W16 2025: Orange Weekly Update

In W16 in the orange landscape, some of the most relevant trends included:
- Orange production trends varied globally: Argentina's exports are thriving due to strong demand and exceptional fruit quality, while Brazil’s production has dropped significantly due to adverse weather conditions and disease, with a recovery expected in the next season.
- Brazil and Florida are both struggling with the ongoing impact of citrus greening, which continues to limit production potential despite efforts to mitigate the damage.
- Argentina’s focus on nearby markets, efficient logistics, and quality improvements continues to support its competitive position, while global demand for oranges remains strong, especially in markets like Brazil.
1. Weekly News
Argentina
Argentina's Orange Export Industry Thrives Amid Rising Global Demand
Global demand for oranges and other citrus fruits continues to rise, benefiting producers like Argentina. An Argentine exporter of mandarins and oranges expects to match last year’s export volumes despite an early shortage of Valencia oranges, due to exceptional fruit quality supported by a dry summer. Since 2022, Argentina’s citrus exports, particularly to Brazil, have grown steadily, with 145 containers shipped last season. Strong demand is projected to continue through at least 2026, with prices ranging from USD 9 to USD 12 per box depending on fruit size. While Argentina faces ongoing economic challenges, its focus on nearby markets, efficient logistics, and continued investment in breeding and quality enhancement supports its competitive position in the global citrus trade.
Brazil
Brazil's 2024/2025 Orange Harvest Hit by Adverse Weather and Diseases
Brazil’s orange production in São Paulo and the Triângulo/Southwest regions of Minas Gerais dropped sharply in the 2024/25 season to 230.87 million 40.8-kilogram (kg) boxes, nearly 25% less than the previous season and the second-lowest output in 37 years. The decline was mainly caused by prolonged drought, extreme heat, and the continued spread of greening disease, which led to an early harvest and smaller, lighter fruit averaging just 159 grams. While a fourth flowering helped prevent further losses, around 50 million boxes were still lost due to fruit drop. Looking ahead, the 2025/26 season is expected to bring a recovery in production.
United States
Florida's Orange Industry Faces Challenges but Shows Signs of Recovery
Florida’s orange industry remains under pressure from the combined impacts of hurricanes and citrus greening, which continue to limit production potential. Despite these challenges, the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) has maintained its forecast for the 2024/25 season at 11.6 million 90-pound (lb) boxes, showing no change from previous estimates. While Hurricane Milton damaged up to half of some groves, recovery efforts have begun to yield positive outcomes, particularly in grapefruit and mandarin production. Early signs of improved tree health and gradual recovery offer cautious optimism for future seasons. Nevertheless, persistent threats from citrus greening and storm-related losses are expected to keep overall production levels subdued.
2. Weekly Pricing
Weekly Orange Pricing Important Exporters (USD/kg)
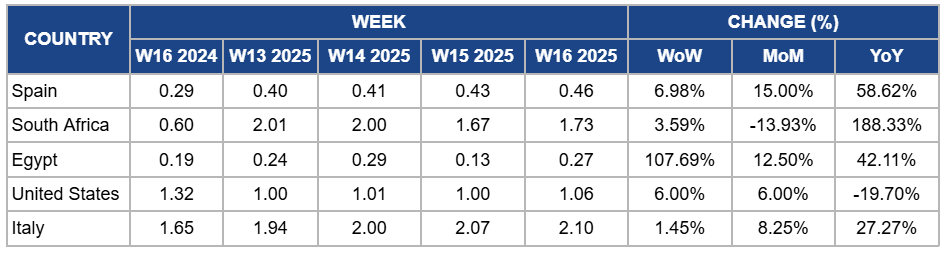
Yearly Change in Orange Pricing Important Exporters (W16 2024 to W16 2025)
Spain
Spain's orange prices rose by 6.98% week-on-week (WoW) to USD 0.46/kg in W16, reflecting a 15% month-on-month (MoM) and a 58.62% year-on-year (YoY) increase. The price increase is due to several factors, including reduced domestic production caused by adverse weather conditions, such as flooding in Oct-24, which damaged key growing regions like Valencia, leading to estimated losses of around USD205 million. Additionally, the increased demand for oranges in processing, driven by limited fresh availability, contributed to higher prices. Global supply constraints, particularly in Brazil and the US, where extreme weather and diseases like citrus greening disease reduced yields, further intensified the price pressures. Moreover, rising transportation costs, partly due to the Red Sea crisis, increased the cost of importing oranges from countries like Egypt, further contributing to the price rise in Spain. These combined factors have driven the observed increase in orange prices.
