W38 2024: Beef Weekly Update

1. Weekly News
Chile
Chilean Ambassador Highlights Strong Trade Ties and Beef Exports During Independence Celebration in Paraguay
During the celebration of the 214th anniversary of Chilean independence at Chile's Embassy in Asunción, Paraguay, , Chile’s Ambassador to Paraguay emphasized the strong trade relationship between the countries. He noted that Paraguay is Chile's fifth-largest trading partner in the region and the tenth-largest globally, with bilateral trade reaching USD 1.8 billion annually. Furthermore, the Ambassador highlighted that according to data from the National Service of Animal Quality and Health (SENACSA), Paraguay exported over 116.11 thousand metric tons (mt) of beef valued at USD 665 million the previous year, accounting for 50% of the country's beef exports.
European Union
EU and UK to Suspend Imports of Brazilian Beef from Female Cattle Over Hormone Concerns
The European Union (EU) announced that starting October 6, it will suspend imports of Brazilian beef from female cattle until it can confirm that these animals were not treated with estradiol, a hormone used in fixed-time artificial insemination (FTAI), the potential use of estradiol raises concerns due to potential hormone residues in meat, which can affect human health. The EU has strict regulations to prevent risks like hormonal imbalances and cancer, leading to the suspension of beef imports from treated female cattle. Only beef from male cattle will be permitted for trade during this period. Based on concerns about hormone residues in the meat, the ban will also apply to the United Kingdom (UK).
United States
US Beef Exports Showed Strong Growth in Jul-24
In Jul-24, the United States (US) beef and pork exports showed strong growth, according to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) data compiled by the US Meat Export Federation (USMEF). Beef exports reached 110.41 thousand mt, a 7% year-on-year (YoY) increase, with export value rising 12% YoY to USD 910.90 million. Key markets driving this growth include Japan, Taiwan, Mexico, and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) region. From Jan-24 to Jul-24, beef export value increased by 6% to USD 6.13 billion, despite a 2% drop in volume.
Pork exports also performed well, with Jul-24 shipments totaling 241.21 thousand mt, up 10% YoY. The export value rose 13% to USD 710.5 million, led by a record USD 244.5 million in exports to Mexico. Other strong markets included Latin America and South Korea.
US lamb exports saw a 13% YoY rise in value in Jul-24 despite a 12% YoY decline in volume. Through Jul-24, lamb exports increased 9% in volume and 18% YoY in value, driven by demand from the Caribbean, Mexico, the Philippines, and Canada.
US Cattle Futures Seek Stability Amid Economic Uncertainty
US cattle futures have been fluctuating despite steady demand. Fed cattle cash trades remained steady at USD 180.00 to USD 182.00 per hundredweight (cwt) in the Plains and slightly lower in the North at USD 288.00 to USD 292.00/cwt dressed. Feeder cattle futures show strength, with a potential rally above USD 240.00/cwt to USD 243.45. However, live cattle futures continue to struggle despite some gains in the Oct-24 contract.
A downturn in 90s trim prices could signal reduced consumer demand for ground beef. After strong growth earlier in the year, prices have plateaued between USD 370.00 and USD 380.00/cwt. A sharp decline would raise concerns about broader beef demand, as consumers may shift toward cheaper meats.
Given economic uncertainties and inflation, advancing live cattle futures near USD 190.00/cwt and feeder cattle futures near USD 250.00/cwt seem unlikely heading into the end of 2024. The outlook for 2025 remains uncertain, with tight cattle supplies and potential shifts in beef demand depending on broader economic conditions. Continued volatility in futures markets is forecasted.
