W7 2025: Banana Weekly Update

In W7 in the banana landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- Flooding in Australia, container shortages in Ecuador, and unpaved roads in Colombia have created logistical challenges, affecting banana transportation, pricing, and market stability.
- Increased freight costs, higher production expenses, and potential tariffs in Mexico are pressuring profit margins, leading to contract renegotiations and pricing uncertainties.
- Compliance with EU sustainability regulations, biosecurity measures against Foc Tr4, and efforts to reduce certification costs are key priorities for major exporting nations.
- Drug contamination concerns in Colombia and co-responsibility discussions in Ecuador emphasize ongoing security challenges in banana exports.
1. Weekly News
Australia
Australia’s Banana Industry Faces Logistical Challenges After Flooding
Banana growers in North Queensland are evaluating the impact of recent heavy rains and flooding. While crop damage has been minimal, transportation challenges due to infrastructure damage, particularly along the Bruce Highway and inland routes, have disrupted logistics. With bananas stranded in trucks awaiting transport south, excess supply in northern regions has driven prices down from USD 1.59 to 1.27 per kilogram (kg) in Townsville, prompting retailers to introduce special pricing to manage the surplus. A temporary supply gap is expected due to ripening delays, but the industry remains resilient, with growers stressing the need for price recovery to offset flood-related costs.
Colombia
Colombia Strengthens Banana Industry Amid Logistics and Security Challenges
Spanning 15 thousand hectares (ha) and exporting nearly 50 thousand containers annually, Colombia’s banana industry faces ongoing logistical, phytosanitary, and security challenges. Key markets include the United States (US), the United Kingdom (UK), and Europe, particularly Belgium, Germany, and the Netherlands. Infrastructure issues, such as unpaved roads and inefficient irrigation, affect quality and production costs, while efforts to combat Fusarium Tropical Race 4 (Foc Tr4) focus on enhanced biosecurity measures and research into tolerant banana varieties. Security concerns over drug contamination in shipments have prompted stricter surveillance. To enhance sustainability, the industry is promoting banana flour production to reduce waste and create new economic opportunities.
Ecuador
Ecuador's Banana Industry Faces Logistics and Rising Cost Challenges
Ecuador’s banana industry is facing rising logistics costs and container shortages. These challenges are driven by the Red Sea crisis, which initially forced shipments through Southern Africa and increased freight rates by USD 3 thousand per container. While costs have stabilized, ongoing equipment shortages heightened by China’s withholding of containers and Chile’s peak cherry exports continue to disrupt supply chains. Despite these challenges, demand remains strong in key markets such as Russia, Europe, and China. Ecuador has successfully adapted to stricter agrochemical regulations in the European Union (EU) and Asia while maintaining its status as free from Foc Tr4, despite localized disease concerns. However, maritime freight costs have surged by 20 to 40%, impacting profitability, while the minimum banana price for the 2024/25 season has increased to USD 7.25 per 18.14 kilogram (kg) box, complicating contract negotiations but providing stability for producers. Looking ahead, improvements in container availability and the development of new trade routes are expected to ease logistical pressures, ensuring Ecuador remains competitive in the global banana market.
Ecuador Engages EU to Strengthen Banana Trade and Sustainability
Ecuador's Banana and Plantain Cluster held strategic meetings in Brussels with EU authorities to address sustainability, competitiveness, and regulatory challenges in the European market. Discussions with Members of the European Parliament (MEPs) and EU trade officials focused on reducing certification costs, mitigating unfair retail practices, and easing compliance with regulations such as the Due Diligence Directive and the Deforestation Act. The Cluster also emphasized the need for co-responsibility in tackling drug trafficking within the banana supply chain. An event in Rotterdam highlighted Ecuador's efforts in sustainability and logistics efficiency, reinforcing the country's commitment to strengthening its banana exports to Europe.
Mexico
Mexico’s Banana Exports Threatened by Tariff Uncertainty
Banana producers in Mexico’s southern region are increasingly concerned about the potential 25% tariff on exports to the US, which could severely impact profitability and competitiveness. Given that 80% of exports rely on the agricultural and manufacturing sectors, industry leaders warn that tariffs could raise banana 18.14 kg box prices by USD 2.20, prompting contract renegotiations with transnational companies. While the Mexican government’s intervention has temporarily stalled the measure, inflation and rising production costs remain key challenges. To mitigate risks and maintain market stability, exporters are actively exploring alternative destinations, such as Japan, to diversify their trade opportunities.
