W41 2024: Beef Weekly Update
.jpg)
1. Weekly News
Global
Global Beef Market Outlook in 2024: Production and Trade
According to the latest Rabobank report, global beef markets experienced strong performance in H1-2024, supported by high demand and lower supply levels across various regions. This positive trend is expected to continue through H2-2024, with a slight increase in global production forecasted for Q4-2024, followed by a decline in 2025.
Australia’s beef production is projected to rise 18% year-on-year (YoY) in 2024, reaching 2.53 million metric tons (mmt), the highest since 2015. It is expected to hit a record 2.55 mmt in 2025, driven by heavier carcass weights, but anticipated to decline in 2026. In Brazil, record slaughter levels were observed in 2024, but production is forecasted to slow by 1% YoY in 2025 as more cattle are retained. Meanwhile, United States (US) beef production has been declining since 2022, a trend expected to continue into 2025, reducing exports, increasing imports, and driving record-high prices, with Australia gaining market share. European Union (EU) beef production rose by 5% YoY in H1-2024 but is forecasted to end the year 0.5% lower than in 2023 and decline further by 1% YoY in 2025 due to herd reductions.
On the trade side, Brazil’s record production and a weaker real led to a 29% increase in beef exports in H1-2024 compared to H1-2023. China’s beef imports grew by 17% YoY, with Brazil remaining its largest supplier. However, its market share slightly decreased as more exports were directed to North America and the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region. In the EU, Brazil remains the second-largest beef supplier although volumes have declined in 2024. United Kingdom (UK) beef exports to the EU increased by 4% YoY between Jan-24 and Jul-24, with the competitiveness of UK beef in the EU market being a key factor moving forward.
Brazil
Brazilian Fresh Beef Exports Surge 30% in 2024, Driving Domestic Price Increases
Brazilian fresh beef exports have continued to grow at a strong pace in 2024, significantly impacting domestic market prices. According to the Secretariat of Foreign Trade (Secex), total fresh beef shipped by Brazil from Jan-24 to Sep-24 increased by 30%, compared to the same period in 2023.
Brazil’s beef exports to China totaled 135.48 thousand metric tons (mt) in Sep-24, slightly below the record of 136.54 thousand mt in Sep-22. Higher export prices to China boosted its share of Brazilian beef exports. In September, China accounted for 54% of the total, marking the highest proportion since Feb-24.
Exports to the US remained robust, with over 20 thousand mt shipped in Sep-24, including 18.86 thousand mt of frozen beef. In contrast, exports to the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Turkey, which serve as intermediaries for sales to Iran, declined. Together, these two countries imported around 7 thousand mt in Sep-24, marking the lowest monthly volume so far this year.
On the domestic side, the Center for Advanced Studies on Applied Economics (Cepea) reports that the limited cattle supply continues to drive up prices in São Paulo and other regions. Adverse weather conditions, including a prolonged dry period and pasture shortages, have hindered the weight gain of pasture-fed cattle, preventing them from reaching ideal slaughter weight. Additionally, most confined cattle sold in H2-2024 are already reserved by slaughterhouses.
Canada
Canadian Beef Market Outlook in 2024 and 2025
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) expects Canadian beef cattle to continue their long-term decline into 2025. However, the situation will likely stabilize by the year's end due to improved prices and increased feed availability. The USDA expects calf production to decrease based on the 2024 breeding herd, while heifer retention is expected to improve if feeding conditions remain stable. This combination will lead to reduced cattle production and slaughter in 2025.
The USDA forecasts a 2% YoY decline in slaughter for 2025, following a 5% YoY drop in 2024, bringing the total to 3.36 million heads. Despite lower production, Canadian beef exports are expected to remain strong, while imports are projected to decline due to weaker consumer demand. Beef exports for 2025 are projected at 580 thousand mt (-15 thousand YoY), while imports are estimated at 245 thousand mt (-15 thousand mt YoY).