2. Weekly Pricing
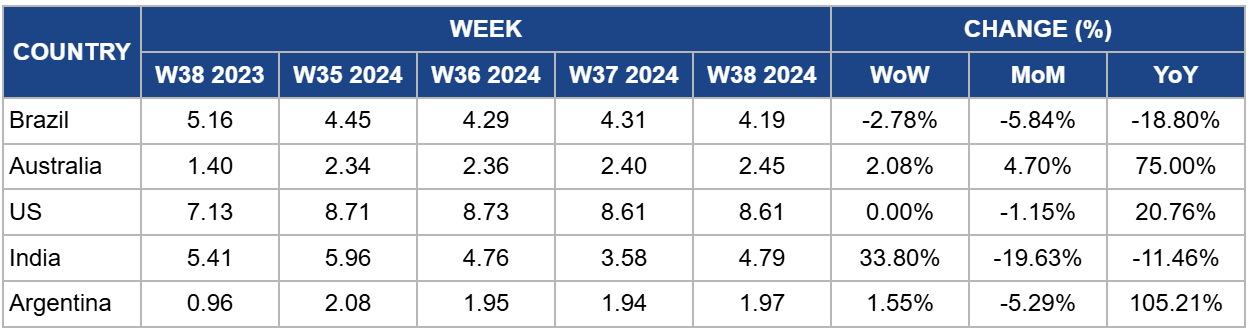
Weekly Beef Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
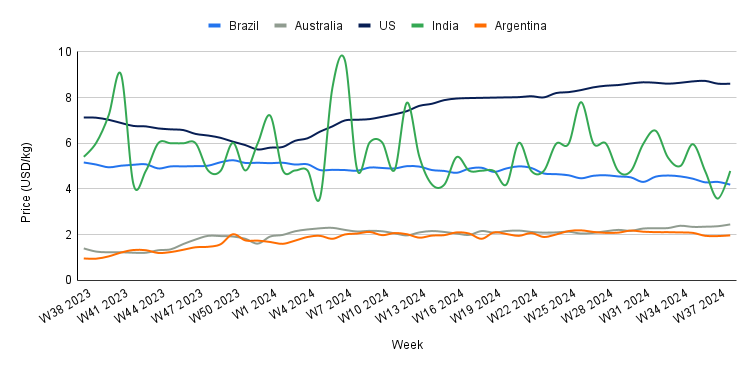
Yearly Change in Beef Pricing Important Exporters (W38 2023 to W38 2024)
Brazil
Brazil's wholesale price of boneless rear beef decreased to USD 4.19 per kilogram (kg) in W38, marking a 2.78% week-on-week (WoW) drop with a further 4.70% month-on-month (MoM) decrease from USD 4.42/kg in W35 2024. However, Brazil's beef cattle market started the week with firm prices, driven by tight supply and strong demand. Slaughter scales remain shortened across the country, supporting upward price momentum in the short-term forecast. Beef exports remain robust, potentially positioning Brazil to set a new shipment record.
Australia
In W38, Australia's national young cattle indicator averaged USD 2.45/kg, experiencing a 2.08% WoW increase and a significant 75% YoY rise from USD 1.40/kg in W38 2023. Australia's cattle market saw a 21% drop in saleyard numbers, with 53,161 heads yarded, though year-to-date throughput remains 29% higher than in 2023. The market was mixed, with restockers benefiting from price recovery. The National Young Cattle Indicator (NYCI) rose primarily due to New South Wales and Queensland online sales. Strong demand and improved cattle conditions led to price increases.
United States
The average price of US lean beef (92% to 94% lean) stood at USD 8.61/kg in W38, showing a significant 75% YoY increase. The US national average price for fresh beef surpassed USD 17.637/kg for the first time, driven by rising interest rates and increased production costs. Despite record retail prices, cattle farmers face challenges from market forces, including droughts affecting hay and forage availability. This leads to a contraction in cattle inventory as cow-calf producers send more female cattle to slaughter. While high beef prices benefit sellers, they create difficulties for buyers and those looking to expand operations. A recent dip in feed prices has provided some relief, though high interest rates remain a barrier to further growth. The USDA's Economic Research Service (ERS) predicts beef demand will decline in 2025, but prices are forecasted to continue climbing in the short term. Farmers are encouraged to use price risk management tools amid ongoing uncertainty.