South Africa
South Africa's orange prices increased by 3.59% WoW to USD 1.73/kg in W16. This reflects a substantial 188.33% YoY surge, primarily due to improved export quality. The 2025 season is showing balanced growth and excellent fruit standards, which have boosted international demand. Additionally, exporters have diversified their markets, particularly toward the Middle East and Asia, in response to new United States (US) tariffs, sustaining global trade flows and supporting elevated price levels. However, prices declined by 13.93% MoM as more fruit was redirected to processing due to attractive juicing prices, reducing fresh export volumes. Currency fluctuations, particularly the weakening of the South African rand, also impacted export competitiveness and contributed to recent price volatility.
Egypt
Orange prices in Egypt rose by 107.69% WoW to USD 0.27/kg in W16, accompanied by a 12.50% MoM and a 42.11% YoY increase. This surge is due to several contributing factors. These include a shortage of larger-sized Valencia oranges, which are in high demand in key export markets such as Eastern Europe, leading to price premiums of 30 to 35% over the previous season. Additionally, fuel prices have increased by up to 14.81% as of April 11, 2025, raising transportation and operational costs, while a 13.6% rise in Egypt's annual urban consumer price inflation in March 2025 has further impacted production expenses. These elements have collectively driven up orange prices despite the ongoing harvest season.
United States
US orange prices increased by 6% WoW and MoM to USD 1.06/kg in W16, primarily due to reduced domestic arrivals and supply challenges stemming from ongoing challenges such as citrus greening disease and adverse weather conditions affecting key growing regions like Florida. However, prices fell by 19.70% YoY as the market corrected from the record highs of early 2024, which were driven by severe supply shortages. The subsequent decline in consumer demand, influenced by elevated retail prices and diminished juice quality, contributed to the YoY price decrease.
Italy
Italy's orange prices increased by 1.45% WoW to USD 2.10/kg in W16, reflecting an 8.25% MoM rise and a 27.27% YoY surge. This upward trend is due to heightened production costs, including high prices for fertilizers, pesticides, and energy, which have significantly impacted the agricultural industry. Additionally, Italy's annual inflation rate reached an 18-month high of 1.9% in Mar-25, further contributing to the overall increase in consumer prices, including those of fresh produce. Despite these cost pressures, the demand for Italian oranges has remained robust, driven by their reputation for quality and freshness. However, the MoM price increase is also influenced by seasonal factors, as the peak harvest period for oranges in Italy typically concludes by March, leading to tighter supplies in April. This seasonal decline in availability and sustained demand has exerted upward pressure on prices. The YoY surge is further amplified by the previous year's lower prices, which were affected by favorable weather conditions and higher yields, making the current prices appear significantly elevated in comparison.
3. Actionable Recommendations
Expand Drought-Resilient Rootstock Use
Citrus growers in São Paulo and Minas Gerais should prioritize planting drought-tolerant rootstocks to reduce future yield losses from climate stress. For example, using rootstocks like Swingle citrumelo or Sunki can improve resilience to water scarcity and high temperatures. These varieties also offer moderate resistance to greening and maintain fruit size and juice content under stress, helping stabilize production even in low-rainfall years.
Strengthen Market Position Through Size Sorting and Branding
Apple exporters in Argentina should capitalize on strong global demand by enhancing fruit size sorting and branding strategies. Tailoring shipments by size preference, larger fruit for Russia and smaller sizes for Southeast Asia, can help secure better pricing. In parallel, exporters should invest in branded packaging that highlights Argentine quality and dry-climate advantages. For instance, clearly labeled boxes emphasizing sweetness and shelf life can improve visibility and buyer confidence in competitive markets like Brazil and Central Asia.
Sources: Tridge, ABC Action News, Agribusiness, Freshplaza, Fruit Portal