2. Weekly Pricing
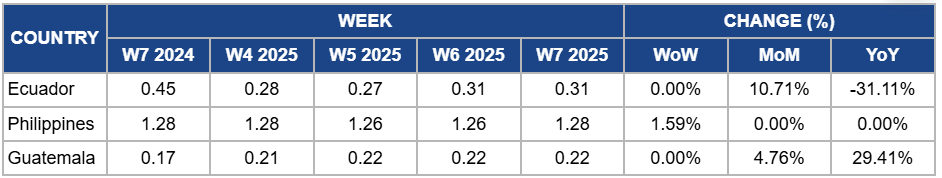
Weekly Banana Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
Yearly Change in Banana Pricing Important Exporters (W7 2024 to W7 2025)
Ecuador
Ecuador's banana prices remained steady at USD 0.31/kg in W7, reflecting a 10.71% month-on-month (MoM) increase. This was driven by strong demand from Russia, Europe, and China, as well as stable export volumes despite shipping delays and container shortages. However, year-on-year (YoY) prices fell by 31.11% due to rising sea freight costs, container shortages, and the impact of Ecuador’s higher minimum banana price per box, which has pressured contract negotiations. While ongoing regulatory discussions with the EU aim to improve market conditions, further price stability will depend on easing supply chain disruptions and improving trade routes.
Philippines
In the Philippines, banana prices increased slightly by 1.59% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 1.28/kg in W7, with no MoM or YoY change due to stable domestic demand and consistent supply from key growing regions. Despite scattered rains causing minor disruptions, overall production remained sufficient to meet market needs, preventing significant price fluctuations.
Guatemala
Guatemala's banana prices held steady at USD 0.22/kg in W7, with a 4.76% MoM increase and a 29.41% YoY surge due to sustained export demand from the US and Europe, combined with higher production costs, including rising fertilizer and labor expenses. Stable supply levels continued to support price stability weekly.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Strengthen Logistics and Pricing Strategies for Market Stability
Banana growers in North Queensland should collaborate with transport companies to secure alternative routes and prioritize shipments to southern markets, minimizing delays and reducing localized oversupply. Cold chain providers can implement temporary storage solutions to manage excess volumes and prevent quality deterioration. Retailers should introduce tiered pricing strategies, such as volume-based discounts and promotional bundling, to accelerate sales while maintaining profitability. Coordinating with wholesalers to redistribute surplus bananas to processing facilities or secondary markets can further stabilize prices and reduce waste.
Optimize Logistics and Contract Flexibility to Maintain Competitiveness
Ecuadorian banana exporters should secure alternative shipping routes via ports in Brazil or Peru to bypass congestion and mitigate rising freight costs. Partnering with logistics firms that offer refrigerated transshipment services can help maintain fruit quality during extended transit times. Exporters should also negotiate container leasing agreements with shipping companies in regions less affected by shortages, such as Central America. Buyers can adjust contract terms by incorporating flexible delivery windows and dynamic pricing models tied to shipping costs, ensuring supply stability while sharing financial risks. Collaborating with importers to diversify distribution through secondary ports can further reduce bottlenecks and prevent supply disruptions.
Diversify Markets and Adjust Pricing to Sustain Competitiveness
Mexican banana exporters should actively expand into high-value markets like Japan and South Korea by establishing direct trade agreements and adapting quality standards to meet import requirements. This includes adhering to Japan’s strict pesticide residue limits and exploring organic certification to capture premium pricing. Producers should also collaborate with Asian retailers to develop promotional campaigns that boost consumer demand. Additionally, exporters must reassess pricing strategies by introducing tiered pricing models based on shipment volume and delivery terms. Adjusting contract terms to include flexible payment schedules and currency hedging can help mitigate financial risks associated with tariff uncertainty.
Sources: Tridge, ABC News, Abrafrutas, America Economia, ASBAMA, Efeagro, Freshplaza, Rnz, The Global





