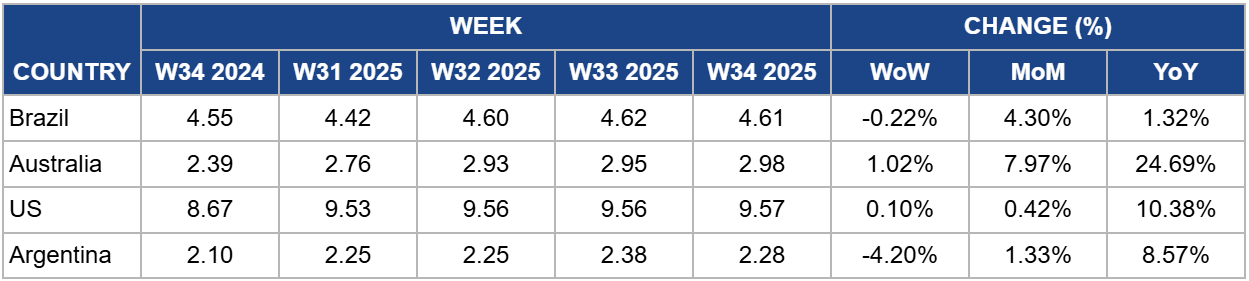
Yearly Change in Beef Pricing Important Exporters (W34 2024 to W34 2025)
Brazil
In W34, Brazil’s wholesale price for boneless rear beef fell slightly by 0.22% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 4.61/kg, though it remained 4.30% higher MoM and 1.32% YoY. In local terms, the price held steady at BRL 25.00/kg, suggesting that currency fluctuations largely drove the USD decline. According to Safras and Mercado, beef hindquarter cuts registered price drops, while frontquarters remained stable, a trend expected to persist in the short term due to slower replenishment between wholesale and retail in the latter half of the month. Chicken meat continues to hold a stronger competitive edge against beef, reinforcing its appeal among consumers. Looking ahead, the physical market points to a more lateral movement for the rest of the month, with meatpackers still facing challenges in aligning slaughter schedules.
Australia
In W34, Australia’s National Young Cattle Indicator (NYCI) rose to USD 2.98/kg, reflecting increases of 1.02% WoW, 7.97% MoM, and 24.69% YoY. According to Meat and Livestock Australia (MLA), the overall cattle market strengthened, except for the processor cow indicator, which recorded a slight decline. Rain-affected supply in New South Wales (NSW) contributed to a 12% WoW fall in national yardings, down to 60.49 thousand heads. Restocker demand was the main driver of price gains, particularly in NSW, where favorable pasture conditions supported stronger competition. The national restocker indicators saw the largest increases for steers and heifers. Meanwhile, the processor cow indicator eased, with Victoria showing the sharpest drop, followed by Western Australia (WA) and NSW, as yardings fell by 1.51 thousand heads to 8.34 thousand heads. Nonetheless, good-quality heavy cows at Dalby attracted strong buyer interest, which helped lift prices despite the broader national easing.
United States
In W34, US lean beef (92% to 94%) averaged USD 9.57/kg, marking a 0.10% WoW rise, a 0.42% MoM increase, and a 10.38% YoY growth. The sustained upward trend is supported by seasonal peak demand during summer alongside tight supply conditions driven by lower cattle herds, recent tariff hikes, and ongoing border closures with Mexico following the screw-worm outbreak. According to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), total US cattle inventory reached 94.2 million heads as of July 1, including 28.7 million beef cattle. While this indicates a modest recovery from Jan-25 levels, when cattle stood at 86.7 million, with 27.9 million beef cattle, inventories still remain 1% below YoY compared to Jul-23. On the trade front, the 50% tariff hike on Brazilian beef implemented in Aug-25 is expected to reshape global supply flows. Meanwhile continued border disruptions with Mexico may place additional strain on availability. Argentina, Australia, Paraguay, and Uruguay are positioned to gain market share, as their exports continue under the 10% baseline tariff set in Apr-25.
Argentina
In W34, Argentina’s average steer beef price fell 4.20% WoW to USD 2.28/kg, though it remained 1.33% higher MoM and 8.57% higher YoY. The weekly decline likely reflects weaker demand following the surge around the August 17 national holiday, which commemorates General José de San Martín. Despite this short-term dip, prices continue to receive support from structural demand growth, particularly as household consumption recovers from the slump experienced in 2024 amid economic difficulties. Data from the Ministry of Agriculture shows that beef per capita consumption reached 50.24 kg in Jul-25, signaling a rebound in domestic demand. This recovery is closely tied to rising real purchasing power, with wages increasing by 52% YoY across both public and private sectors, according to the National Institute of Statistics and Census of Argentina (INDEC). Given beef’s role as a cultural staple in Argentina, additional household income is often first allocated to beef purchases before other products, reinforcing the sustained upward momentum in prices despite temporary demand fluctuations.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Strengthen the Competitiveness of EU Beef Amid Trade Pressures
Since beef was deliberately excluded from tariff concessions in the EU–US trade agreement, European policymakers need to strengthen support for beef farmers through targeted subsidies, innovation in sustainable livestock systems, and promotion of premium EU beef in global markets. In turn, farmer associations should advocate for stronger trade defense mechanisms to offset the indirect disadvantages created by cheaper US agricultural imports in related sectors. Positioning EU beef as a high-quality, sustainable, and traceable product will be essential to mitigating competitive pressures and safeguarding rural livelihoods. Although shielding beef from tariff concessions offers short-term protection, indirect pressure from lower-cost US imports could still undermine competitiveness. To address this risk, the EU should increase investment in high-quality certifications such as organic and grass-fed labels, support climate-smart farming practices, and promote EU beef through strategic marketing campaigns both at home and abroad.
Build Sustainable Growth for Argentina’s Beef Exports
Argentina should leverage its export rebound by pursuing long-term structural reforms that enhance market access and productivity. While the currency shift and modest tax relief boosted competitiveness in the short term, fiscal pressures mean producers cannot rely solely on temporary government measures. A priority should be modernizing the FMD vaccination system to meet international standards, unlocking higher-value export markets beyond China. Additionally, Argentina can diversify its export destinations through new bilateral trade agreements, while incentivizing efficiency in feedlots and ranching practices to ensure a stable supply. Supporting value-chain integration between ranchers, processors, and exporters will also maximize margins and reduce volatility.
Maximize Nicaragua’s Entry into the Chinese Market
Nicaragua should consolidate its recent breakthrough in China by developing branding strategies that emphasize the quality and safety of its beef. Expanding bilateral cooperation on sanitary standards will be key to sustaining long-term access. To support production, the government should prioritize training and technical assistance for family farmers to enhance livestock efficiency, genetics, and feed management. Additionally, investment in cold-chain logistics and marketing campaigns in China could help Nicaragua capture higher-value segments of the market, reinforcing beef’s role as a pillar of national exports and employment.
Leverage Hanwoo Premium Branding in South Korea
South Korea should capitalize on the growing consumer demand for premium Hanwoo beef by investing in genetic improvement, feed innovation, and marketing campaigns that highlight Hanwoo as a national brand. Competitions and high auction prices show strong domestic support, but to remain competitive internationally, the government must also shield the sector from overexposure in trade negotiations. Expanding export opportunities in niche markets such as premium restaurants and diaspora communities abroad would add resilience. At the same time, ensuring affordability through balanced pricing strategies will help maintain consumer trust and strengthen beef’s role in cultural traditions like Chuseok.
Sources: Tridge, Efeagro, Foodmate