Beef consumption in Canada is expected to decrease by 1% YoY in 2025, reaching 970 thousand mt, following a 2% YoY drop in 2024. Rising costs and concerns about living expenses limit spending, leading consumers to opt for lower-priced beef products. Despite this, demand for high-quality beef remains strong, although it is purchased less frequently.
United States
US Beef Herd Rebuilding and Market Outlook in 2024
According to Rabobank, US beef cow inventories are expected to stabilize in 2024, with the herd size projected to remain between 27.9 million heads and 28.3 million heads through 2026. Producers remain cautious about restocking due to uncertainties in production and pricing. The current US herd rebuild began in 2014, with key events like peak heifer slaughter in 2010, increased cow slaughter in 2011, and rising replacement heifers in 2012. Recently, heifer slaughter peaked in 2023, and cow culling hit multi-decade highs in 2022, with the focus now on heifer retention.
Over the past 30 years, the US beef market has seen decreasing supply and rising demand, with retail beef prices hitting USD 17.97 per kilogram (kg) in Jul-24. Rabobank expects prices to reach USD 20.94/kg by 2027. By 2026, 500-pound calves could average USD 881.85, and replacement heifers may fetch up to USD 4,000 per head compared to current prices of USD 2,800 per head, as estimated by CattleFax, an industry resource specializing in market analysis and forecasts for the cattle and beef industry. However, part-time producers remain cautious due to high production risks and financial uncertainty.
Climate conditions have worsened the outlook, as El Niño failed to recover pastures in 2023/24, and La Niña is set to return in late 2024, threatening forage availability. Rising interest rates, from between 3% and 4% a decade ago to 8% to 9% currently, have pressured producers, particularly older farmers. These factors are expected to accelerate consolidation in the cow-calf segment, limiting growth opportunities for smaller operations.
2. Weekly Pricing
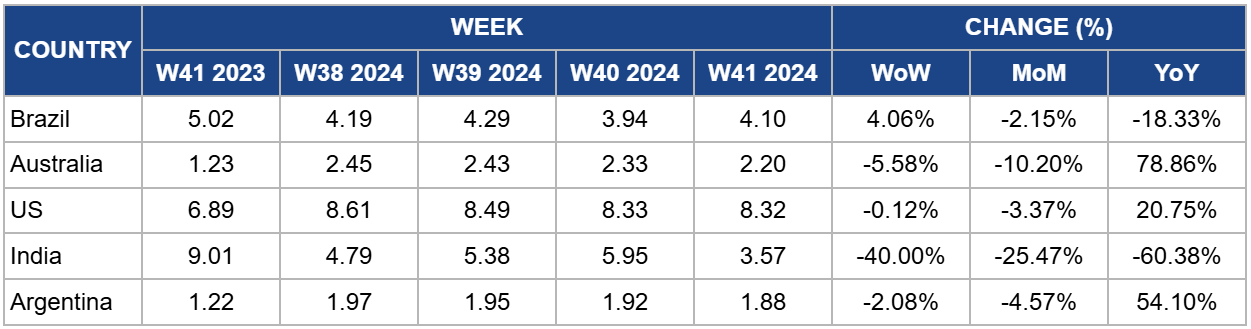
Weekly Beef Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
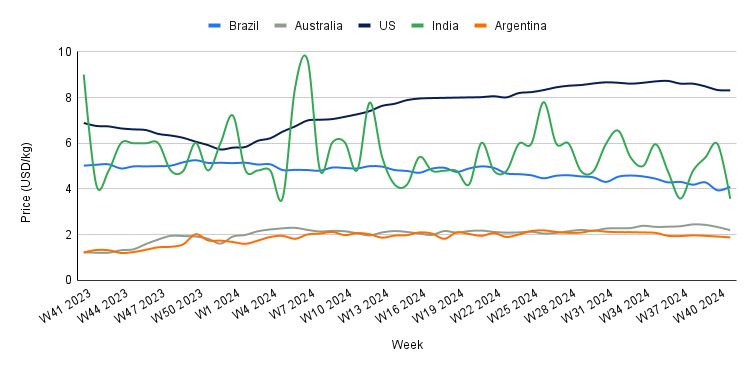
Yearly Change in Beef Pricing Important Exporters (W41 2023 to W41 2024)
Brazil
In W41, Brazil's wholesale price for boneless rear beef averaged USD 4.10/kg, reflecting a 4.06% week-on-week (WoW) rebound but an 18.33% YoY decline. The WoW price increase can be attributed to low market supply. According to Cepea, dry weather and insufficient pasture have hindered the weight gain of grazing animals, preventing them from reaching the required slaughter weight. Furthermore, most cattle scheduled for sale in H2-2024 are already reserved at slaughterhouse scales.
