W29 2024: Orange Weekly Update

1. Weekly News
Bangladesh
Increased Import Duties Challenge Vidarbha's Orange Exports to Bangladesh
Bangladesh has increased import duty from USD 0.75 per kilogram (BDT 88/kg) to USD 0.86/kg (BDT 101/kg), posing challenges for orange exporters from Vidarbha, a leading region in orange cultivation. The region spans over 126 thousand hectares (ha), including 78 thousand ha in Amravati district. The Indo-Bangla Orange Association (IBOA) has requested help from the Indian government because increased duties will likely reduce orange exports to Bangladesh from 25% to less than 15% of Vidarbha's total production. Usually, Vidarbha sends about 60 truckloads of oranges to Bangladesh daily during the season, but this number has reportedly dropped by half due to the higher duties.
Brazil
Rising Orange Prices Persist Amid Limited Supply in Brazil
Orange prices in Brazil have increased for the 10th week in a row in W29 because the market has a limited supply. A quick drop in the volume of early-ripening oranges available worsens this shortage. Even the reduced demand caused by mild weather has not prevented further price increases. Additionally, orange production remains low in São Paulo and the Triângulo Mineiro region, coinciding with high demand from juice factories that ended the 2023/24 season with very restricted stocks.
South Africa
South African Orange Growers Shift Focus to Processing Amid High Global Prices
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) reports that South African orange growers increasingly divert their produce to processing plants due to record-high international orange juice prices. While late 2023 rainfall ensured adequate irrigation water, drought conditions in the northern regions have led to smaller fruit sizes and reduced export volumes of oranges, grapefruits, and lemons. In the 2023/24 season, South Africa's orange planting area is projected to remain steady at 42.9 thousand ha, shifting from early-maturing to late-maturing navel oranges. Despite high rainfall boosting production to 1.69 million tons, a 3% year-on-year (YoY) increase, hot weather has resulted in smaller fruit sizes. Investments in protective nets are expected to improve overall orange quality and yield. Nevertheless, orange exports are projected to decline by 12% YoY in the 2023/24 season due to the smaller fruit sizes being exported.
United States
USDA Adjusts Florida Orange Harvest Forecast Upwards for 2023/24
The USDA has raised its forecast for the Florida citrus harvest for the second month in a row. The latest 2023/24 season estimate is 17.97 million boxes of oranges, a small increase from the early Jun-24 forecast. However, this is still much lower than the peak of 244 million boxes harvested in the 1997/98 season.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Orange Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Orange Pricing Important Exporters (W29 2023 to W29 2024)
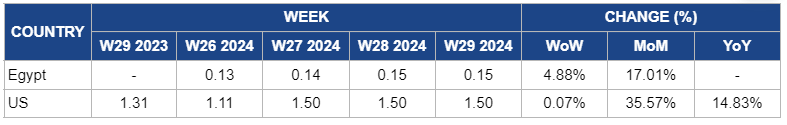
Egypt
In Egypt, orange prices slightly rose by 4.88% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 0.15/kg in W29 due to the devaluation of the Egyptian pound. This has increased the cost of agricultural inputs and made imported oranges more expensive, boosting demand for cheaper local oranges. Additionally, higher transportation costs and logistical challenges have further pushed up prices.
United States
Orange prices in the US during W29 remained steady at USD 1.50/kg due to a balance between supply and demand. The USDA's latest estimate projected a slight increase in Valencia orange production, reaching 18 million boxes for the 2023/24 season. This includes an additional 100 thousand boxes of Valencia oranges, contributing to a marginal supply boost. Despite this increase, the overall supply remains aligned with current demand levels.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Invest in Protective Nets to Improve Orange Quality
South African orange growers should invest in protective nets to enhance fruit quality and yield. Focus on mitigating the impact of hot weather on fruit size and quality to improve export volumes and market competitiveness. Implement this strategy to stabilize production and increase export potential in the 2023/24 season.
Address Orange Supply Shortages in Brazil
Brazilian orange producers should enhance production planning by diversifying harvesting schedules and improving crop management practices. This includes adopting early and late-ripening orange varieties to stabilize supply throughout the year and investing in more efficient irrigation and fertilization techniques to boost yields. Additionally, industry stakeholders should collaborate with juice factories to better align production with market demand and reduce price volatility.
Mitigate Rising Orange Prices in Egypt
Producers should adopt more affordable agricultural inputs and optimize transportation logistics to enhance cost-efficiency in Egypt's orange production amidst rising prices. Producers can lower input costs by purchasing inputs like fertilizers and pesticides in bulk or exploring less expensive, locally sourced alternatives. Implementing integrated pest management (IPM) practices can reduce reliance on costly chemicals. On the transportation front, optimizing routes through logistics software, consolidating shipments with other producers, investing in fuel-efficient or electric vehicles, and streamlining loading and unloading processes can help cut costs and improve efficiency. These measures will help stabilize prices and mitigate the financial impact of economic fluctuations and logistical challenges.
Sources: Tridge, Freshplaza, Guojiguoshu, USDA, Times of India,