India
India's average price of cow beef significantly increased to USD 4.79/kg in W38, marking a significant 33.80% WoW rise from USD 3.58/kg in W37. India's beef and cattle prices may face volatility due to social and political tensions arising from the Gau Dhwat Sthapana Bharat Yatra rally, which seeks a nationwide ban on cow slaughter. Political and social leaders have expressed strong opposition in northeastern states like Meghalaya and Nagaland, where beef consumption is culturally significant. If cow protection movements gain traction, beef supply could be disrupted in these regions, leading to potential price increases. Such actions could also create tension in the broader cattle market, affecting the supply chain for both domestic consumption and exports, mainly if stricter regulations are imposed. Any significant restriction on cattle slaughter in India could lead to a tighter market, driving up prices due to reduced availability.
Argentina
Argentina's average price of steer beef stood at USD 1.97/kg in W38, a 1.55% WoW increase but a 5.29% MoM decrease from USD 2.08/kg in W35. Furthermore, cattle prices are lagging behind inflation despite significant supply restrictions. Over the past year, calf prices rose by 190% YoY, below the 205% increase in the Wholesale Domestic Price Index (WPI). Young bull prices also declined by 3.4% YoY in Sep- 24, reflecting this trend. Slaughter numbers are down 8.6% YoY, yet consumer demand remains weak due to falling purchasing power, as wages fail to keep pace with inflation. This situation caps potential price increases in the cattle market, though tighter supply may support some recovery. Overall, the gap between beef prices and inflation will likely persist, impacting domestic consumption and market dynamics.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Strengthen Trade Relationships Between Chile and Paraguay
As highlighted during Chile's President's visit to Paraguay in Jul-24, Chile and Paraguay should enhance their trade relationship, particularly in beef. With Paraguay as Chile's fifth-largest trading partner and a trade exchange of over USD 1.8 billion in 2023, there is significant growth potential. To capitalize on this, both countries should initiate joint marketing campaigns and trade missions to boost beef exports. Establishing regular dialogue between trade officials will streamline customs processes and tackle trade barriers. Updating agreements like the economic complementarity agreement (ACE 35) can encourage mutual investment and market access. By fostering cooperation, Chile and Paraguay can leverage their strong diplomatic ties to strengthen their beef trade and serve as a model for regional integration in Latin America.
Enhancing US Beef Export Competitiveness
Producers should explore value-added products and niche markets, such as organic or grass-fed beef, to capitalize on the growth in US beef exports and differentiate their offerings. Strengthening supply chain partnerships, especially with importers in high-demand markets like Japan and Mexico, can facilitate smoother transactions and bolster sales. Expanding marketing efforts in ASEAN countries could also provide new avenues for growth.
Monitoring Political and Economic Developments in India and Argentina
To anticipate potential challenges and opportunities, producers in India and Argentina should actively monitor political and economic developments affecting their cattle markets.
Engaging in proactive dialogue with local communities about cow protection and related regulations in India can mitigate potential supply disruptions. For instance, forming partnerships with local leaders and advocacy groups can foster mutual understanding and create collaborative strategies that respect cultural practices while addressing concerns around cattle management.
In Argentina, cattle producers should advocate for policy measures to support purchasing power and address inflation, which could stabilize consumer demand for beef. Collaborating with industry associations to lobby for subsidies or financial assistance for farmers can help alleviate the impact of rising costs on production. Additionally, launching educational campaigns to inform consumers about the benefits of beef can help maintain demand during economic downturns. For example, producers might work with retailers to create promotions highlighting the nutritional value of beef, thereby incentivizing purchases despite financial challenges.
Sources: Tridge, MercoPress, Ohio Country Journal, Beef Magazine, Canal Rural, Meat & Livestock Australia (MLA), Page Valley News, The Hindu, Noticias Agropecuarias (NAP), Gob.cl