Australia
Australia's national young cattle indicator averaged USD 2.20/kg in W41, marking a third consecutive weekly decline of 5.58%. However, this figure represents a substantial 78.86% YoY increase. According to Meat and Livestock Australia (MLA), a lack of sales in New South Wales (NSW) and Queensland on October 6, 2024, adversely affected yardings. Additionally, reductions in cattle yardings were observed across all other states, indicating a nationwide market slowdown. Total cattle yardings decreased by 23.77 thousand heads to 48.17 thousand heads, the lowest level since Apr-24. Market reports from major saleyards highlighted mixed quality as the primary factor influencing prices and demand.
United States
In W41, the average price of lean beef (92% to 94% lean) in the US was USD 8.32/kg, reflecting a slight 0.12% WoW drop but a notable 20.75% YoY rise. This decrease represents the fifth consecutive week of price reductions, bringing prices to their lowest level since W26. The decline in demand, following the peak summer season and the typical seasonal drop in beef demand as winter approaches, has contributed to this downward trend. Despite the price drop, lean beef prices remain elevated, largely due to reduced domestic production resulting from a shrinking cow herd, which has impacted overall supply.
India
The average price of cow beef in India fell to USD 3.57/kg in W41, marking a significant 40% WoW drop and a notable 60.38% YoY decrease. These fluctuations highlight the volatility of India's beef market, which has been particularly evident over the past year. The instability is primarily driven by changing domestic and international regulations, along with variations in domestic supply. As a result, prices remain unpredictable, heavily influenced by policy developments and supply chain dynamics.
Argentina
In W41, the average price of steer beef in Argentina fell to USD 1.88/kg, reflecting a 2.08% WoW drop and marking the lowest price since W18. This reduction is largely attributed to weakened domestic demand, as beef consumption has dropped to historic lows amid the ongoing economic crisis. The Rosario Board of Trade (BCR) projects that Argentina's per capita beef consumption will decrease to 44.8 kg by the end of 2024, representing the lowest level in 110 years and a significant drop from the historical average of 72.9 kg. This trend highlights a broader shift in consumption patterns influenced by economic challenges and reduced purchasing power.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Diversify Export Markets
Given Brazil's strong export growth to China and the US, it is crucial to diversify export markets to mitigate risks associated with over-reliance on these regions. Identify emerging markets in Asia, Africa, and South America, and explore trade agreements or partnerships that can enhance beef sales. Focus on marketing strategies tailored to the preferences and demand trends of these new markets.
Invest in Heifer Retention Programs
Canadian beef producers should prioritize heifer retention to stabilize herd numbers amidst declining production forecasts. Implementing targeted breeding programs and providing financial incentives for producers who retain heifers could enhance future production capacity. Additionally, supporting farmers with resources and training in pasture management can improve overall herd health and productivity.
Enhance Consumer Education and Marketing Strategies
In Canada and the US, where consumers are shifting towards lower-priced beef products, beef industry stakeholders should focus on consumer education about the value of high-quality beef cuts. Marketing campaigns that emphasize the nutritional benefits, ethical sourcing, and cooking versatility of premium beef products can help retain consumer interest despite economic pressures. Engaging with consumers through social media and promotional events can also enhance brand loyalty and awareness.
Sources: AHDB, Beefpoint, Portal Do Agronegocio, Opresenterural, Canal Rural, Elagro, MLA



